Abstract
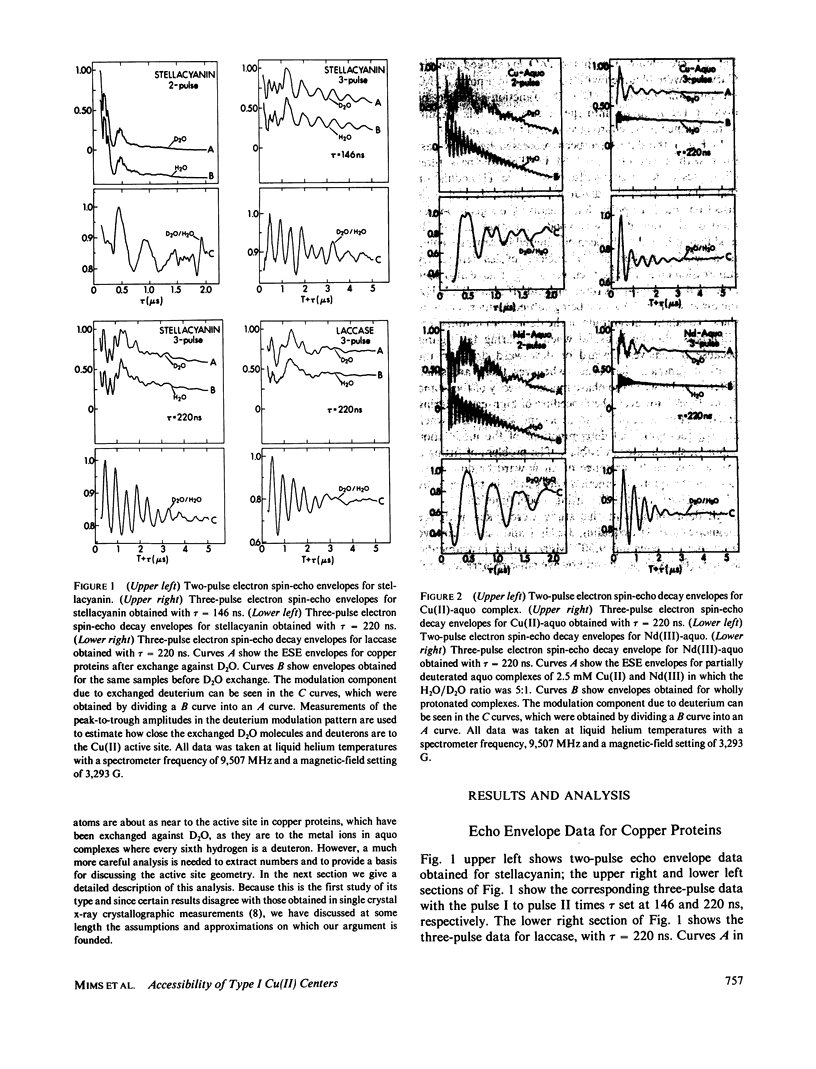
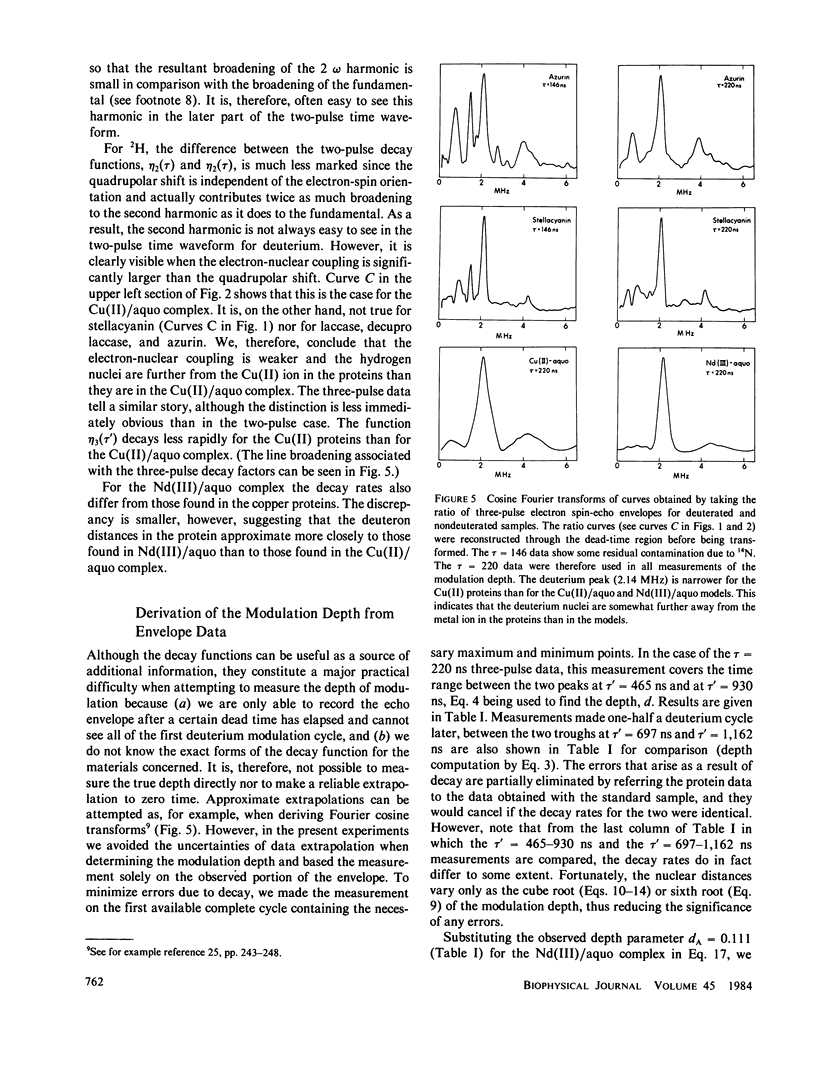
The characteristic deuterium modulation pattern was observed in the electron spin-echo envelopes for laccase, decupro laccase (from which Type 2 copper had been removed), stellacyanin, and azurin that had been exchanged against D2O. From the decay rate of the modulation pattern and from a quantitative analysis of the modulation depth, we conclude that the Cu(II) sites in these proteins are directly accessible to solvent. Similar results were obtained for laccase and decupro laccase.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E. T., Stenkamp R. E., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. A crystallographic model for azurin a 3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 25;123(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergaman C., Gandvik E. K., Nyman P. O., Strid L. The amino acid sequence of Stellacyanin from the lacquer tree. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1052–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani M. T., Morpurgo L., Rotilio G., Mondovì B. Selective removal of type 2 copper from Rhus vernicifera laccase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80732-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. A., Lee W. K. Investigation of the structure of the blue copper protein from Rhus vernicifera stellacyanin by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Inorg Biochem. 1979 Oct;11(2):101–113. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. A., Smith B. E. Characteristics of azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa via 270-MHz 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Inorg Biochem. 1979 Oct;11(2):79–93. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Brown R. D. Anomalous relaxation of water protons in solutions of copper-containing proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:752–763. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Malmström B. G. The state and function of copper in biological systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:177–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley J. L., Ulrich E. L., Berg S. P., Krogmann D. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the copper binding sites of blue copper proteins: oxidized, reduced, and apoplastocyanin. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4428–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillin D. R., Rosenberg R. C., Gray H. B. Preparation and spectroscopic studies of cobalt(II) derivatives of blue copper proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4760–4762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims W. B., Peisach J. Assignment of a ligand in stellacyanin by a pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance method. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3863–3869. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims W. B., Peisach J. Measurement of 14N superhyperfine frequencies in stellacyanin by an electron spin echo method. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4321–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondoví B., Graziani M. T., Mims W. B., Oltzik R., Peisach J. Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance studies of types I and II coper of Rhus vernicifera laccase and porcine ceruloplasmin. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4198–4202. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Levine W. G., Blumberg W. E. Structural properties of stellacyanin, a copper mucoprotein from Rhus vernicifera, the Japanese lac tree. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2847–2858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Mims W. B., Davis J. L. Studies of the electron-nuclear coupling between Fe(III) and 14N in cytochrome P-450 and in a series of low spin heme compounds. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12379–12389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Mims W. B. The linear electric field effect in stellacyanin, azurin and in some simple model compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhammar B. Purification and properties of laccase and stellacyanin from Rhus vernicifera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 7;205(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E. I., Hare J. W., Gray H. B. Spectroscopic studies and a structural model for blue copper centers in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1389–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Norton R. S., Allerhand A., Bersohn R. Studies of individual carbon sites of azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa by natural-abundance carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):886–894. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L., Peisach J., Mims W. B. Electron spin echo studies of the copper complexes of conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10314–10316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J., Aisen P., Peisach J., Mims W. B. Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance studies of the copper complexes of transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3512–3515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]