Abstract
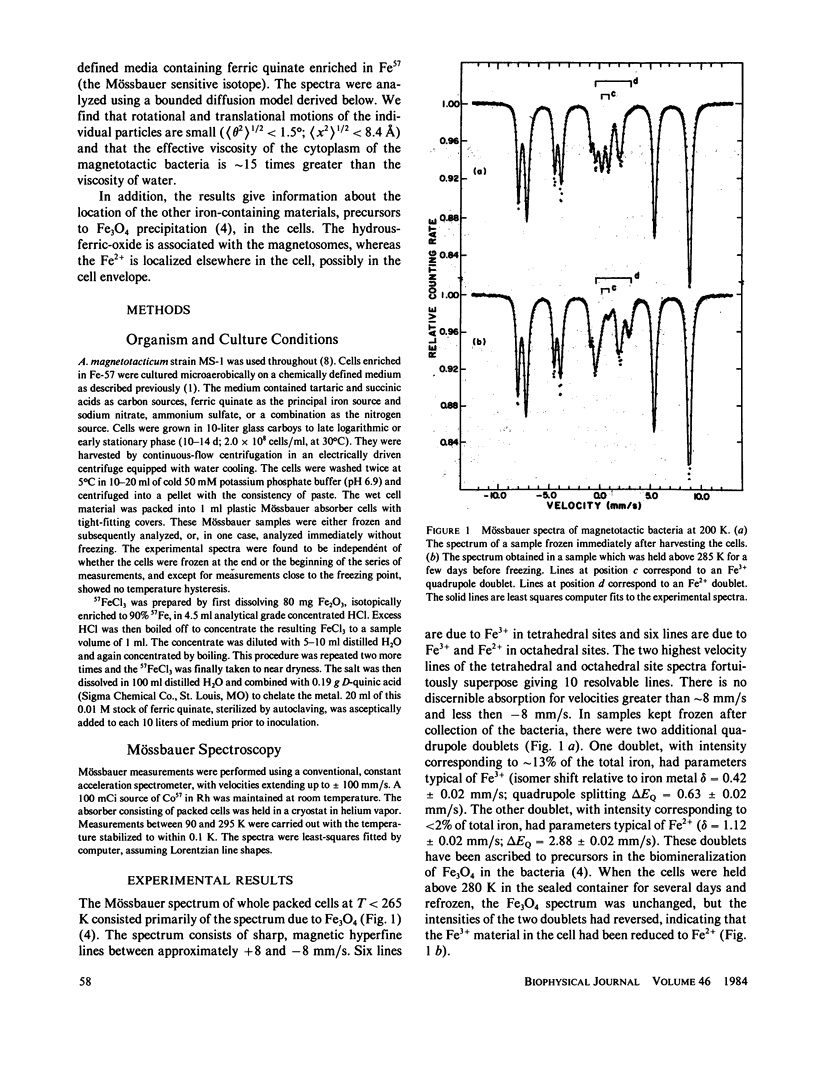
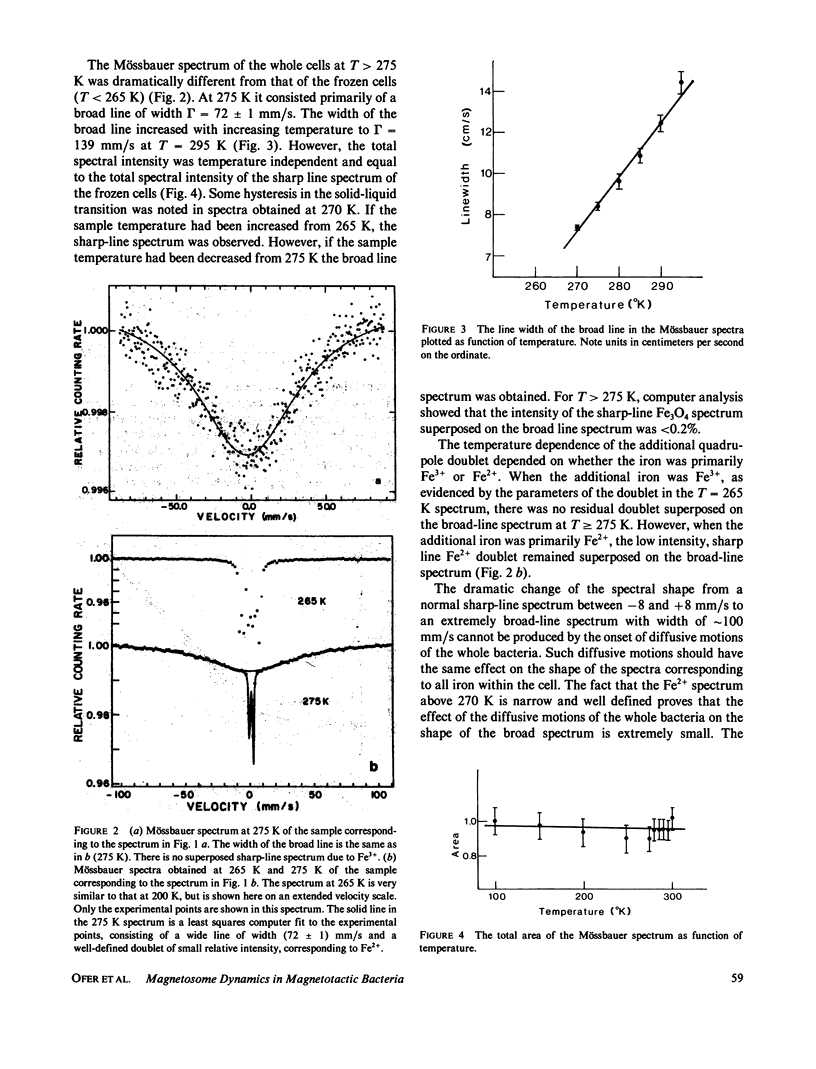
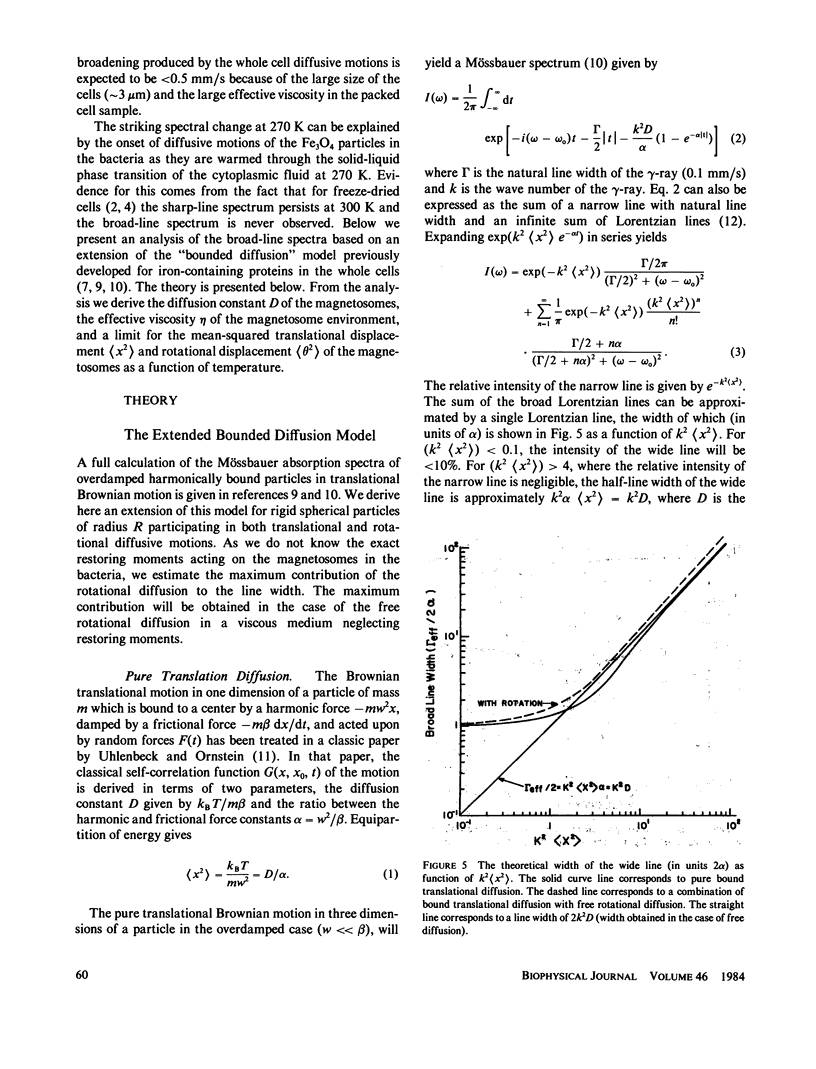
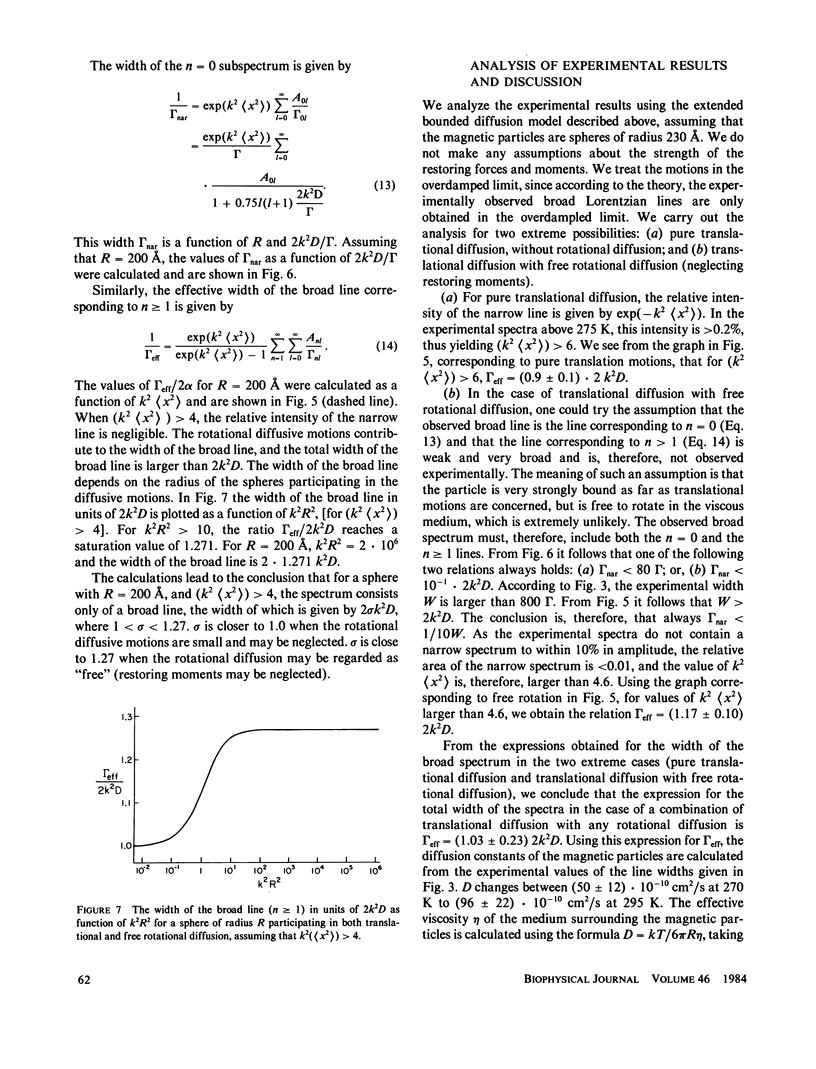
Diffusive motions of the magnetosomes (enveloped Fe3O4 particles) in the magnetotactic bacterium Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum result in a very broad-line Mössbauer spectrum (T approximately 100 mm/s) above freezing temperatures. The line width increases with increasing temperature. The data are analyzed using a bounded diffusion model to yield the rotational and translational motions of the magnetosomes as well as the effective viscosity of the material surrounding the magnetosomes. The results are [theta 2] l/2 less than 1.5 degrees and [x2] 1/2 less than 8.4 A for the rotational and translational motions, respectively, implying that the particles are fixed in whole cells. The effective viscosity is 10 cP at 295 K and increases with decreasing temperature. Additional Fe3+ material in the cell is shown to be associated with the magnetosomes. Fe2+ material in the cell appears to be associated with the cell envelope.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill D. L., Maratea D., Blakemore R. P. Ultrastructure of a magnetotactic spirillum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1399–1408. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1399-1408.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Nowik I., Ofer S., Yariv J. Dynamics of heme iron in crystals of metmyoglobin and deoxymyoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):736–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Ofer S., Bachrach U. Study of storage iron in cultured chick embryo fibroblasts and rat glioma cells, using Mössbauer spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;720(2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Forsberg C. W., Doyle R. J. Major sites of metal binding in Bacillus licheniformis walls. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1438–1448. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1438-1448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P., Maratea D., Wolfe R. S. Isolation and pure culture of a freshwater magnetic spirillum in chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):720–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.720-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel R. B., Blakemore R. P., Wolfe R. S. Magnetite in freshwater magnetotactic bacteria. Science. 1979 Mar 30;203(4387):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.203.4387.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A. D., Snipes W. Viscosity of cellular protoplasm. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):666–668. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parak F., Knapp E. W., Kucheida D. Protein dynamics. Mössbauer spectroscopy on deoxymyoglobin crystals. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):177–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Shumate S. E., Parrott J. R. Microbial Cells as Biosorbents for Heavy Metals: Accumulation of Uranium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):237–245. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.237-245.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


