Abstract
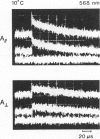
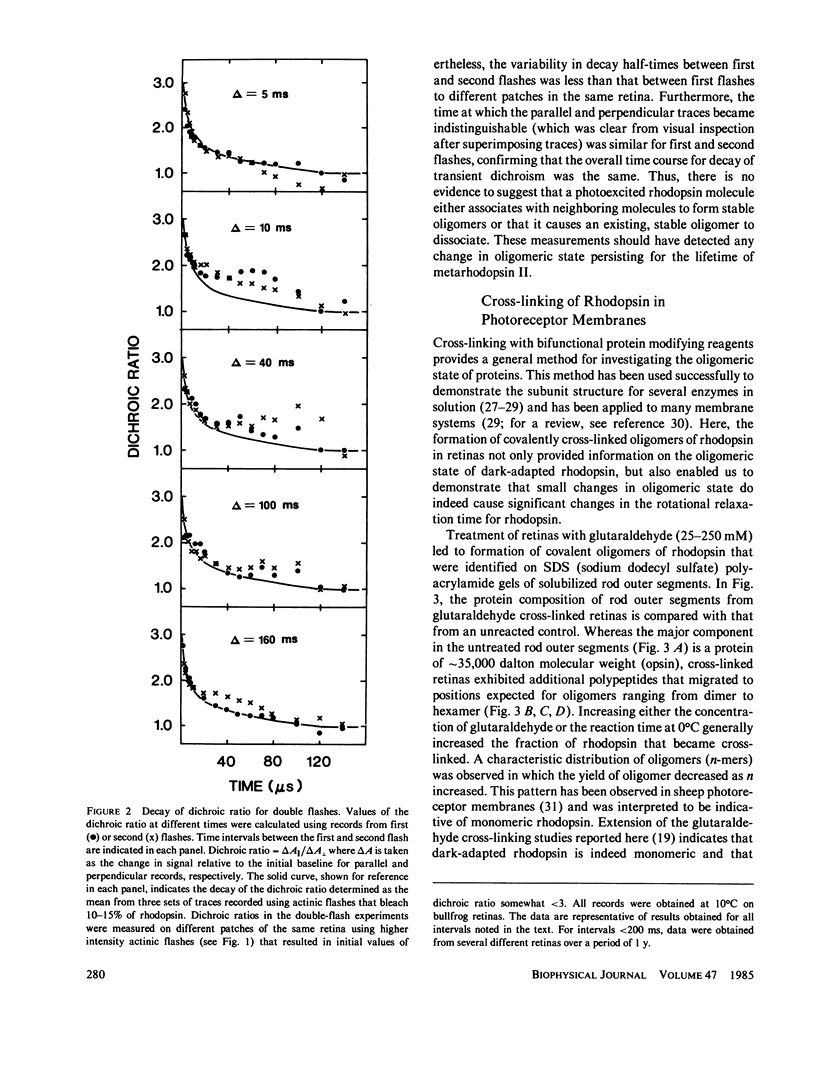
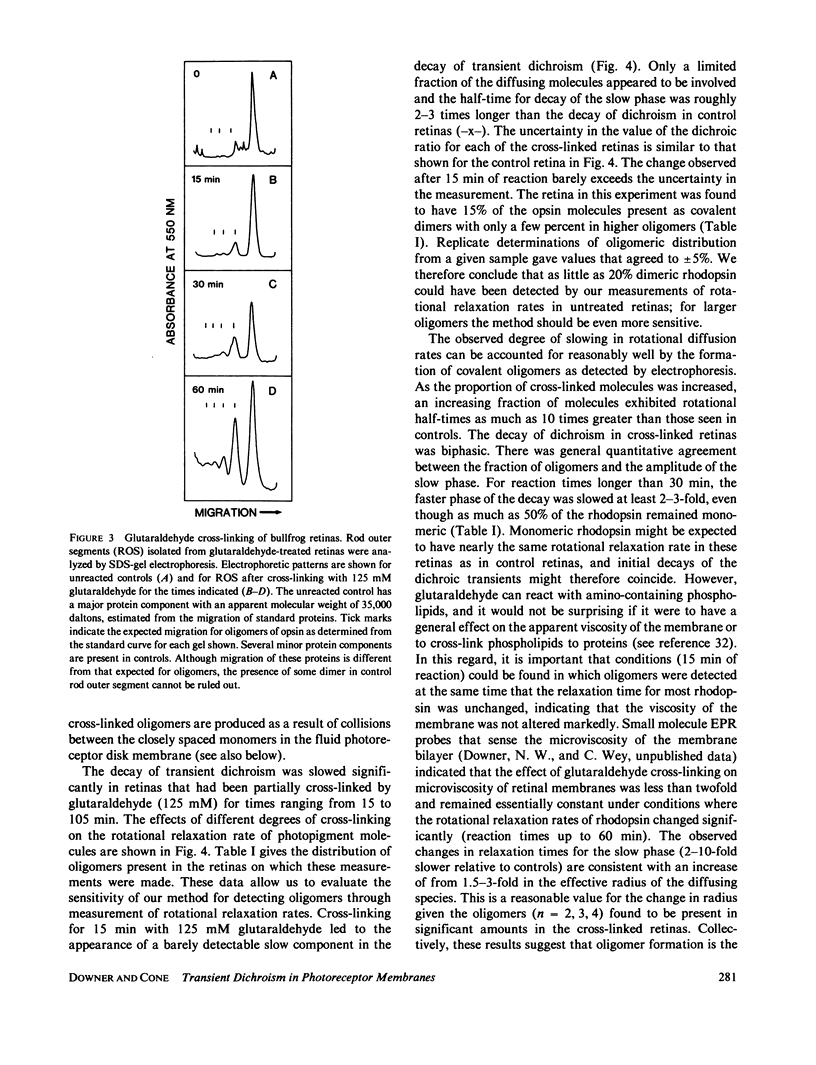
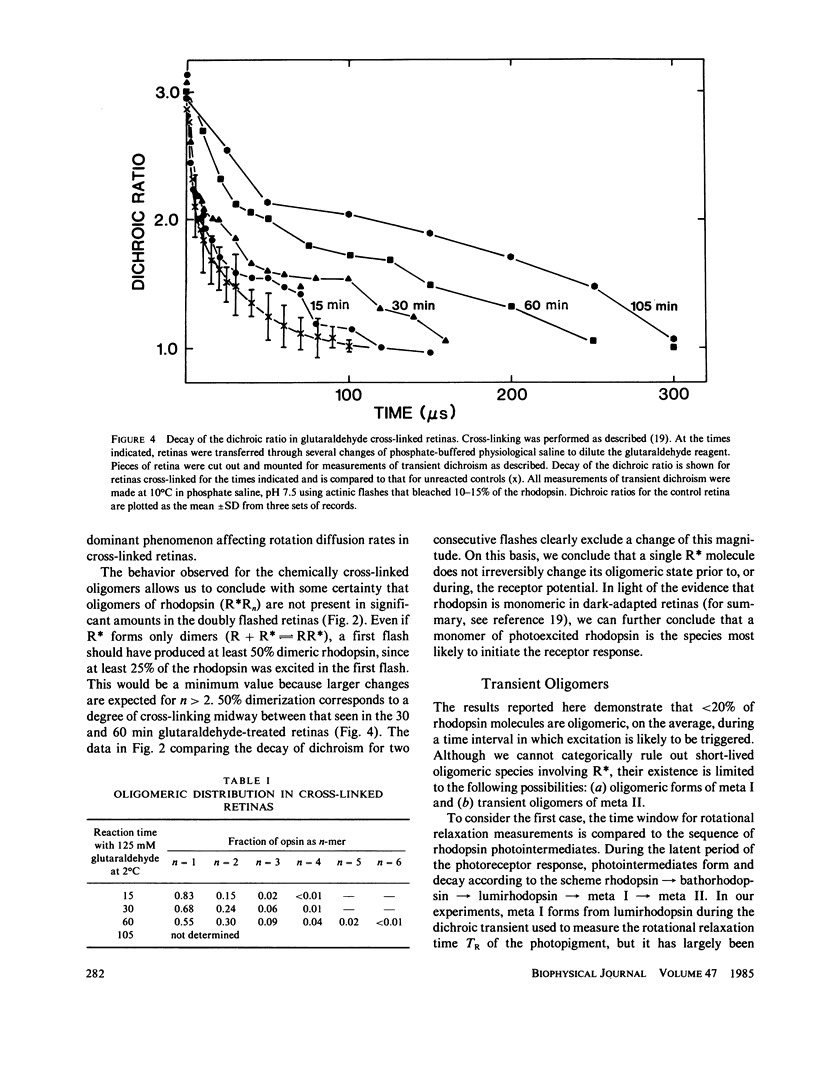
If a photoexcited rhodopsin molecule initiates the formation of rhodopsin oligomers during the process of visual excitation, the rate of rotational diffusion of the rhodopsin molecules involved should change markedly. Using microsecond-flash photometry, we have observed the rotational diffusion of rhodopsin throughout the time period of visual excitation and found that no detectable change occurs in its rotational diffusion rate. Partial chemical cross-linking of the retina yields oligomers of rhodopsin and causes a significant decrease in the rotational diffusion rate of rhodopsin even when as little as 20% of rhodopsin is dimeric. Moreover, the pattern of oligomers formed by cross-linking, taken together with the magnitude of decreases in rotational diffusion rate accompanying the cross-linking reaction, suggests that rhodopsin is a monomer in the dark-adapted state. The experiments reported here show that photoexcited rhodopsin molecules do not irreversibly associate with unbleached neighbors during the time course of the receptor response. Hence, it is not likely that stable oligomers of rhodopsin trigger the excitation of the photoreceptor cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bownds D. Site of attachment of retinal in rhodopsin. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1178–1181. doi: 10.1038/2161178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett M., Findlay J. B. Investigation of the organization of rhodopsin in the sheep photoreceptor membrane by using cross-linking reagents. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):215–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1770215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. K. Rhodopsin rotates in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):35–38. doi: 10.1038/newbio236035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hubbell W. L. Temperature- and light-dependent structural changes in rhodopsin-lipid membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A., Cobbs W. H., 3rd Rhodopsin cycle in the living eye of the rat. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):820–822. doi: 10.1038/221820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain R. C., Marinetti G. V., O'Brien D. F. Topology of amino phospholipids in bovine retinal rod outer segment disk membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4186–4192. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer N. W. Cross-linking of dark-adapted frog photoreceptor disk membranes. Evidence for monomeric rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83918-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer N. W., Englander S. W. Hydrogen exchange study of membrane-bound rhodopsin. II. Light-induced protein structure change. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8101–8104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. S., Hagins W. A. Control of Ca2+ in rod outer segment disks by light and cyclic GMP. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):344–348. doi: 10.1038/303344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold G. H., Korenbrot J. I. Light-induced calcium release by intact retinal rods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A. The visual process: Excitatory mechanisms in the primary receptor cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1972;1:131–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.01.060172.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Müllner H., Sund H. Investigation of the symmetry of oligomeric enzymes with bifunctional reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):79–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):969–970. doi: 10.1038/211969a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Bennett N., Michel-Villaz M., Chabre M. Interactions between photoexcited rhodopsin and GTP-binding protein: kinetic and stoichiometric analyses from light-scattering changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6873–6877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Lateral diffusion of visual pigment in photorecptor disk membranes. Science. 1974 Aug 2;185(4149):457–459. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4149.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Jagger W. S., Kaplan M. W., Bargoot F. G. Membrane structure changes in rod outer segments associated with rhodopsin bleaching. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):31–36. doi: 10.1038/251031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Darszon A., Trissl H. W. Transmembrane channel formation in rhodopsin-containing bilayer membranes. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):221–225. doi: 10.1038/267221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M. Rhodopsin in model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 20;559(2-3):231–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D. F., Costa L. F., Ott R. A. Photochemical functionality of rhodopsin-phospholipid recombinant membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1295–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D. F., Zumbulyadis N., Michaels F. M., Ott R. A. Light-regulated permeability of rhodopsin:egg phosphatidylcholine recombinant membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5222–5226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Richards F. M. Chemical cross-linking: reagents and problems in studies of membrane structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:523–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):438–441. doi: 10.1038/247438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. G., Jr, Fager R. S., Litman R. J. Light-activated calcium release from sonicated bovine retinal rod outer segment disks. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1399–1405. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. Cross-linking the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyminski P. N., Klingbiel R. T., Ott R. A., O'Brien D. F. Photoinduced calcium release from rhodopsin-phospholipid membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1197–1204. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALD G., BROWN P. K., GIBBONS I. R. The problem of visual excitation. J Opt Soc Am. 1963 Jan;53:20–35. doi: 10.1364/josa.53.000020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. L., Bownds D., Green S. H., Morrisey J. L., Shedlovsky A. Guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and the in vitro physiology of frog photoreceptor membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 May;69(5):667–679. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Lamb T. D., Baylor D. A. Light-induced fluctuations in membrane current of single toad rod outer segments. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):78–80. doi: 10.1038/269078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikami S., George J. S., Hagins W. A. Light-induced calcium fluxes from outer segment layer of vertebrate retinas. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):395–398. doi: 10.1038/286395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]