Abstract
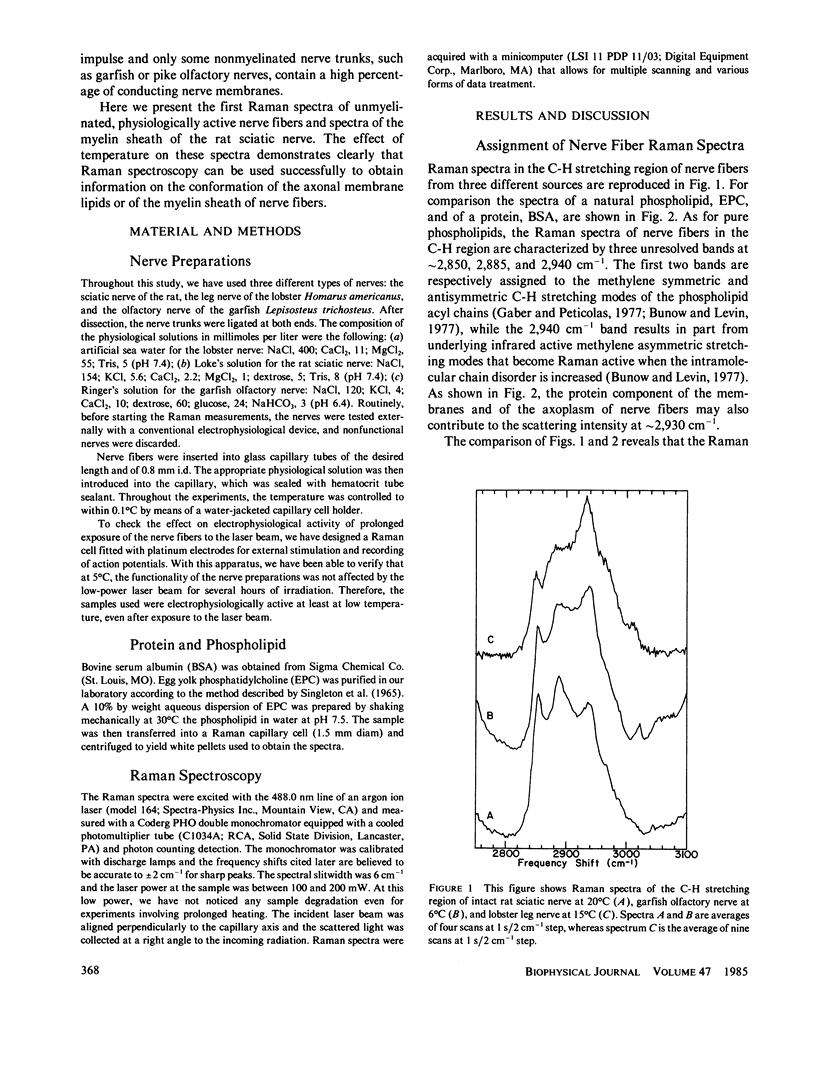
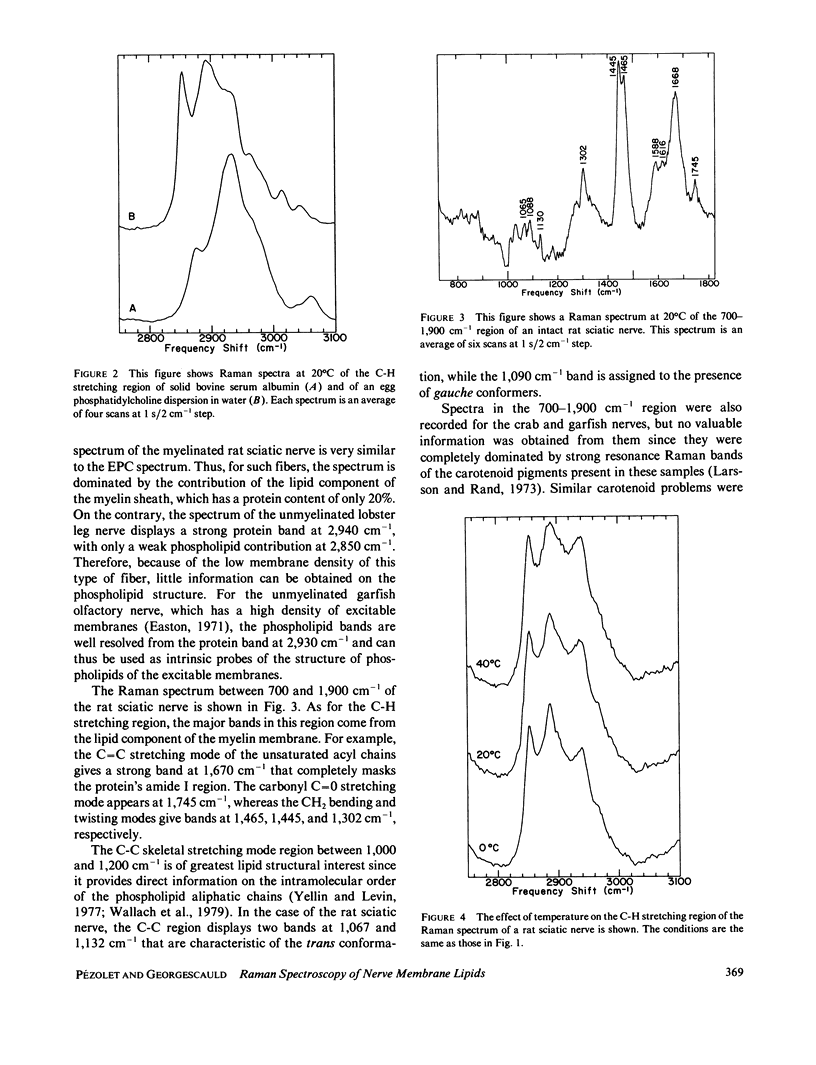
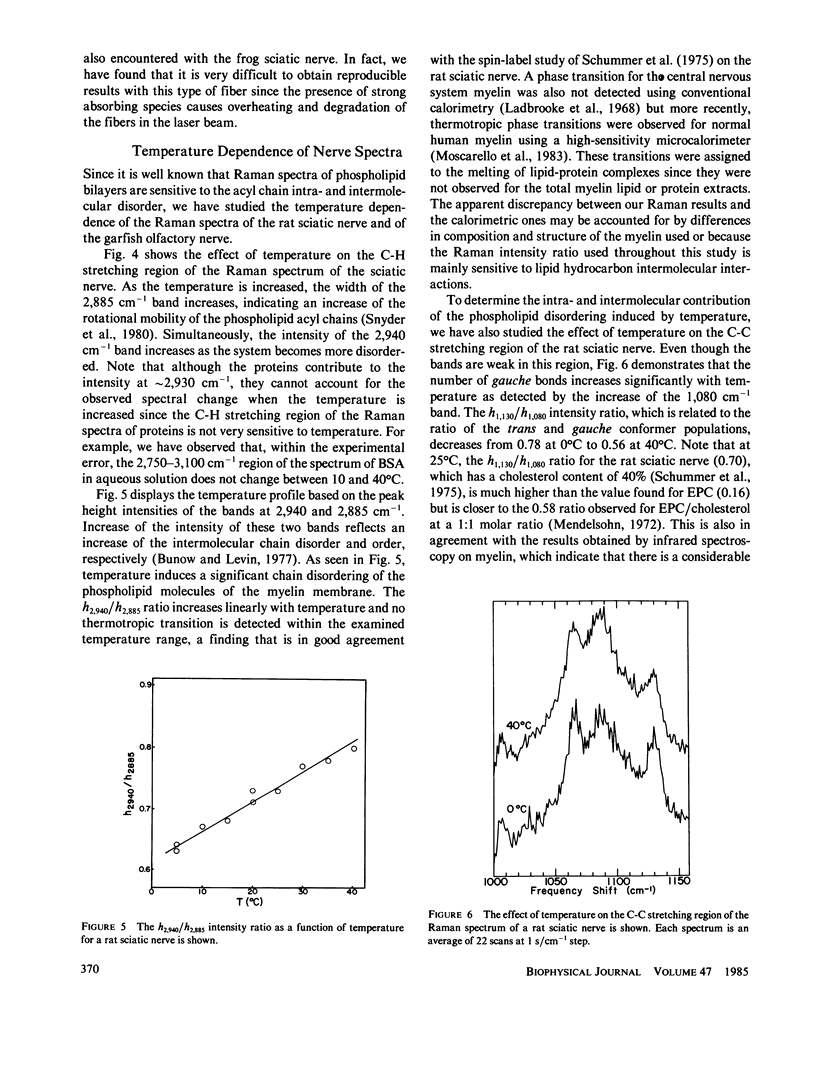
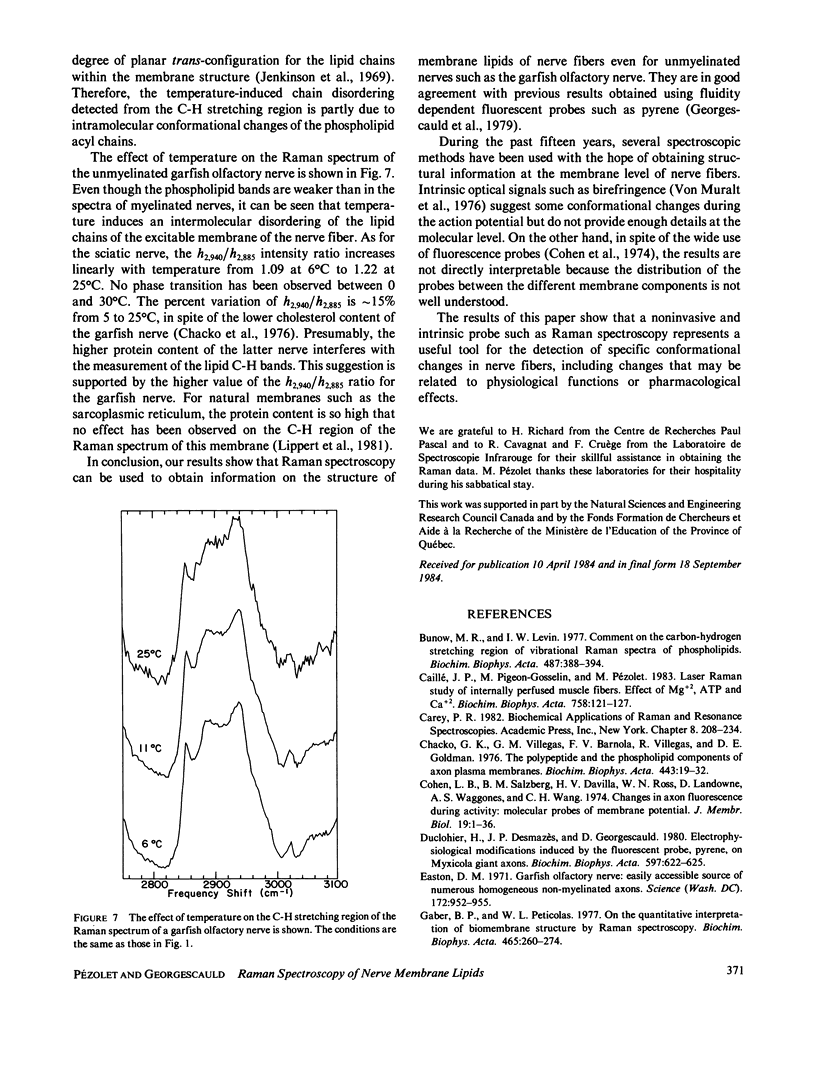
The molecular structures of different nerve fibers kept in good physiological conditions were studied by laser Raman spectroscopy. For myelinated nerves like the rat sciatic nerve, the Raman spectrum is dominated by bands due to the lipid component of the myelin sheath. The temperature dependence of these bands does not reveal any thermotropic phase transition between 0 and 40 degrees C. There is, however, with temperature, a linear increase in the intermolecular disorder that is accompanied by an increase in the number of gauche bonds of the phospholipid acyl chains. For unmyelinated nerves such as the lobster leg nerve, the C-H stretching region of the Raman spectrum is covered by bands arising from the protein component of the axoplasm. However, for the garfish olfactory nerve that has a high density of excitable membranes, phospholipid bands are observed and can be used as intrinsic structural probes of the excitable membranes. The relative intensity of these bands is also temperature dependent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunow M. R., Levin I. W. Comment on the carbon-hydrogen stretching region of vibrational Raman spectra of phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 25;487(2):388–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé J. P., Pigeon-Gosselin M., Pézolet M. Laser Raman study of internally perfused muscle fibers. Effect of Mg2+, ATP and Ca2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 29;758(2):121–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko G. K., Villegas G. M., Barnola F. V., Villegas R., Goldman D. E. The polypeptide and the phospholipid components of axon plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 4;443(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Salzberg B. M., Davila H. V., Ross W. N., Landowne D., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H. Changes in axon fluorescence during activity: molecular probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(1):1–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01869968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duclohier H., Desmazes J. P., Georgescauld D. Electrophysiological modifications induced by the fluorescent probe, pyrene, on Myxicola giant axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 24;597(3):622–625. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. M. Garfish olfactory nerve: easily accessible source of numerous long, homogeneous, nonmyelinated axons. Science. 1971 May 28;172(3986):952–955. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3986.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber B. P., Peticolas W. L. On the quantitative interpretation of biomembrane structure by Raman spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):260–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgescauld D., Desmazes J. P., Duclohier H. Temperature dependence of the fluorescence of pyrene labeled crab nerve membranes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;27(3):147–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00215363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgescauld D., Duclohier H. Transient fluorescence signals from pyrene labeled pike nerves during action potential. Possible implications for membrane fluidity changes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):1186–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic channels in excitable membranes. Current problems and biophysical approaches. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85489-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Orientation and motion of amphiphilic spin labels in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):20–27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson T. J., Kamat V. B., Chapman D. Physical studies of myelin. II. Proton magnetic resonance and infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D. Excitable membranes. Nature. 1972 Sep 1;239(5366):29–32. doi: 10.1038/239029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Jenkinson T. J., Kamat V. B., Chapman D. Physical studies of myelin. I. Thermal analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 2;164(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte A., Richard H., Bonnaud E., Henry P., Vital A., Georgescauld D. A spin label study of myelin fluidity with normal and pathological peripheral nerves. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Nov;43(3):345–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson K., Rand R. P. Detection of changes in the environment of hydrocarbon chains by Raman spectroscopy and its application to lipid-protein systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 29;326(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippert J. L., Lindsay R. M., Schultz R. Laser Raman characterization of conformational changes in sarcoplasmic reticulum induced by temperature, Ca2+, and Mg2+. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12411–12416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R. Laser-Raman spectroscopic study of egg lecithin and egg lecithin-cholesterol mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muralt A., Weibel E. R., Howarth J. V. The optical spike. Structure of the olfactory nerve of pike and rapid birefringence changes during excitation. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Nov 30;367(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00583658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pézolet M., Pigeon-Gosselin M., Nadeau J., Caillé J. P. Laser Raman scattering. A molecular probe of the contractile state of intact single muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Jul;31(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85036-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schummer S., Hegner D., Schnepel G. H., Wellhöner H. H. Investigations of thermotropic phase changes in peripheral nerve of frog and rat. A spin label study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 11;394(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. G., Scherer J. R., Gaber B. P. Effects of chain packing and chain mobility on the Raman spectra of biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 2;601(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szalontai B., Bagyinka C., Horváth L. I. Changes in the Raman spectrum of frog sciatic nerve during action potential propagation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):660–665. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91551-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Verma S. P., Fookson J. Application of laser Raman and infrared spectroscopy to the analysis of membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 20;559(2-3):153–208. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


