Abstract
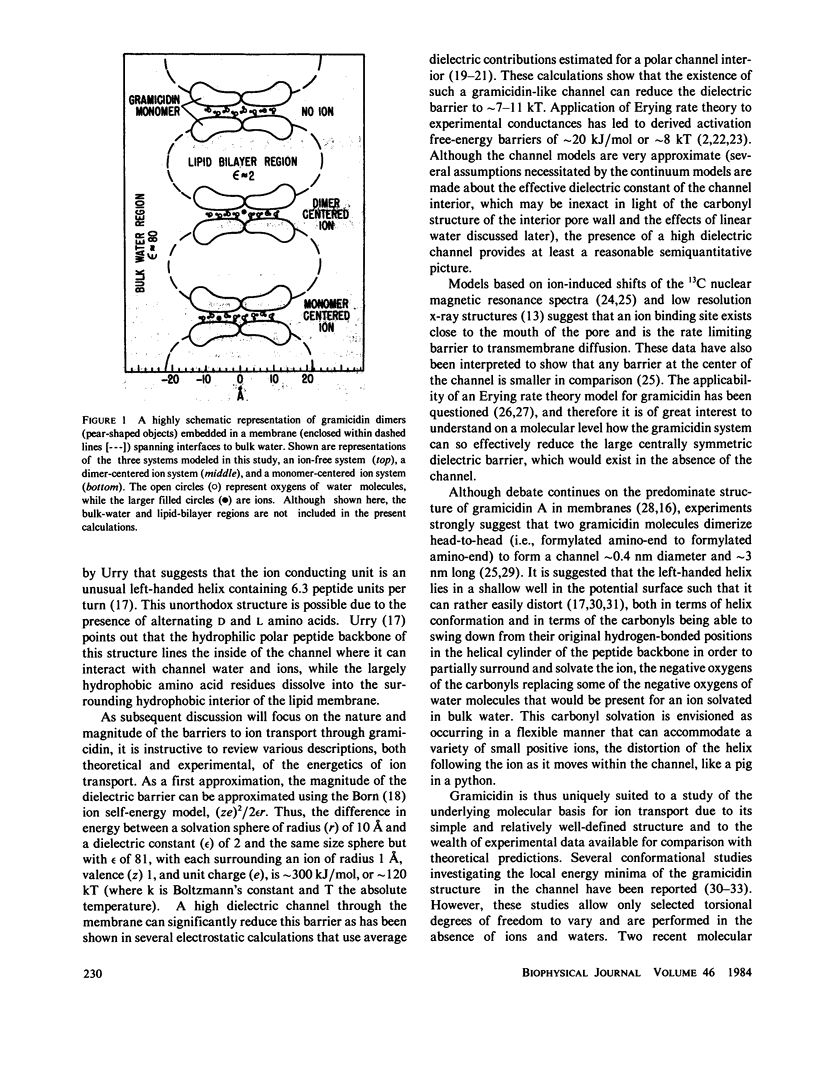
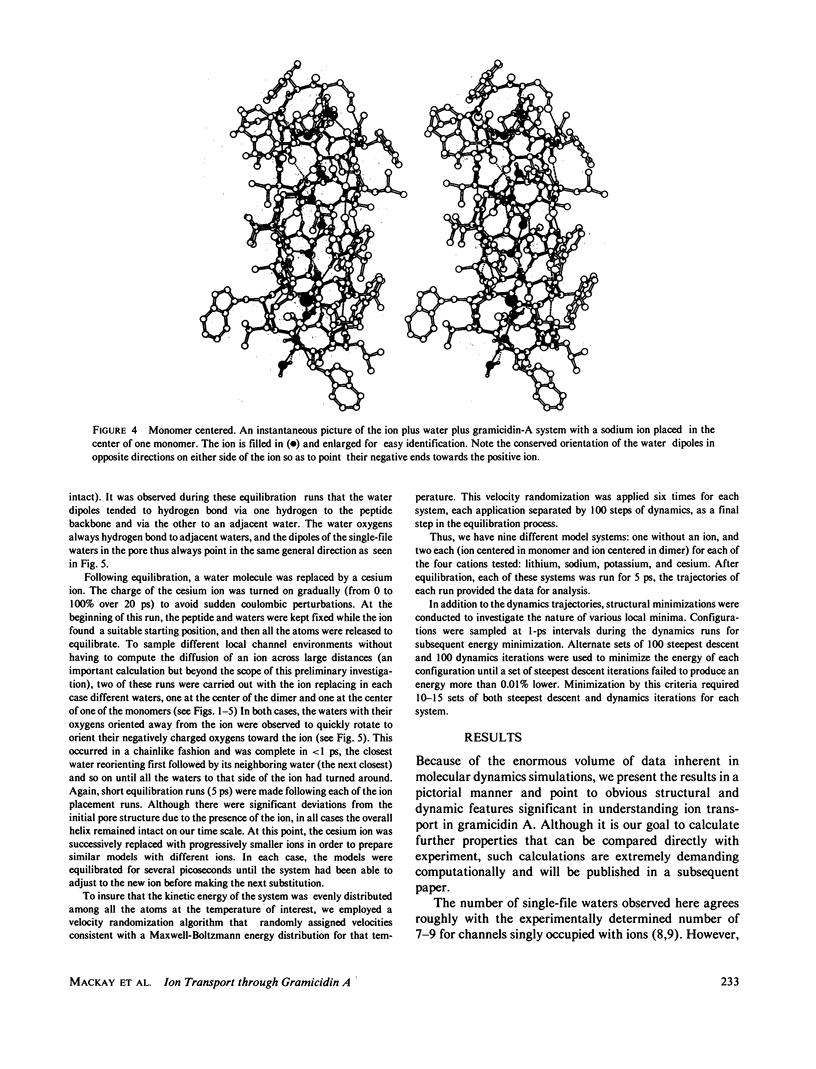
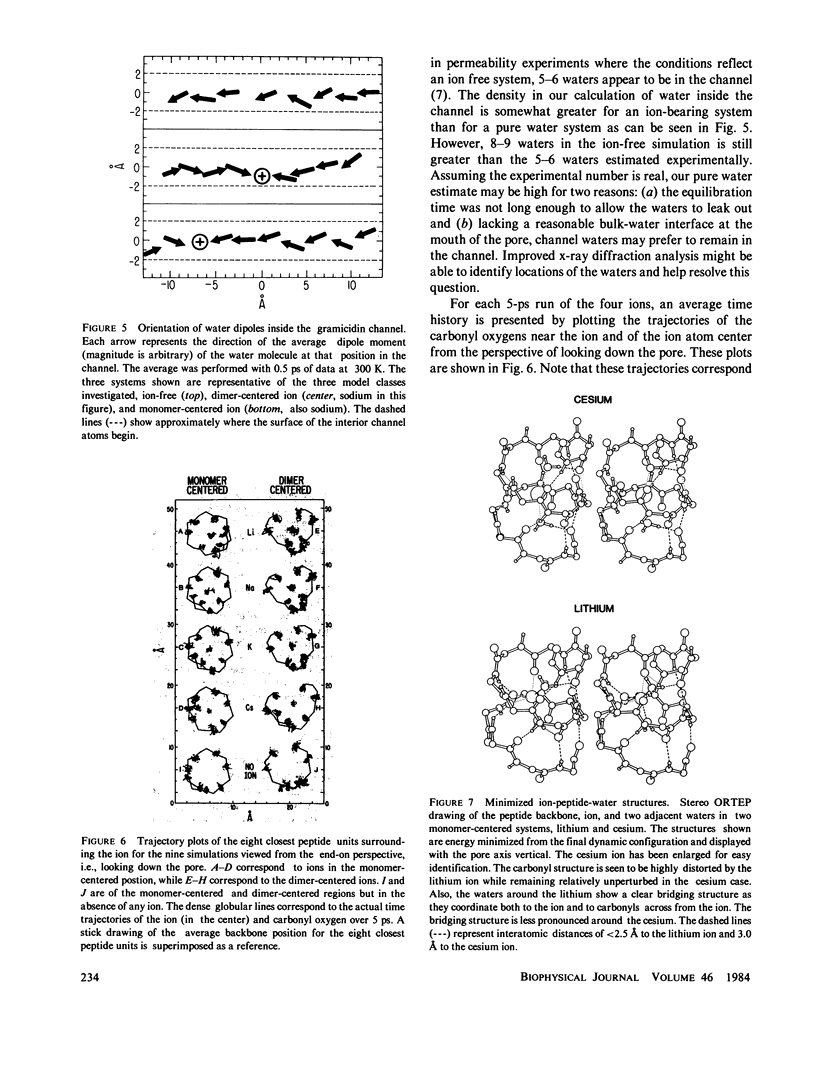
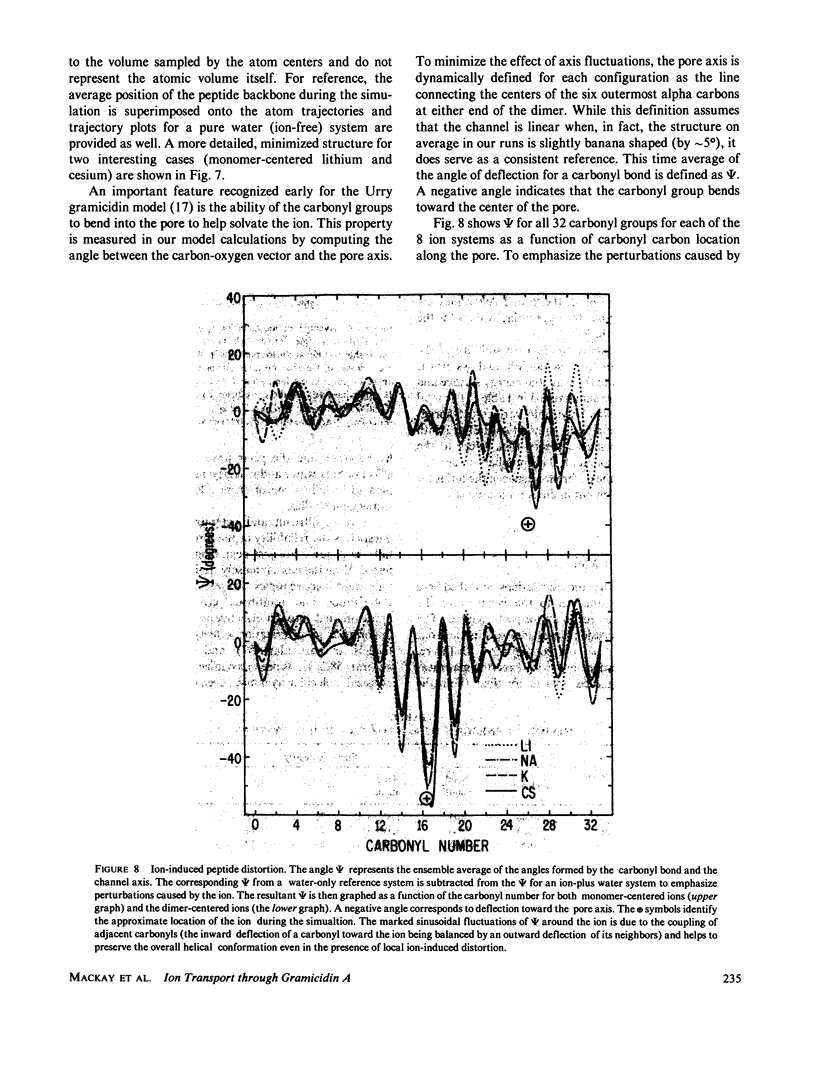
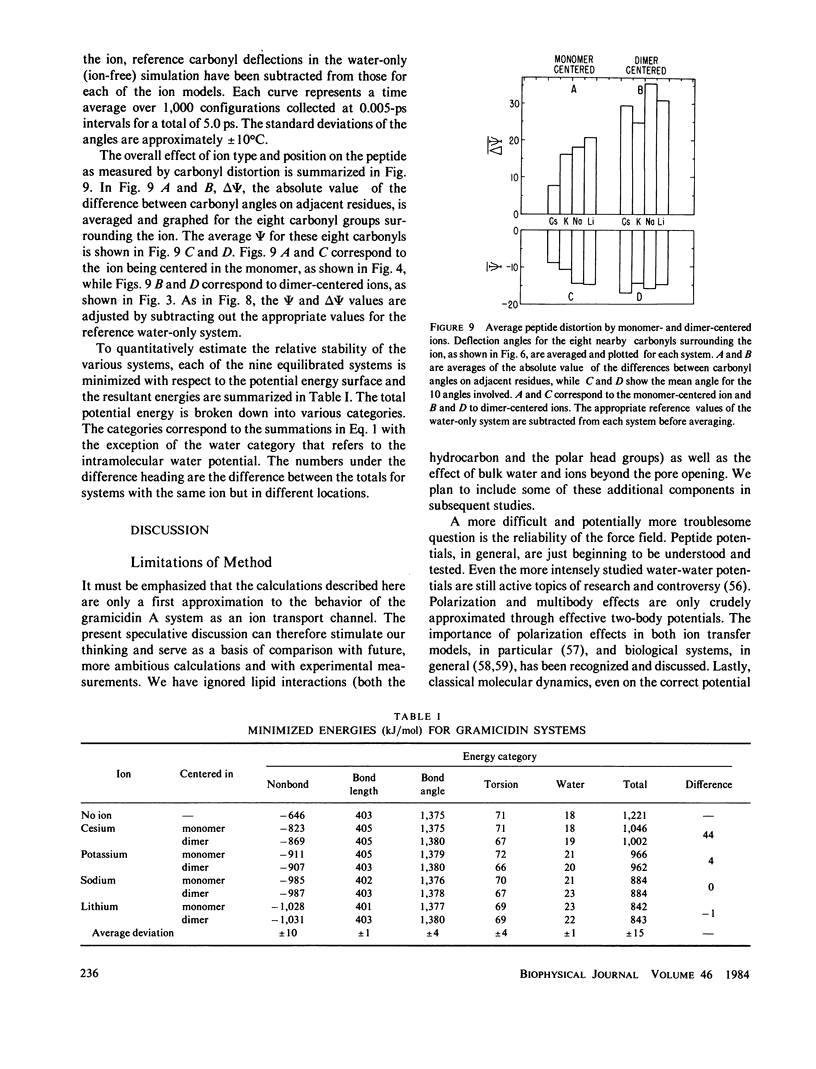
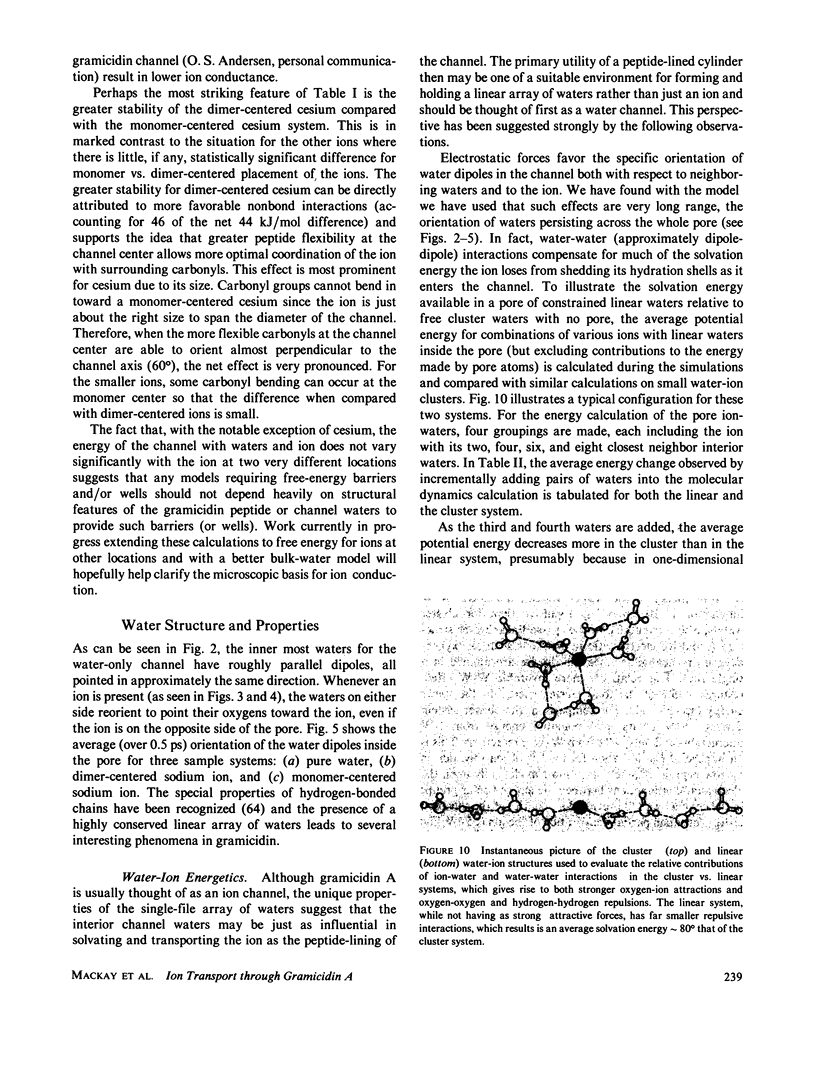
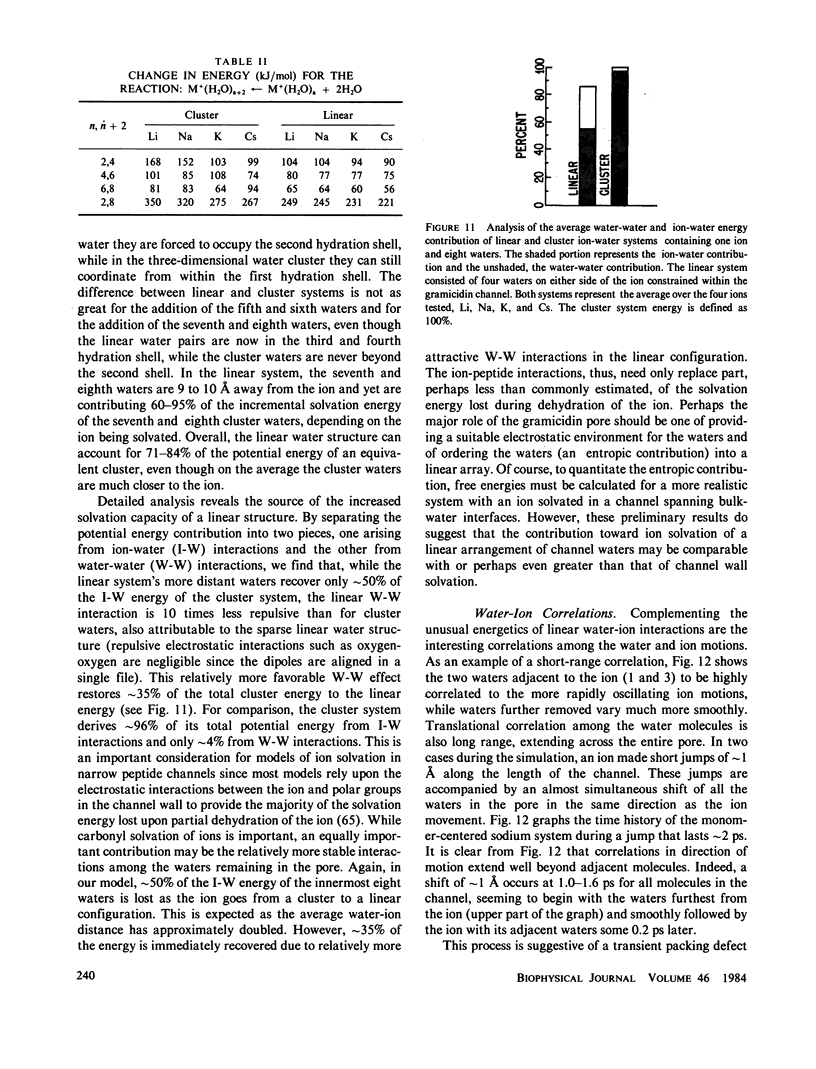
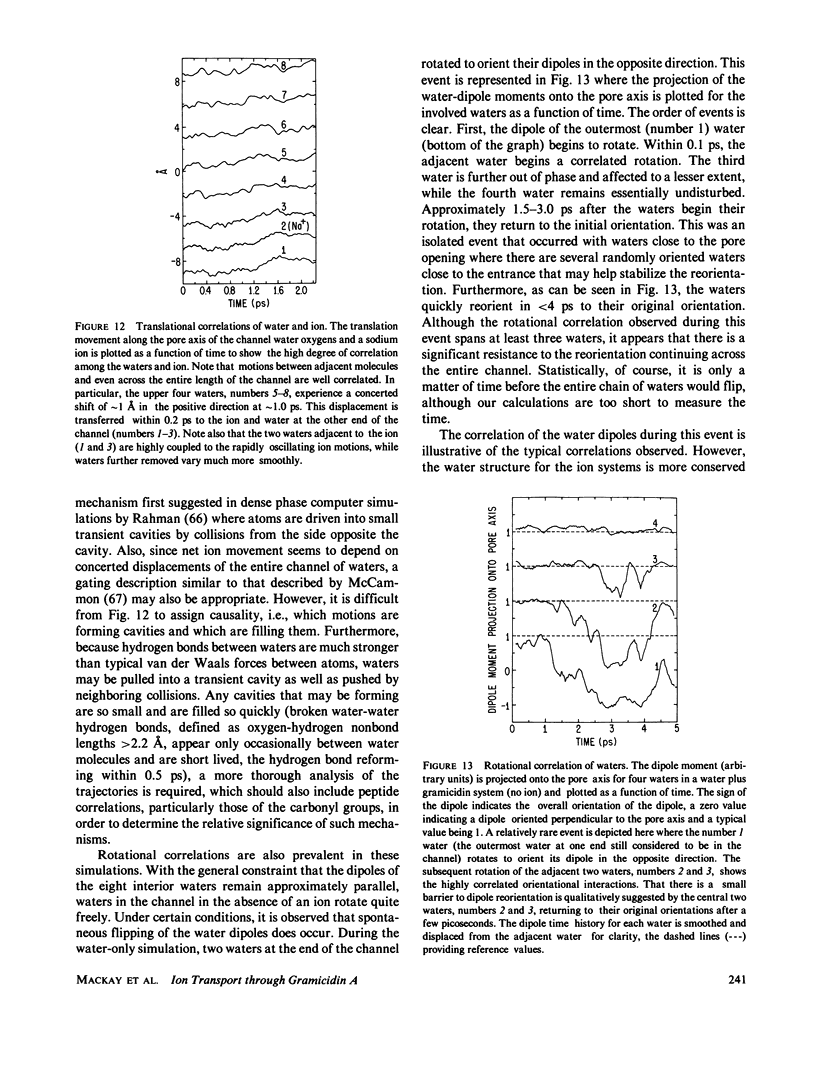
Molecular dynamics calculations in which all atoms were allowed to move were performed on a water-filled ion channel of the polypeptide dimer gramicidin A (approximately 600 atoms total) in the head-to-head Urry model conformation. Comparisons were made among nine simulations in which four different ions (lithium, sodium, potassium, and cesium) were each placed at two different locations in the channel as well as a reference simulation with only water present. Each simulation lasted for 5 ps and was carried out at approximately 300 K. The structure and dynamics of the peptide and interior waters were found to depend strongly on the ion tested and upon its location along the pore. Speculations on the solution and diffusion of ions in gramicidin are offered based on the observations in our model that smaller ions tended to lie off axis and to distort the positions of the carbonyl oxygens more to achieve proper solvation and that the monomer-monomer junction was more distortable than the center of the monomer. With the potential energy surface used, the unique properties of the linear chain of interior water molecules were found to be important for optimal solvation of the various ions. Strongly correlated motions persisting over 25 A among the waters in the interior single-file column were observed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Procopio J. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. On the importance of the aqueous diffusion resistance and ion-water interactions. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1980;481:27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apell H. J., Bamberg E., Alpes H., Läuger P. Formation of ion channels by a negatively charged analog of gramicidin A. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):171–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01869403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Alpes H., Apell H. J., Bradley R., Härter B., Quelle M. J., Urry D. W. Formation of ionic channels in black lipid membranes by succinic derivatives of gramicidin A. J Membr Biol. 1979 Nov 30;50(3-4):257–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01868892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Apell H. J., Alpes H., Gross E., Morell J. L., Harbaugh J. F., Janko K., Läuger P. Ion channels formed by chemical analogs of gramicidin A. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2633–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Janko K. The action of a carbonsuboxide dimerized gramicidin A on lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickmann J., Fischer W. Entropy effects on the ion-diffusion rate in transmembrane protein channels. Biophys Chem. 1983 Apr;17(3):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(83)87007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Enos B., Hägglund J., Sandblom J. Gramicidin as an example of a single-filing ionic channel. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;339:8–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Sandblom J. P. Modeling the gramicidin channel: interpretation of experimental data using rate theory. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):88–90. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84119-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Brickmann J., Läuger P. Molecular dynamics study of ion transport in transmembrane protein channels. Biophys Chem. 1981 Apr;13(2):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. An interaction between gramicidin and the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1045–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow J. M. Cooperative effects in water-biomolecule crystal systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4977–4979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow J. M., Finney J. L., Barnes P. Monte Carlo computer simulation of water-amino acid interactions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jan 22;214(1195):213–228. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler A. T., Huler E., Lifson S. Energy functions for peptides and proteins. I. Derivation of a consistent force field including the hydrogen bond from amide crystals. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Aug 21;96(17):5319–5327. doi: 10.1021/ja00824a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler A. T., Lifson S. Energy functions for peptides and proteins. II. The amide hydrogen bond and calculation of amide crystal properties. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Aug 21;96(17):5327–5335. doi: 10.1021/ja00824a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Energy barriers for passage of ions through channels. Exact solution of two electrostatic problems. Biophys Chem. 1981 Jun;13(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Berg J. M., Hodgson K. O., Stryer L. Gramicidin A crystals contain two cation binding sites per channel. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):723–725. doi: 10.1038/279723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. A., Bamberg E. Influence of membrane thickness and ion concentration on the properties of the gramicidin a channel. Autocorrelation, spectral power density, relaxation and single-channel studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Comparison of Nernst-Planck and reaction rate models for multiply occupied channels. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):575–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P., Stephan W., Frehland E. Fluctuations of barrier structure in ionic channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 16;602(1):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sandblom J., Eisenman G. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in gramicidin A channels. II. Saturation behavior of single channel conductances and evidence for the existence of multiple binding sites in the channel. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 26;40(2):97–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01871143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A. Ion-membrane interactions as structural forces. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:161–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov E. M., Lipkind G. M. Konformatsionnoe sostoianie i mekhanizm funktsionirovaniia gramitsidina A. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1979 Mar-Apr;13(2):363–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B. V., Chandrasekaran R. Conformation of polypeptide chains containing both L- and D-residues. II. Double-helical structures of poly-LD-peptides. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;10(2):129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachnandran G. N., Chandrasekaran R. Conformation of peptide chains containing both L- & D-residues. I. Helical structures with alternating L- & D-residues with special reference to the LD-ribbon & the LD-helices. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;9(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Finkelstein A. Interaction of ions and water in gramicidin A channels: streaming potentials across lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):327–340. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Finkelstein A. Water permeability of gramicidin A-treated lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):341–350. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom J., Eisenman G., Neher E. Ionic selectivity, saturation and block in gramicidin A channels: I. Theory for the electrical properties of ion selective channels having two pairs of binding sites and multiple conductance states. J Membr Biol. 1977 Mar 23;31(4):383–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01869414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schagina L. V., Grinfeldt A. E., Lev A. A. Interaction of cation fluxes in gramicidin A channels in lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 May 18;273(5659):243–245. doi: 10.1038/273243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Molecular perspectives of monovalent cation selective transmembrane channels. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1979;21:311–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60642-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Prasad K. U., Trapane T. L. Location of monovalent cation binding sites in the gramicidin channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Fossel E. T., Blout E. R. The conformation of gramicidin A. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5249–5256. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S., Wallace B. A., Morrow J. S., Veatch W. R. Conformation of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study of 13C-enriched gramicidin in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


