Abstract
We studied activation of the nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptor on cells of a mouse clonal muscle cell line (BC3H1). We analyzed single-channel currents through outside-out patches elicited with various concentrations of acetylcholine (ACh), carbamylcholine (Carb) and suberyldicholine (Sub). Our goal is to determine a likely reaction scheme for receptor activation by agonist and to determine values of rate constants for transitions in that scheme. Over a wide range of agonist concentrations the open-time duration histograms are not described by single exponential functions, but are well-described by the sum of two exponentials, a brief-duration and a long-duration component. At high concentration, channel openings occur in groups and these groups contain an excess number of brief openings. We conclude that there are two open states of the ACh receptor with different mean open times and that a single receptor may open to either open state. The concentration dependence of the numbers of brief and long openings indicates that brief openings do not result from the opening of channels of receptors which have only one agonist molecule bound to them. Closed-time duration histograms exhibit a major brief component at low concentrations. We have used the method proposed by Colquhoun and Sakmann (1981) to analyze these brief closings and to extract estimates for the rates of channel opening (beta) and agonist dissociation (k-2). We find that this estimate of beta does not predict our closed-time histograms at high agonist concentration (ACh: 30-300 microM; Carb: 300-1,000 microM). We conclude that brief closings at low agonist concentrations do not result solely from transitions between the doubly-liganded open and the doubly-liganded closed states. Instead, we postulate the existence of a second closed-channel state coupled to the open state.
Full text
PDF

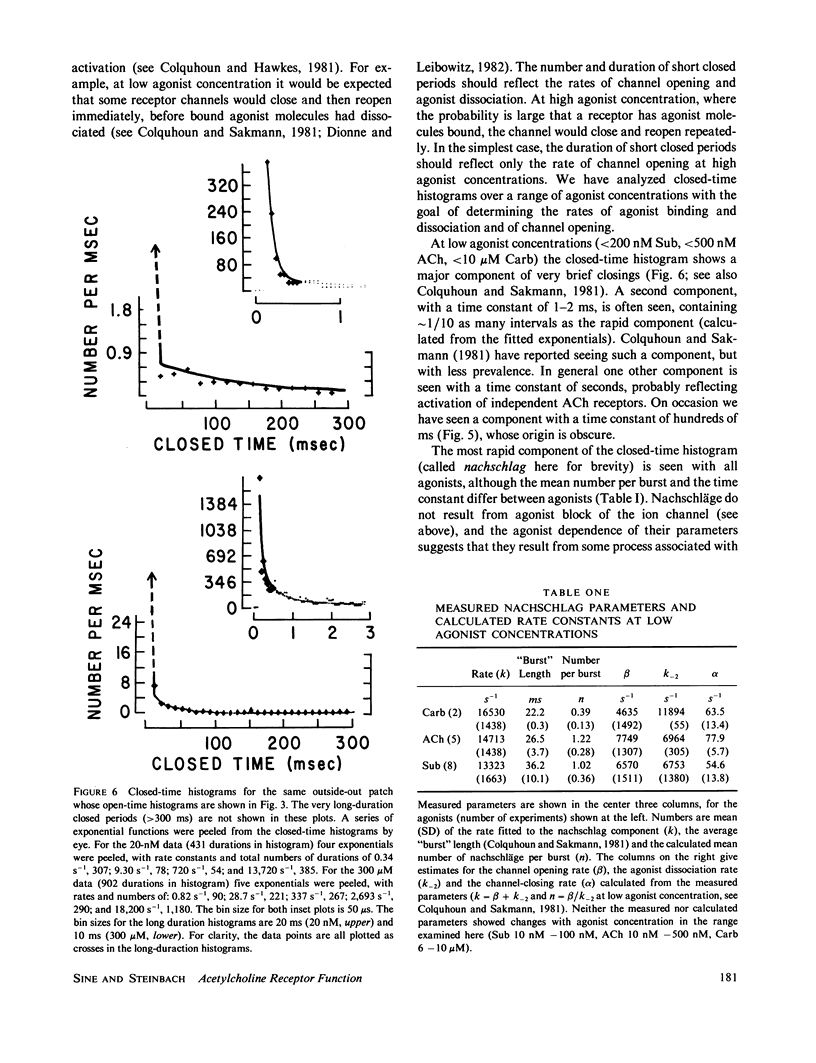



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Nonner W., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. Block of endplate channels by permeant cations in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Dec;78(6):593–615. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.6.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Acetylcholine receptor kinetics. J Membr Biol. 1981 Feb 28;58(3):161–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01870902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Sakmann B. Decamethonium both opens and blocks endplate channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Sachs F. Flickering of a nicotinic ion channel to a subconductance state. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84362-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Patrick J. Purification of an acetylcholine receptor from a nonfusing muscle cell line. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4900–4908. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese R., England J. M. Decamethonium in depolarized muscle and the effects of tubocurarine. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):345–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Leibowitz M. D. Acetylcholine receptor kinetics. A description from single-channel currents at snake neuromuscular junctions. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84515-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. An analysis of the dose-response relationship at voltage-clamped frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:421–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Wong B. S., Morris C. E., Lecar H., Christian C. N. Successive openings of the same acetylcholine receptor channel are correlated in open time. Biophys J. 1983 Apr;42(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84375-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Dionne V. E. Single-channel acetylcholine receptor kinetics. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84144-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor subunits transit a precursor pool before acquiring alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3605–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Labarca P., Fredkin D. R., Suarez-Isla B. A. Channel properties of the purified acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica reconstituted in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84145-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., McMillan J., Wolfson H., O'Brien J. C. Acetylcholine receptor metabolism in a nonfusing muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2143–2153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Taylor P. Relationship between reversible antagonist occupancy and the functional capacity of the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6692–6699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Taylor P. The relationship between agonist occupation and the permeability response of the cholinergic receptor revealed by bound cobra alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10144–10156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S., Taylor P. Functional consequences of agonist-mediated state transitions in the cholinergic receptor. Studies in cultured muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3315–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


