Abstract
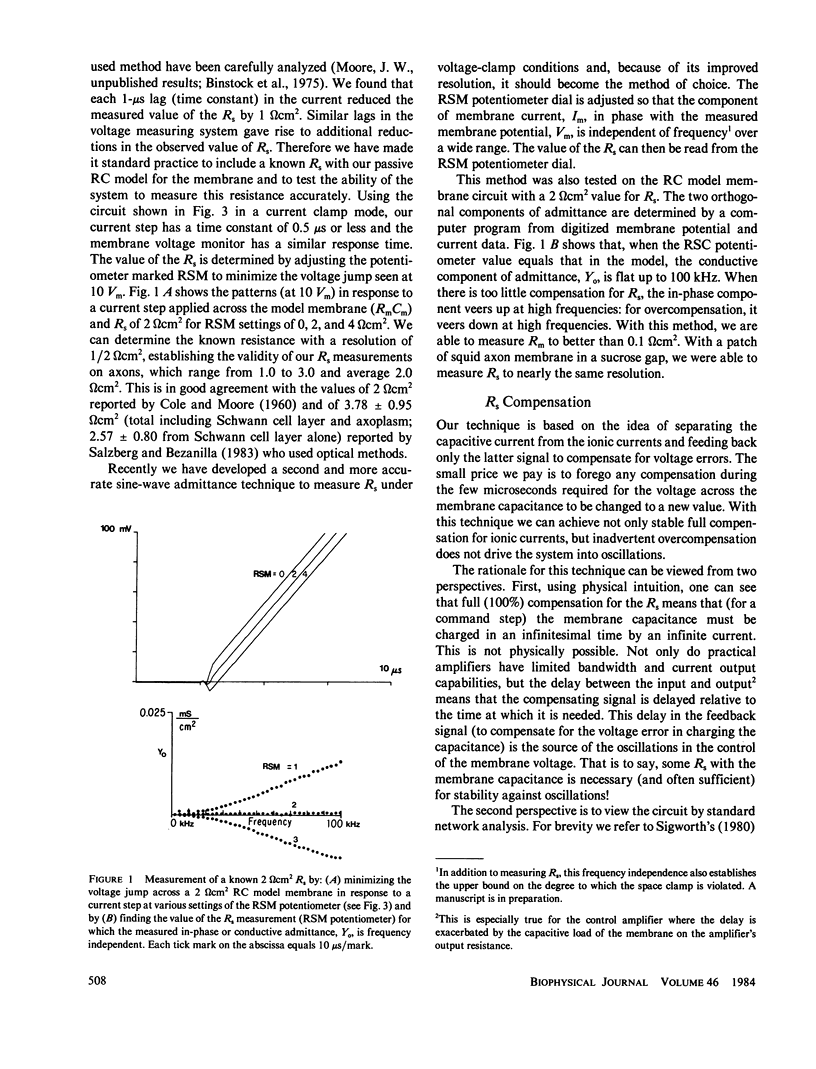
Extracellular resistance in series (Rs) with excitable membranes can give rise to significant voltage errors that distort the current records in voltage-clamped membranes. Electrical methods for measurement of and compensation for such resistances are described and evaluated. Measurement of Rs by the conventional voltage jump in response to a current step is accurate but the measurement of sine-wave admittance under voltage-clamp conditions is better, having about a fivefold improvement in resolution (+/- 0.1 omega cm2) over the conventional method. Conventional feedback of the membrane current signal to correct the Rs error signal leads to instability of the voltage clamp when approximately two-thirds of the error is corrected. We describe an active electronic bridge circuit that subtracts membrane capacitance from the total membrane current and allows full, yet stable, compensation for the voltage error due to ionic currents. Furthermore, this method provides not only fast and accurate control of the membrane potential in response to a command step, but also fast recovery following an abrupt change in the membrane conductance. Marked changes in the kinetics and amplitude of ionic currents resulting from full compensation for Rs are shown for several typical potential patterns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Moses J., Rive R. V. An anatomical basis for the resistance and capacitance in series with excitable membrane of the squid giant axon. J Neurocytol. 1977 Dec;6(6):621–646. doi: 10.1007/BF01176377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binstock L., Adelman W. J., Jr, Senft P., Lecar H. Determination of the resistance in series with the membranes of giant axons. J Membr Biol. 1975 Apr 23;21(1-2):25–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01941060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Ionic current measurements in the squid giant axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:123–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geren B. B., Schmitt F. O. THE STRUCTURE OF THE SCHWANN CELL AND ITS RELATION TO THE AXON IN CERTAIN INVERTEBRATE NERVE FIBERS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Sep;40(9):863–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.9.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. I., Meves H. The time course of sodium inactivation in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:289–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt R. C., Adelman W. J., Jr Sodium inactivation. Experimental test of two models. Biophys J. 1970 Jul;10(7):610–617. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86323-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE J. W., NARAHASHI T., ULBRICHT W. SODIUM CONDUCTANCE SHIFT IN AN AXON INTERNALLY PERFUSED WITH A SUCROSE AND LOW-POTASSIUM SOLUTION. J Physiol. 1964 Aug;172:163–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S. Some kinetic and steady-state properties of sodium channels after removal of inactivation. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):1–22. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palti Y., Cohen-Armon M. Numerical method for correcting the series resistance error in voltage clamp experiments. Isr J Med Sci. 1982 Jan;18(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón F., Anderson N., Joyner R. W., Moore J. W. Axon voltage-clamp simulations. A multicellular preparation. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85791-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg B. M., Bezanilla F. An optical determination of the series resistance in Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Dec;82(6):807–817. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. E., MOORE J. W., COLE K. S. Analysis of certain errors in squid axon voltage clamp measurements. Biophys J. 1960 Nov;1:161–202. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86882-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEGAS R., VILLEGAS G. M. Characterization of the membranes in the giant nerve fiber of the squid. J Gen Physiol. 1960 May;43:73–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.5.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas G. M. Electron microscopic study of the giant nerve fiber of the giant squid Dosidicus gigas. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Mar;26(5):501–504. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


