Abstract
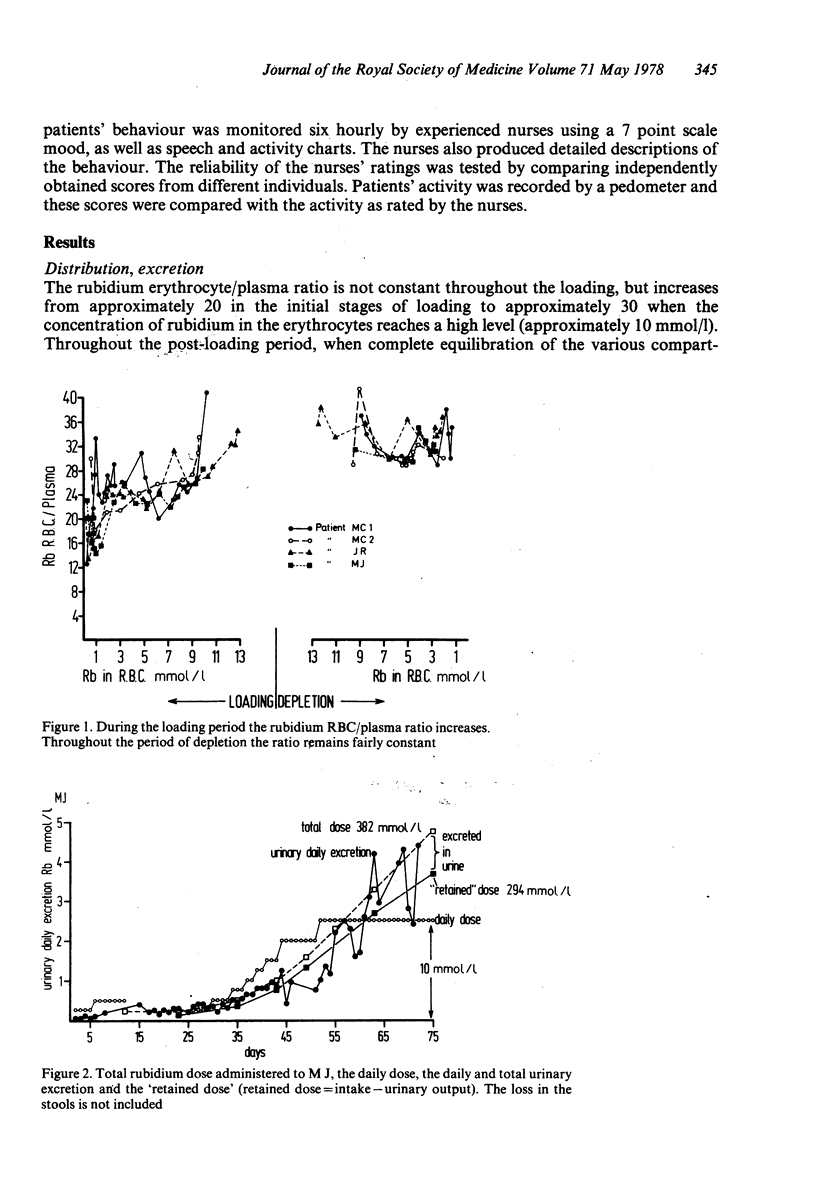
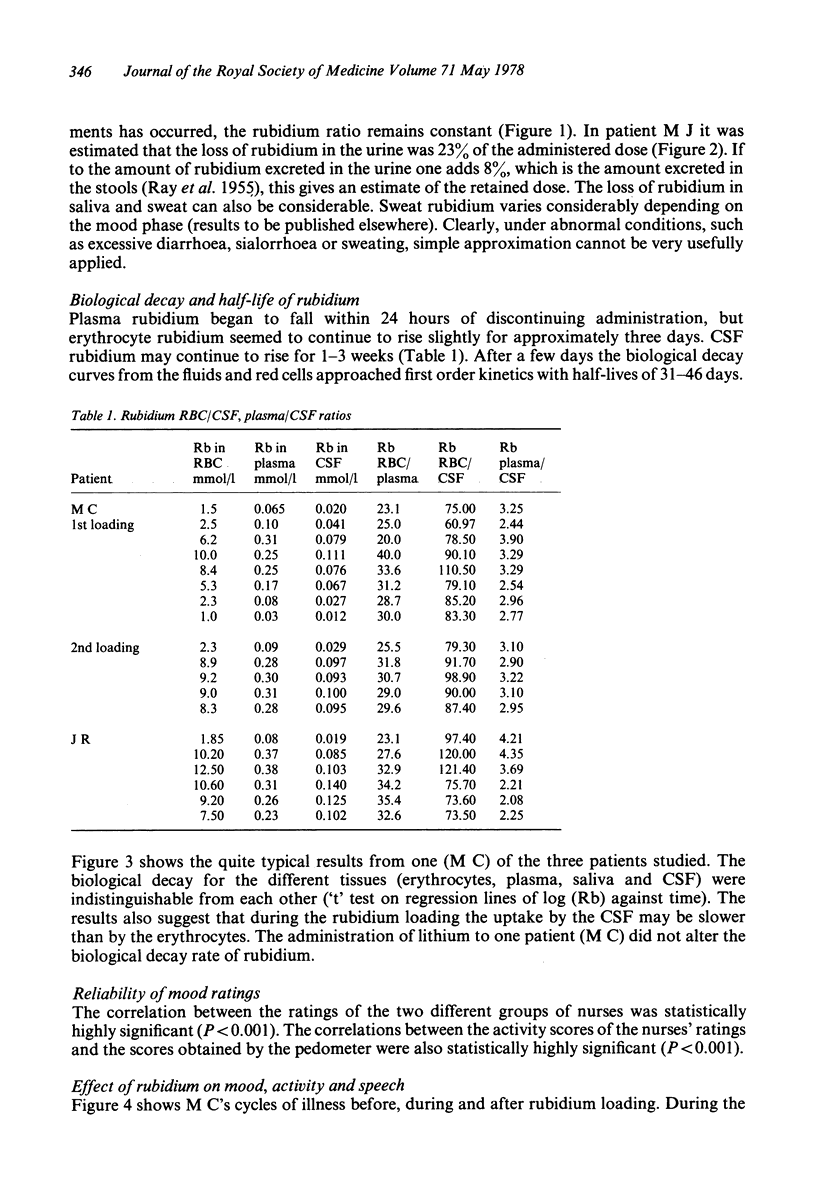
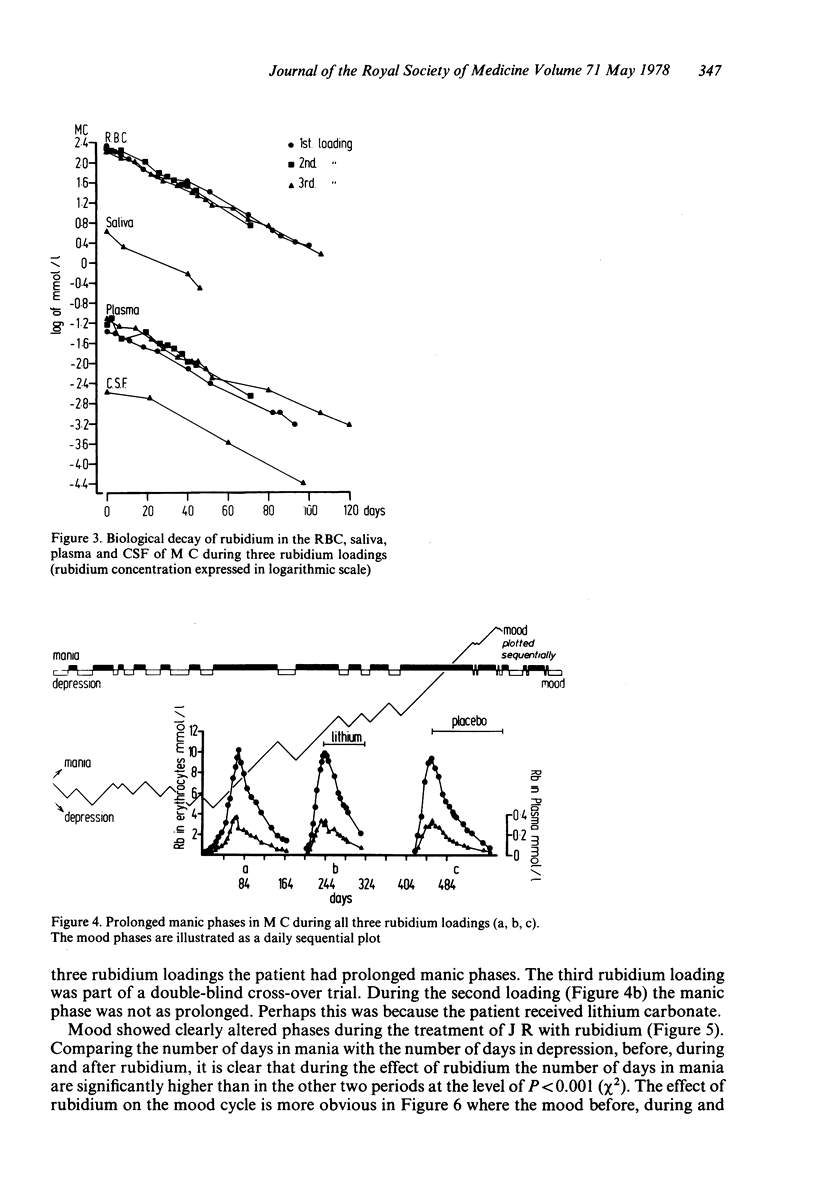
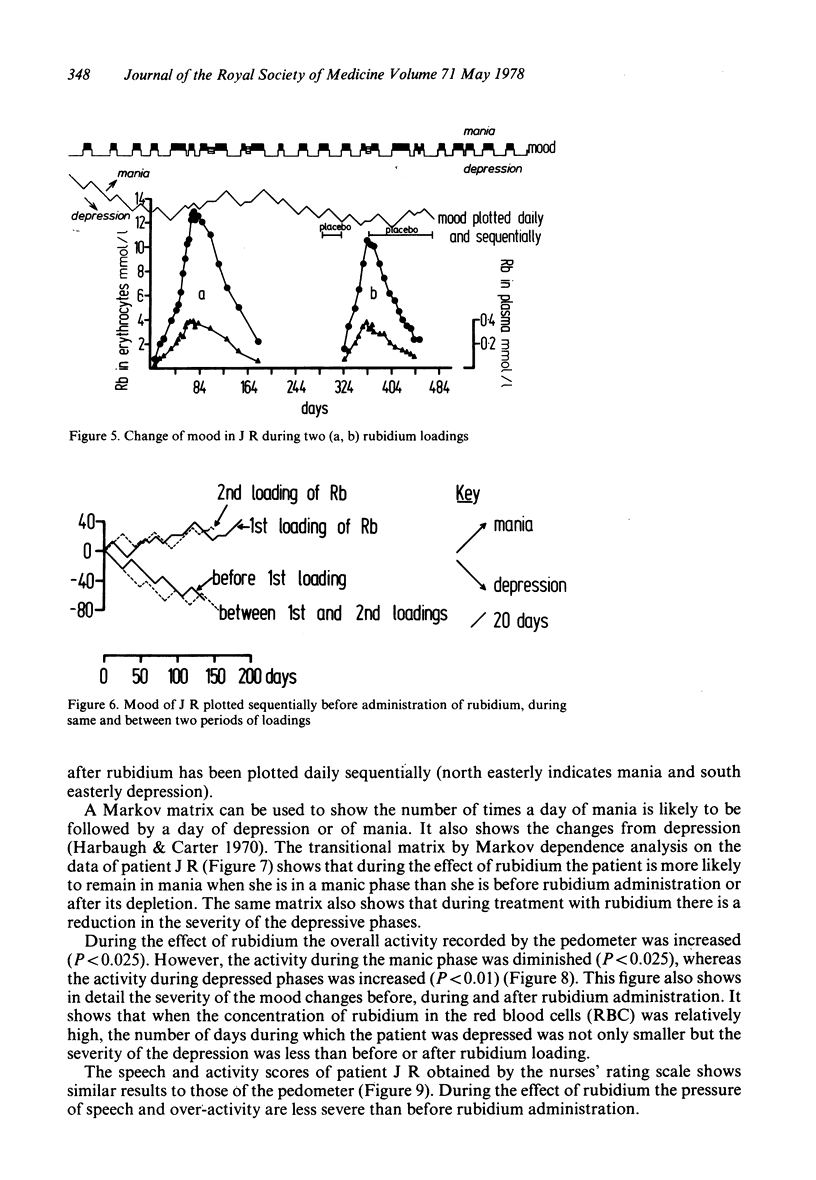
Clinical studies of the effects of rubidium ions on the course of manic-depressive illness are reported. It seems that rubidium tends to increase the length of manic phases and possibly reduces the extremes of mood. Rubidium did not seem to produce any severe side effects in the dose administered, but it has a long biological half-life and caution is still required. Some details of the CSF, RBC, saliva and plasma and urine kinetics are also reported.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W. The effect of rubidium on the distribution and movement of potassium between blood, brain and cerebrospinal fluid in the rabbit. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 1;24(2):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. J., Sharp P. T. Rubidium and lithium: opposite effects on amine-mediated excitement. Science. 1971 Jun 25;172(3990):1355–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3990.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieve R. R., Meltzer H. L. Proceedings: Rubidium salts--toxic effects in humans and clinical effects as an antidepressant drug. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1974 Jan;10(1):38–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieve R. R., Meltzer H. L., Taylor R. M. Rubidium chloride ingestion by volunteer subjects: initial experience. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;20(4):307–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00403562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieve R. R., Meltzer H., Dunner D. L., Levitt M., Mendlewicz J., Thomas A. Rubidium: biochemical, behavioral, and metabolic studies in humans. Am J Psychiatry. 1973 Jan;130(1):55–61. doi: 10.1176/ajp.130.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENDENING B. L., PARRISH D. B., SCHRENK W. G. Effects of rubidium in purified diets fed rats. J Nutr. 1956 Dec 10;60(4):563–579. doi: 10.1093/jn/60.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. T., Lewis T. R., Wagner W. D. Acute toxicity of cesium and rubidium compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 May;32(2):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILPATRICK R., RENSCHLER H. E., MUNRO D. S., WILSON G. M. A comparison of the distribution of 42K and 86Rb in rabbit and man. J Physiol. 1956 Jul 27;133(1):194–201. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. L., Lieberman K. W. Chronic ingestion of rubidium without toxicity: implications for human therapy. Experientia. 1971 Jun;27(6):672–674. doi: 10.1007/BF02136954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer H. L., Taylor R. M., Platmann S. R., Fieve R. R. Rubidium: a potential modifier of affect and behaviour. Nature. 1969 Jul 19;223(5203):321–322. doi: 10.1038/223321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platman S. R. Lithium and rubidium: a role in the affective disorders. Dis Nerv Syst. 1971 Sep;32(9):604–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY C. T., THREEFOOT S. A., BURCH G. E. The excretion of radiorubidium Rb86, radiopotassium, K42, and potassium, sodium, and chloride by man with and without congestive heart failure. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Mar;45(3):408–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Welt L. G. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):65–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI105512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghvi I., Gershon S. Rubidium and lithium: evaluation as antidepressant and anti-manic agents. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;6(1):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard M. H. Effect of lithium on foot shock aggression in rats. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):284–285. doi: 10.1038/228284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolk J. M., Conner R. L., Barchas J. D. Rubidium-induced increase in shock-elicited aggression in rats. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;22(3):250–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00401787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolk J. M., Nowack W. J., Barchas J. D., Platman S. R. Brain norepinephrine: enhanced turnover after rubidium treatment. Science. 1970 Apr 24;168(3930):501–503. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3930.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


