Abstract
An expression is derived for the lipid-mediated intermolecular interaction between protein molecules embedded in a lipid bilayer. It is assumed that protein particles are accommodated by the bilayer, but they distort the lipids in some manner from their equilibrium protein-free configuration. We treat this situation by expanding the free energy density in the plane of the membrane as a Taylor series in some arbitrary parameter and its gradient. Minimization of the total membrane energy for a given particle configuration yields the interparticle interaction energy for that configuration. A test of the model is provided by measurement of the protein-protein pair distribution function from freeze-fracture micrographs of partially aggregated membranes. The measured functions can be simulated by adjustment of two parameters (a) a lipid correlation length that characterizes the distance over which a distortion of the bilayers is transmitted laterally through the bilayer, and (b) a term quantifying the energy of the protein-lipid interaction at the protein-lipid boundary. Correlation lengths obtained by fitting the calculated particle distribution functions to the data are found to be several nanometers. Protein-lipid interaction energies are of the order of a few kT.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branton D. Freeze-etching studies of membrane structure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 May 27;261(837):133–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadio R., Stoeckenius W. Effect of protein-protein interaction on light adaptation of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3374–3381. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Cornell B. A., Ellasz A. W., Perry A. Interactions of helical polypepetide segments which span the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Studies of the gramicidin A lipid-water system. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):517–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hubbell W. L. Temperature- and light-dependent structural changes in rhodopsin-lipid membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U., Holenstein C., Heyn M. P. Lateral segregation of proteins induced by cholesterol in bacteriorhodopsin-phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 15;596(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U. Temperature-dependent aggregation of bacteriorhodopsin in dipalmitoyl- and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copps T. P., Chelack W. S., Petkau A. Variation in distribution of membrane particles in Acholeplasma laidlawii B with pH. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Apr;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell B. A., Davenport J. B., Separovic F. Low-frequency motion in membranes. The effect of cholesterol and proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 28;689(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davoust J., Bienvenue A., Fellmann P., Devaux P. F. Boundary lipids and protein mobility in rhodopsin-phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Effect of lipid phase transitions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 15;596(1):28–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Perelson A. The kinetics of aggregation phenomena. I. Minimal models for patch formation of lymphocyte membranes. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 7;62(1):159–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Friend D. S. Assembly of gap junctions during amphibian neurulation. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):32–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnell J. T., 2nd, Finegold L. X. Testing of aggregation measurement techniques for intramembranous particles. Biophys J. 1981 Sep;35(3):783–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84827-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold L. Cell membrane fluidity: molecular modeling of particle aggregations seen in electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Rudolf I. Acrosomal disruption in sperm. Freeze-fracture of altered membranes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):466–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon N. D., Demsey A., Stackpole C. W. Analysis of local order in the spatial distribution of cell surface molecular assemblies. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. B., Kirk R. G. Anion transport and membrane morphology. J Membr Biol. 1976;27(3):265–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01869140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. The purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:87–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
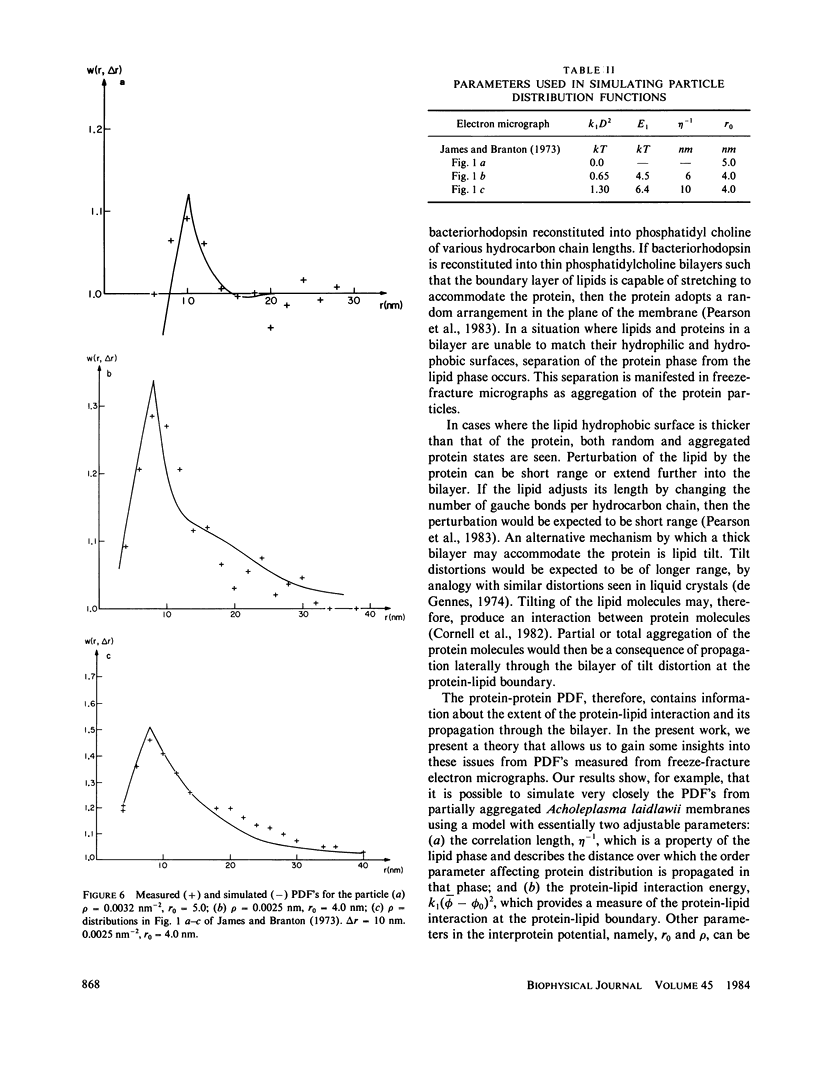
- James R., Branton D. Lipid- and temperature-dependent structural changes in Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima Y., Sekiya T., Nozawa Y. Freeze-fracture ultrastructural alterations induced by filipin, pimaricin, nystatin and amphotericin B in the plasmia membranes of Epidermophyton, Saccharomyces and red complex-induced membrane lesions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):452–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann W., McConnell H. M. Interactions of proteins and cholesterol with lipids in bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):206–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barrow D. A., Hoechli M. Cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine interactions in multilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1943–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Lipid-mediated protein interaction in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu L., Caron F., Luzzati V., Billecocq A. The influence of protein-lipid interactions on the order-disorder conformational transitions of the hydrocarbon chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 21;508(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Analysis of freeze-fracture electron micrographs by a computer-based technique. Biophys J. 1976 Jun;16(6):613–625. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85716-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. M., Lentz B. R., Meissner G. Effects of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase on phospholipid bilayer fluidity: boundary lipid. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5248–5255. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive J., Benedetti E. L., van Breugel P. J., Daemen F. J., Bonting S. L. Biochemical aspects of the visual process. XXXVII. Evidence for lateral aggregation of rhodopsin molecules in phospholipase C-treated bovine photoreceptor membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 4;509(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., Springgate M. W., McConnell H. M. Theoretical study of protein--lipid interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1616–1619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L. T., Chan S. I., Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Pair distribution functions of bacteriorhodopsin and rhodopsin in model bilayers. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84337-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. P., Hui S. W., Stewart T. P. Correlative statistical analysis and computer modelling of intramembraneous particle distributions in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth V., Wallach D. F., Weidekamm E., Knüfermann H. Micromorphologic consequences following perturbation of erythrocyte membranes by trypsin, phospholipase A, lysolecithin, sodium dodecyl sulfate and saponin. A correlated freeze-etching and biochemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., Kastelijn D., van Deenen L. L. The asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the human red cell membrane. A combined study using phospholipases and freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):178–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Verma S. P., Fookson J. Application of laser Raman and infrared spectroscopy to the analysis of membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 20;559(2-3):153–208. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Volotovski I. D., Marsh D. Rhodopsin-lipid associations in bovine rod outer segment membranes. Identification of immobilized lipid by spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


