Abstract
The small intestine plays a key role in lipid metabolism by absorbing fat and synthesising apoproteins. Fat malabsorption secondary to intestinal disease results in abnormalities of lipoprotein concentration and composition and can lead to deficiency of essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins. Malabsorption of fat can be induced by administration of neomycin and malabsorption of bile acids by administration of anion-exchange resins or by creating a partial ileal bypass. These induced forms of malabsorption are useful in the treatment of hyperlipidaemic patients liable to atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF

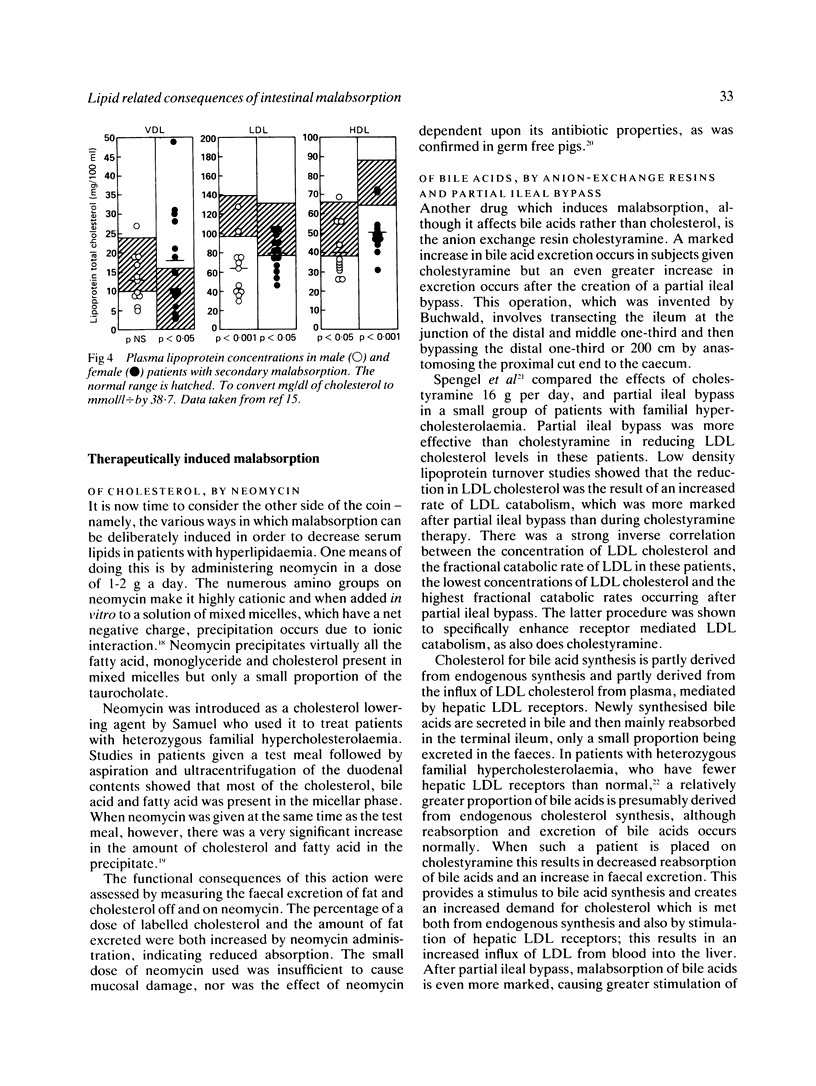

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M. Intestinal lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1153–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harders-Spengel K., Wood C. B., Thompson G. R., Myant N. B., Soutar A. K. Difference in saturable binding of low density lipoprotein to liver membranes from normocholesterolemic subjects and patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6355–6359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon M. T., Neale G. The absorption of alpha-tocopherol in control subjects and in patients with intestinal malabsorption. Clin Sci. 1970 Feb;38(2):197–210. doi: 10.1042/cs0380197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon M. T., Neale G., Thompson G. R. Lymphatic and portal venous transport of alpha-tocopherol and cholesterol. Eur J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;1(4):288–294. doi: 10.1111/eci.1971.1.4.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon M. T., Thompson G. R. Comparison of the absorption of a polar lipid, oleic acid, ad a non-polar lipid, alpha-tocopherol from mixed micellar solutions and emulsions. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;1(3):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. P., Thompson G. R. Plasma cholesterol esterification in patients with secondary hypocholesterolaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;3(5):401–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M., Kikuchi H., Shimoyama T., Thompson G. R. Diagnosis and treatment of essential fatty acid deficiency in man. Br Med J. 1974 May 4;2(5913):247–250. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5913.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M., Thompson G. R. Plasma post-heparin lipolytic activity in patients with malabsorption: effect of intravenous fat administration. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jun;46(6):743–751. doi: 10.1042/cs0460743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabesin S. M., Frase S. Electron microscopic studies of the assembly, intracellular transport, and secretion of chylomicrons by rat intestine. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):496–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama T., Kikuchi H., Press M., Thompson G. R. Fatty acid composition of plasma lipoproteins in control subjects and in patients with malabsorption. Gut. 1973 Sep;14(9):716–722. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.9.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengel F. A., Jadhav A., Duffield R. G., Wood C. B., Thompson G. R. Superiority of partial ileal bypass over cholestyramine reducing cholesterol in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Lancet. 1981 Oct 10;2(8250):768–770. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Barrowman J., Gutierrez L., Dowling R. H. Action of neomycin on the intraluminal phase of lipid absorption. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):319–323. doi: 10.1172/JCI106497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Ford J., Jenkinson M., Trayner I. Efficacy of mevinolin as adjuvant therapy for refractory familial hypercholesterolaemia. Q J Med. 1986 Aug;60(232):803–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Henry K., Edington N., Trexler P. C. Effect of neomycin on cholesterol metabolism in the germ-free pig. Eur J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;2(5):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1972.tb00663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Lewis B., Booth C. C. Absorption of vitamin D3-3H in control subjects and patients with intestinal malabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):94–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI105327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Lewis B., Booth C. C. Vitamin-D absorption after partial gastrectomy. Lancet. 1966 Feb 26;1(7435):457–458. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91458-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., MacMahon M., Claes P. Precipitation by neomycin compounds of fatty acid and cholesterol from mixed micellar solutions. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;1(1):40–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Miller J. P. Plasma lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities in patients with malabsorption. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):583–592. doi: 10.1042/cs0450583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Ockner R. K., Isselbacher K. J. Effect of mixed micellar lipid on the absorption of cholesterol and vitamin D3 into lymph. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):87–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI105977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]