Abstract
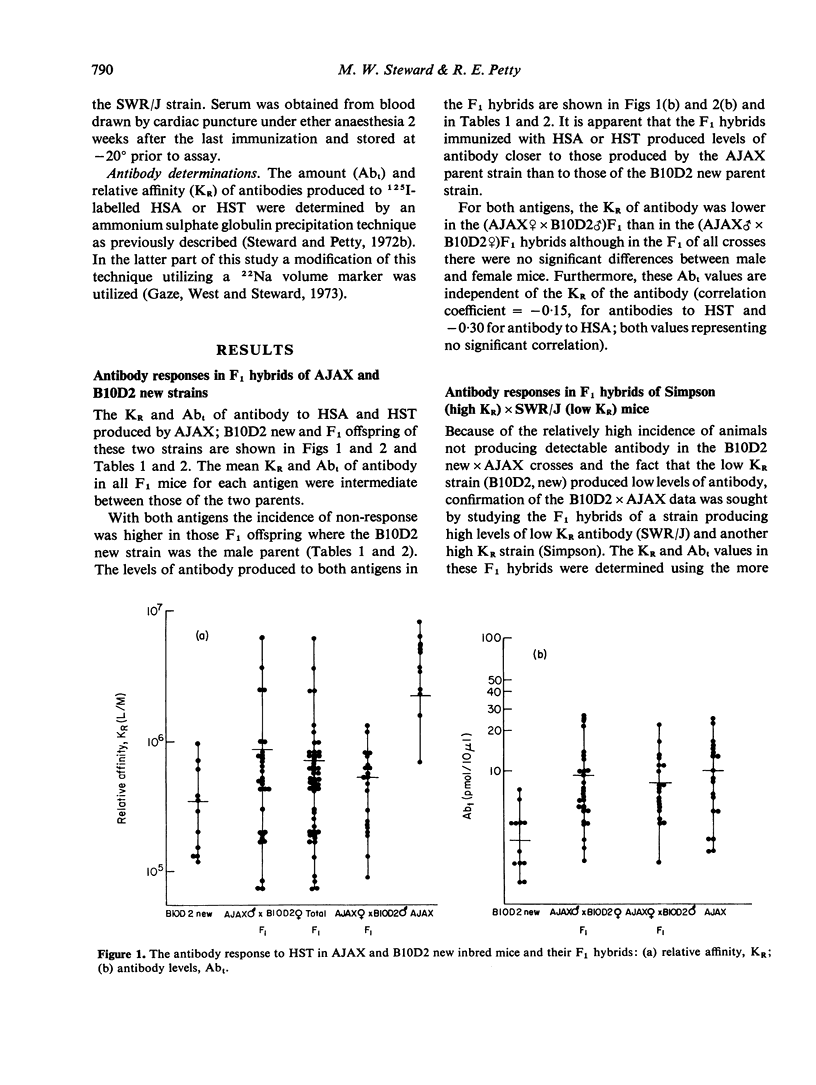
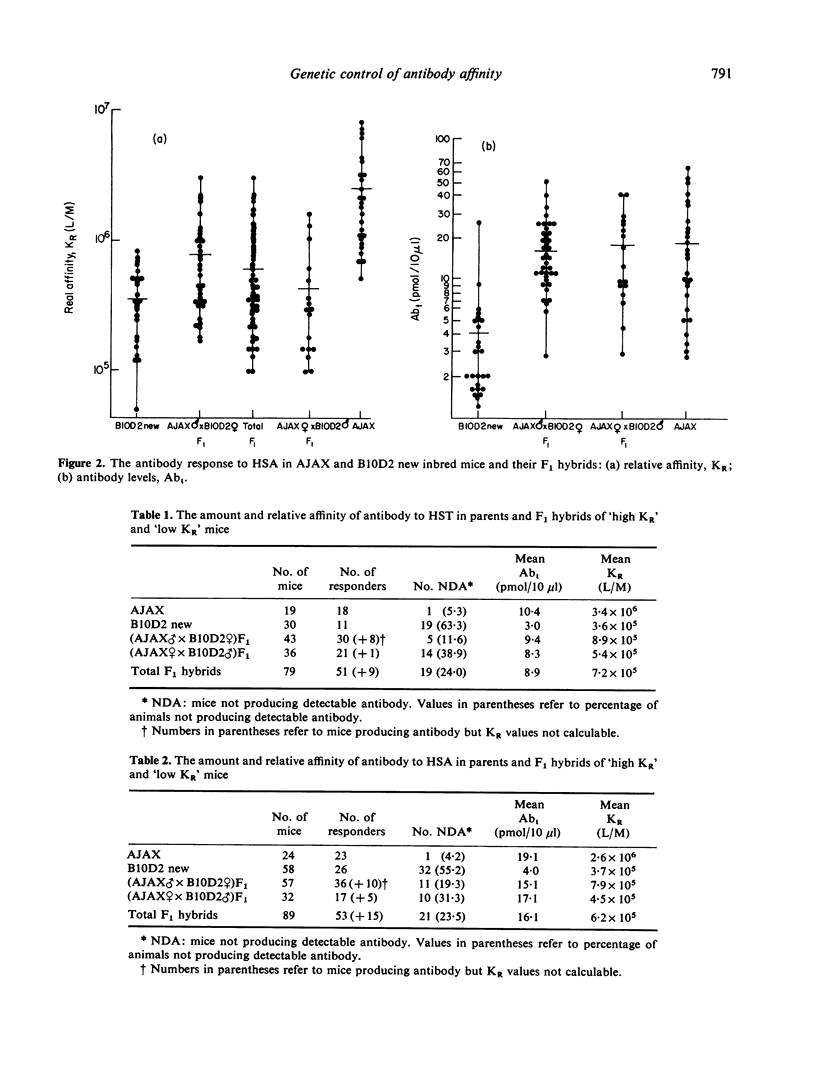
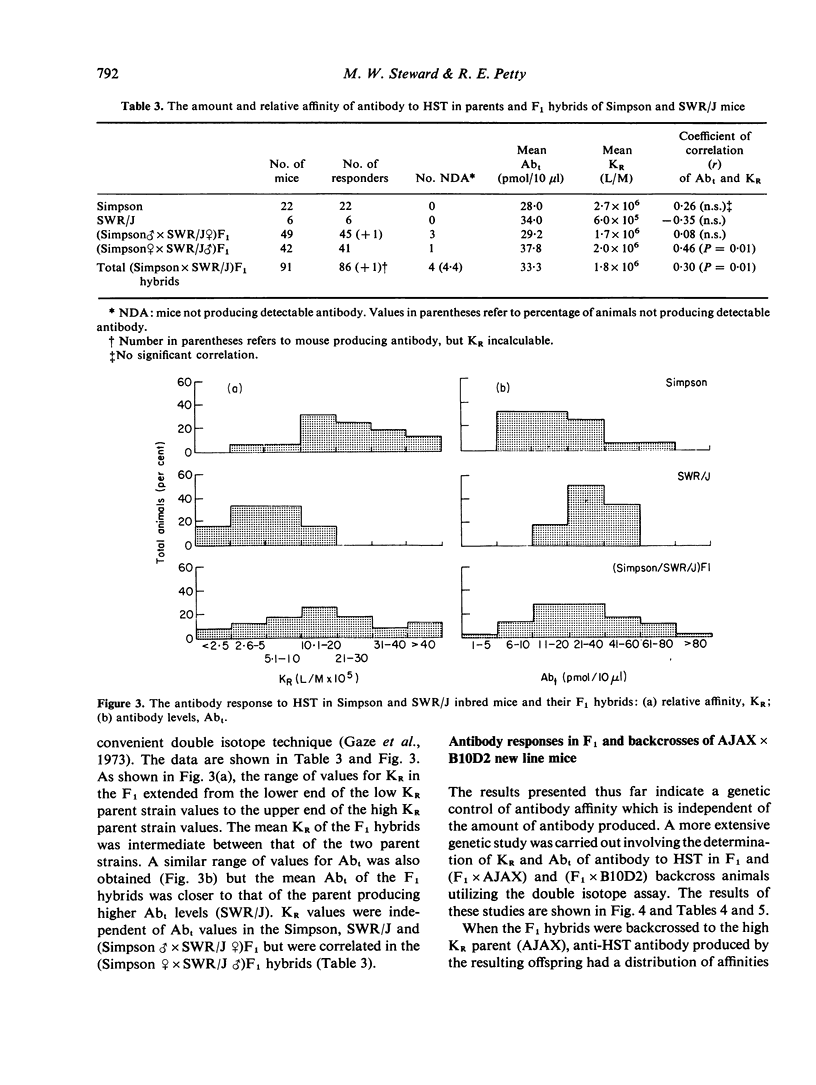
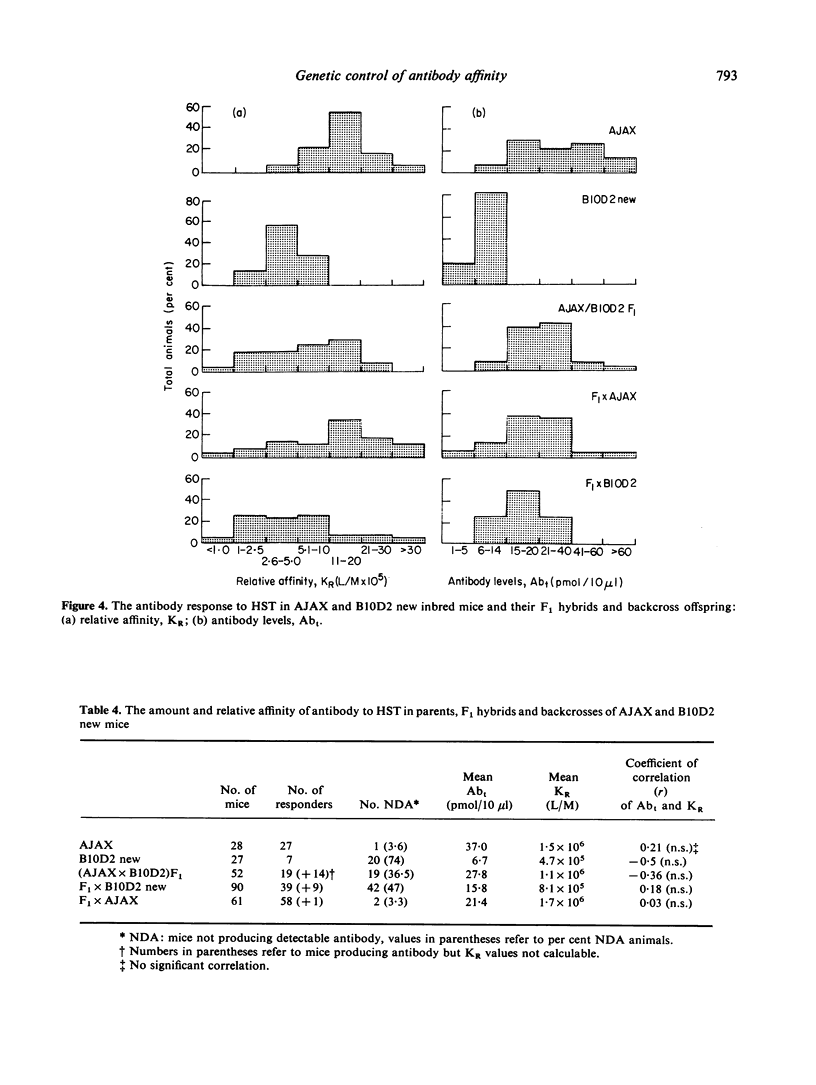
The amount (Abt) and relative affinity (KR) of antibody produced in response to protein antigens injected in saline has been measured in the parents, F1 hybrids and backcross offspring of inbred mice which produce high and low KR antibody to these antigens. The results obtained support the view that antibody affinity is under polygenic control. Furthermore, strain related variation in Abt is independent of KR and the breeding experiments indicate that these two parameters are under independent genetic control.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers J. H., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. Differences in immune elimination in inbred mice. The role of low affinity antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):121–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M., Denman E. J. Depletion of long-lived lymphocytes in old New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Apr;6(4):457–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M. Cell interactions in the immune response in vitro. II. The requirement for macrophages in lymphoid cell collaboration. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1049–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaze S., West N. J., Steward M. W. The use of a double isotope method in the determination of antibody affinity. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Dec;3(4):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Paul W. E. Effect of thymus-derived lymphocytes on amount and affinity of anti-hapten antibody. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):872–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. E., Steward M. W. The genetic control of antibody affinity in mice. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):543–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. G., Soothill J. F. Relationship between macrophage clearance of PVP and affinity of anti-protein antibody response in inbred mouse strains. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):711–712. doi: 10.1038/254711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. I. Relationship of antibody production to disease in neonatally infected mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):483–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. Inter-mouse strain differences in macrophage function and its relationship to antibody responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):159–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The effects of protein malnutrition on macrophage function and the amount and affinity of antibody response. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):491–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W. Relative affinity of anti-protein antibodies in New Zealand mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Nov;12(3):343–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Steward M. W. The immunopathological significance of the heterogeneity of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Gaze S. E., Petty R. E. Low affinity antibody production in mice - a form of immunological tolerance? Eur J Immunol. 1974 Nov;4(11):751–757. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Katz F. E., West N. J. The role of low affinity antibody in immune complex disease. The quantity of anti-DNA antibodies in NZB/W F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):121–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Petty R. E. The antigen-binding characteristics of antibody pools of different relative affinity. Immunology. 1972 Dec;23(6):881–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Petty R. E. The use of ammonium sulphate globulin precipitation for determination of affinity of anti-protein antibodies in mouse serum. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):747–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Voller A. The effect of malaria on the relative affinity of mouse antiprotein antibody. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Apr;54(2):198–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Cerottini J. C. The function of macrophages in the immune response. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):225–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


