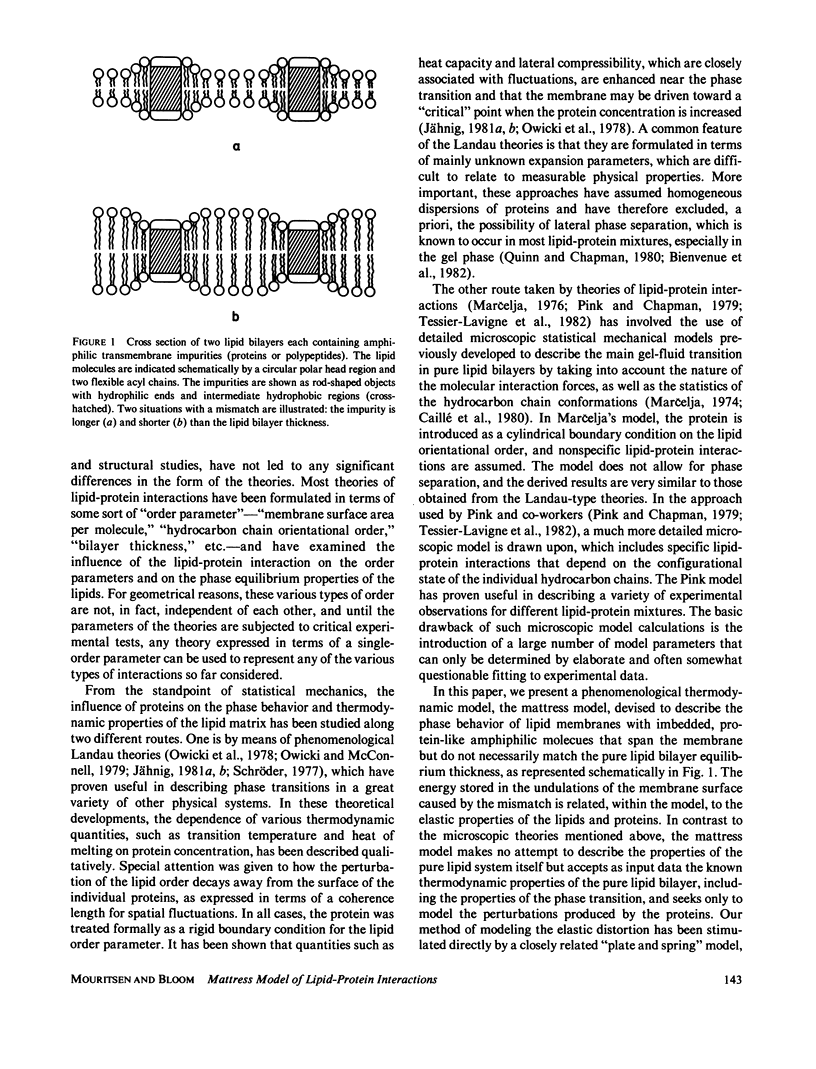
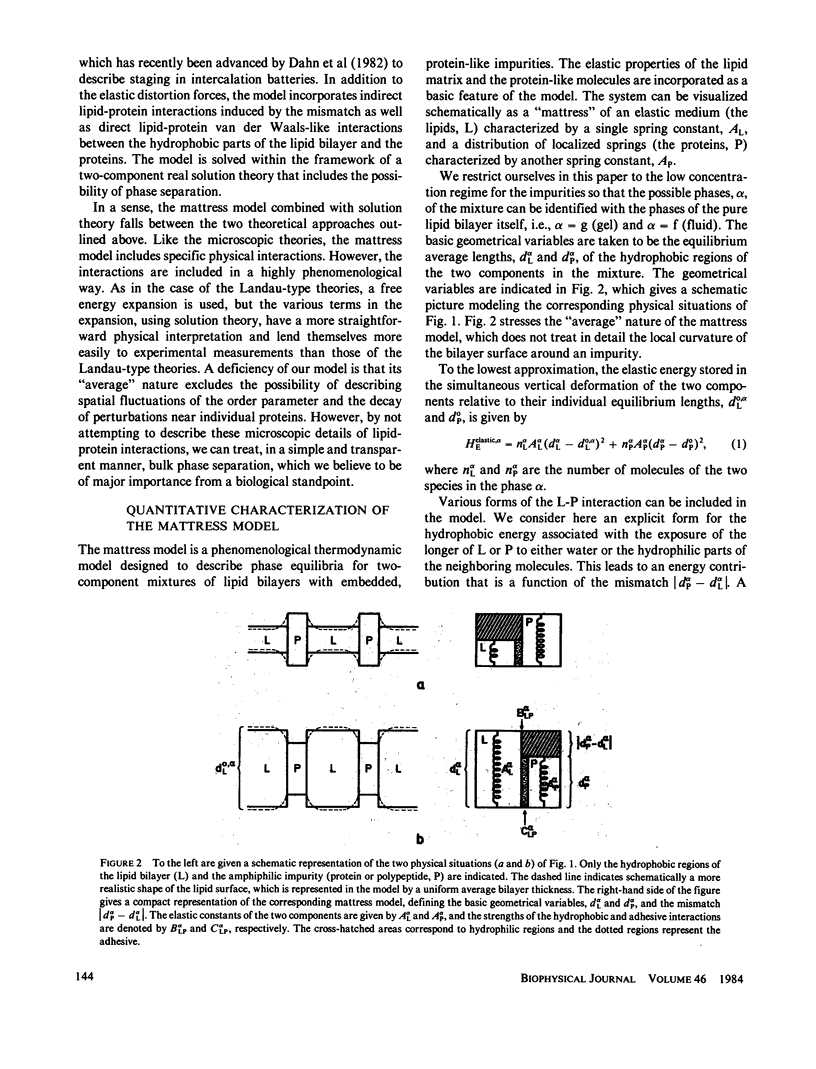
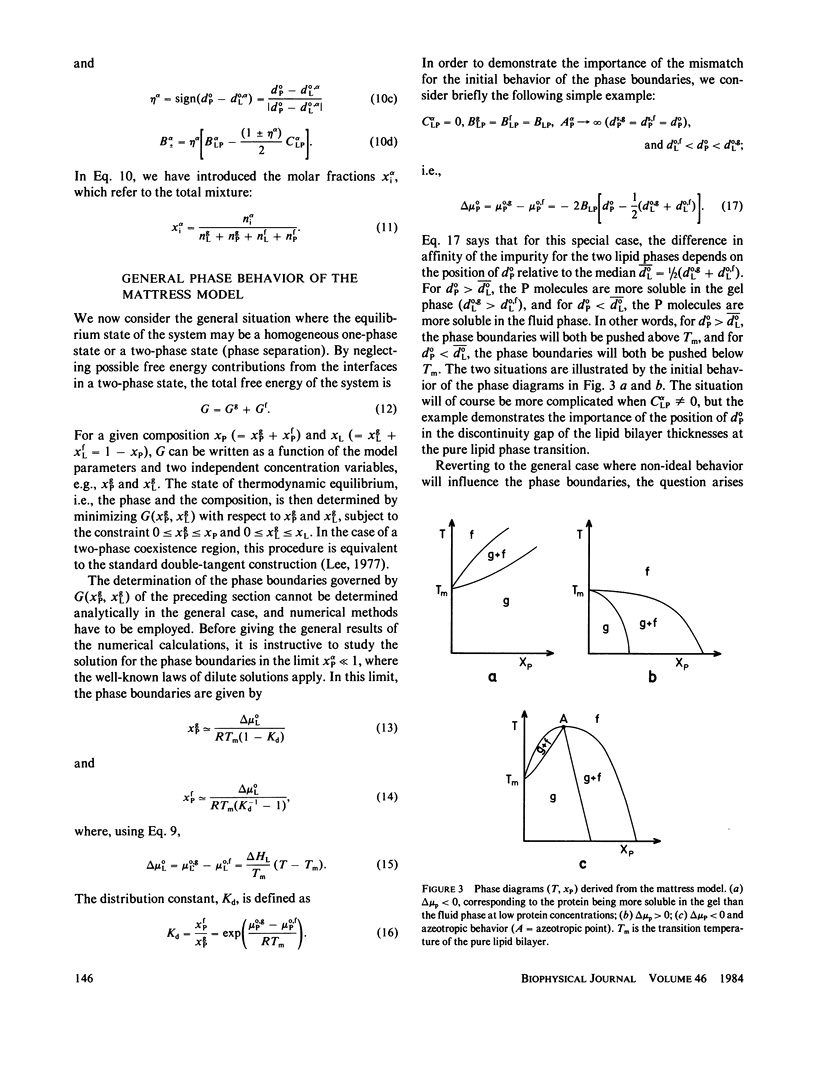
Abstract
A thermodynamic model is proposed for describing phase diagrams of mixtures of lipid bilayers and amphiphilic proteins or polypeptides in water solution. The basic geometrical variables of the model are the thickness of the hydrophobic region of the lipid bilayer and the length of the hydrophobic region of the proteins. The model incorporates the elastic properties of the lipid bilayer and the proteins, as well as indirect and direct lipid-protein interactions expressed in terms of the geometrical variables. The concept of mismatch of the hydrophobic regions of the lipids and proteins is an important ingredient of the model. The general phase behavior is calculated using simple real solution theory. The phase behavior turns out to be quite rich and is used to discuss previous experiments on planar aggregations of proteins in phospholipid bilayers and to propose a systematic study of synthetic amphiphilic polypeptides in bilayers of different thicknesses. The model is used to interpret the influence of the lipid-protein interaction on calorimetric measurements and on local orientational order as determined by deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienvenue A., Bloom M., Davis J. H., Devaux P. F. Evidence for protein-associated lipids from deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance studies of rhodopsin-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine recombinants. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. M., Moscarello M. A. Dependence of boundary lipid on fatty acid chain length in phosphatidylcholine vesicles containing a hydrophobic protein from myelin proteolipid. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5734–5739. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Cornell B. A., Ellasz A. W., Perry A. Interactions of helical polypepetide segments which span the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Studies of the gramicidin A lipid-water system. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):517–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Gómez-Fernández J. C., Goñi F. M. Intrinsic protein--lipid interactions. Physical and biochemical evidence. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):185–235. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W., Sakura J. D., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Protein-lipid interactions: recombinants of the proteolipid apoprotein of myelin with dimyristoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2313–2319. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H., Hodges R. S., Bloom M. The Interaction between a Synthetic Amphiphilic Polypeptide and Lipids. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):170–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84655-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Zaccai G. Bacteriorhodopsin is an inside-out protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 2. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Nov;3(4):331–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Kwok R. Mechanical calorimetry of large dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles in the phase transition region. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4874–4879. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Fernandez J. C., Goni F. M., Bach D., Restall C. J., Chapman D. Protein-lipid interaction. Biophysical studies of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase reconstituted systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 6;598(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. Crystallizing membrane proteins. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):490–490. doi: 10.1038/287490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Blume A., Rehorek M., Dencher N. A. Calorimetric and fluorescence depolarization studies on the lipid phase transition of bacteriorhodopsin--dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7109–7115. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. E., Hudson B. S., Andersen H. C. A theory of phase transitions and phase diagrams for one- and two-component phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4349–4359. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Critical effects from lipid-protein interaction in membranes. I. Theoretical description. Biophys J. 1981 Nov;36(2):329–345. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84735-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Critical effects from lipid-protein interaction in membranes. II. Interpretation of experimental results. Biophys J. 1981 Nov;36(2):347–357. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84736-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi A., Hyde J. S. Spin-label saturation-transfer electron spin resonance detection of transient association of rhodopsin in reconstituted membranes. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5978–5983. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok R., Evans E. Thermoelasticity of large lecithin bilayer vesicles. Biophys J. 1981 Sep;35(3):637–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84817-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. II. Mictures involving lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):285–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer thickness varies linearly with acyl chain length in fluid phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., McAlister M., Fuller N., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Measurement of the lateral compressibility of several phospholipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):667–672. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay A. L., Burnell E. E., Bienvenue A., Devaux P. F., Bloom M. Flexibility of membrane proteins by broad-line proton magnetic resonance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 9;728(3):460–462. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Lipid-mediated protein interaction in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Henderson R. Structure of the bacteriorhodopsin proton pump of Halobacterium halobium and other membrane proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Dec;8(6):677–678. doi: 10.1042/bst0080677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montecucco C., Smith G. A., Dabbeni-sala F., Johannsson A., Galante Y. M., Bisson R. Bilayer thickness and enzymatic activity in the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase and ATPase complex. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80588-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., Springgate M. W., McConnell H. M. Theoretical study of protein--lipid interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1616–1619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddy M. R., Dahlquist F. W., Davis J. H., Bloom M. Dynamical and temperature-dependent effects of lipid-protein interactions. Application of deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to the same reconstitutions of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3152–3162. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink D. A., Chapman D. Protein-lipid interactions in bilayer membranes: a lattice model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1542–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Chapman D. The dynamics of membrane structure. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(1):1–117. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Gilbert D. B., Tanford C. Empirical correlation between hydrophobic free energy and aqueous cavity surface area. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2925–2927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr Regulation of membrane enzymes by lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):209–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Seelig J. Deuterium order parameters in relation to thermodynamic properties of a phospholiped bilayer. A statistical mechanical interpretation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2283–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. Deuterium magnetic resonance: theory and application to lipid membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1977 Aug;10(3):353–418. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai G., Büldt G., Seelig A., Seelig J. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. II. Chain conformation and segmental disorder. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):693–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Dijck P. W., de Kruijff B., Verkleij A. J., van Deenen L. L. Effect of glycophorin incorporation on the physico-chemical properties of phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):9–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


