Abstract
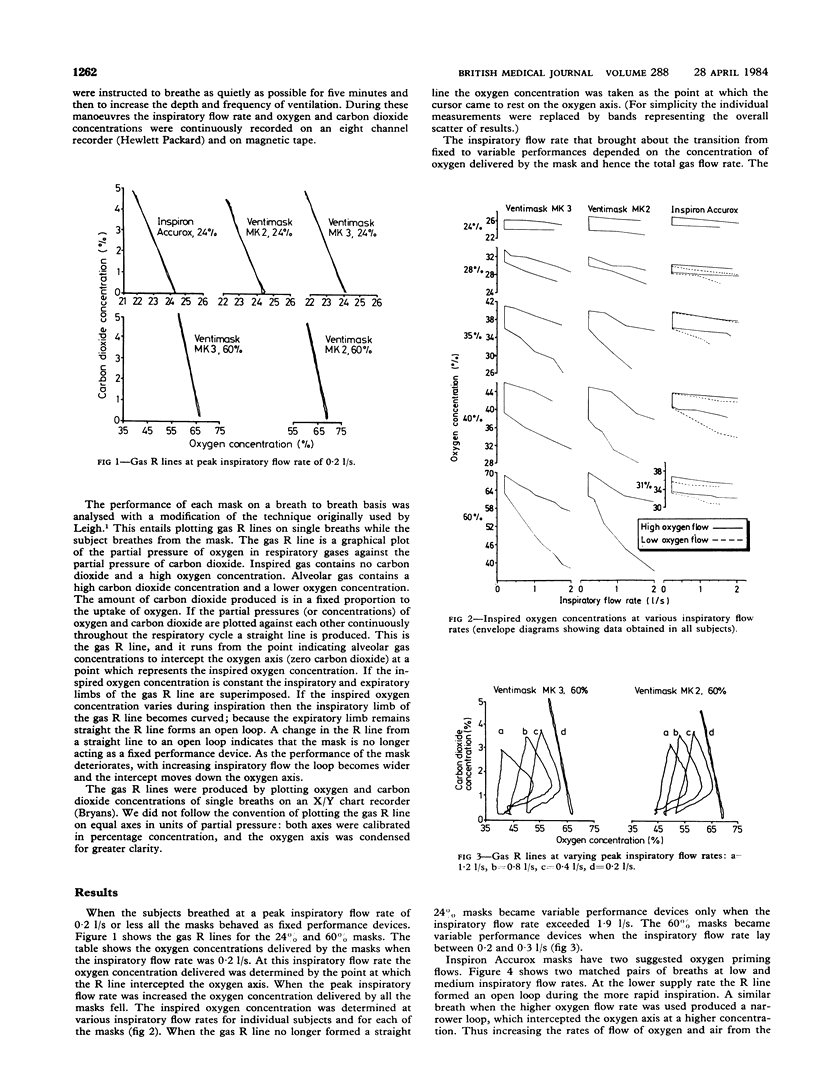
Fixed performance oxygen masks operate by supplying mixtures of oxygen and air at rates exceeding the inspiratory flow rate of the patient. In this study the oxygen concentration delivered by three fixed performance oxygen masks was determined non-invasively at various inspiratory flow rates. At low inspiratory flow rates all the masks studied acted as fixed performance devices. When the peak inspiratory rate increased the performance of all the masks showed some variability. The change from fixed to variable performance depended on the relation between inspiratory flow rate and the total gas flow delivered by the mask and was independent of the volume of the mask. Hence the use of low volume masks and high oxygen flow rates should produce more consistent results than high volume masks and lower flow rates.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell E. J. How to use the Venturi mask. Lancet. 1982 Nov 27;2(8309):1206–1206. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Minty K. B. Controlled oxygen therapy at 60% concentration. Why and how. Lancet. 1976 Jun 5;1(7971):1199–1203. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D., Gillbe C. Fixed performance oxygen masks. Hypoxic hazard of low-capacity drugs. Anaesthesia. 1981 Oct;36(10):958–964. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1981.tb08657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. A., Weber B., Briscoe W. A., Smith J. P., King T. K. Oxygen therapy. Evaluation of various air-entraining masks. JAMA. 1974 Apr 22;228(4):474–478. doi: 10.1001/jama.228.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. L., Blackburn J. P., Williams T. R. Measurement of respiratory flow by inductance pneumography. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1982 Jul;20(4):517–518. doi: 10.1007/BF02442415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. M. Variation in performance of oxygen therapy devices. Towards the rational employment of 'The dephlogisticated air described by Priestley'. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1973 Apr;52(4):234–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolner D. F., Larkin J. An analysis of the performance of a variable venturi-type oxygen mask. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1980 Feb;8(1):44–51. doi: 10.1177/0310057X8000800109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


