Abstract
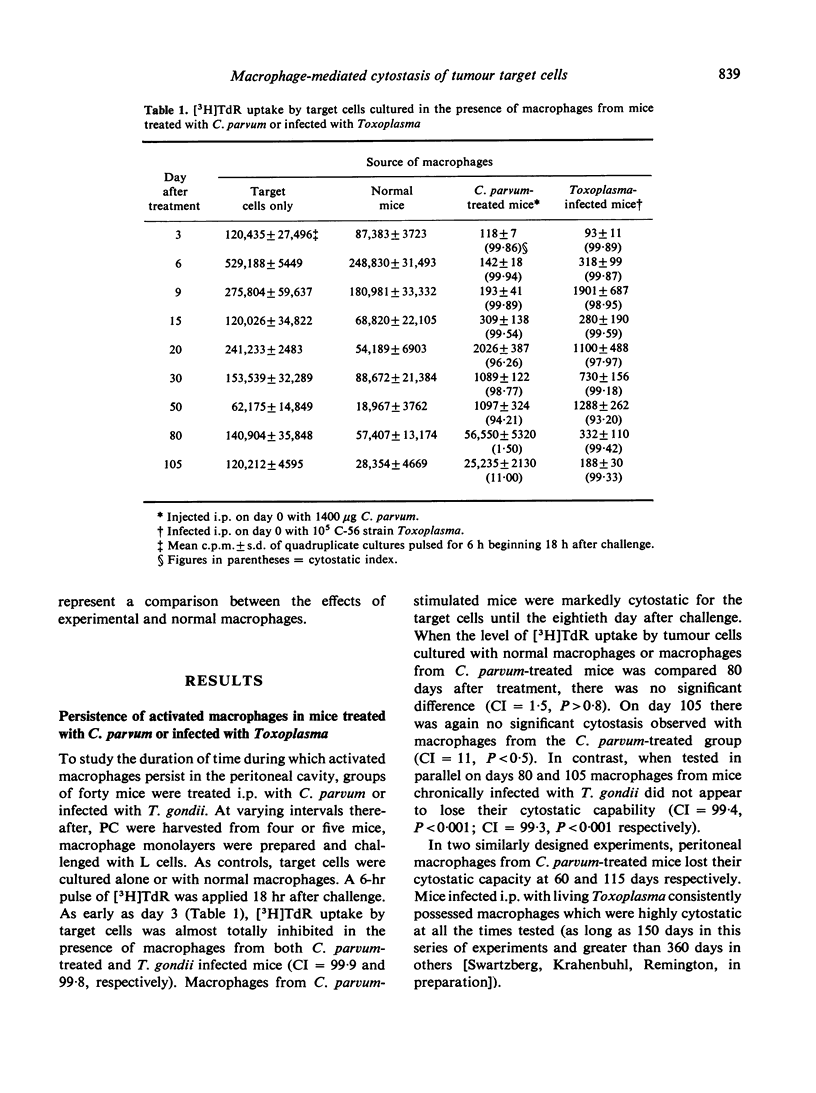
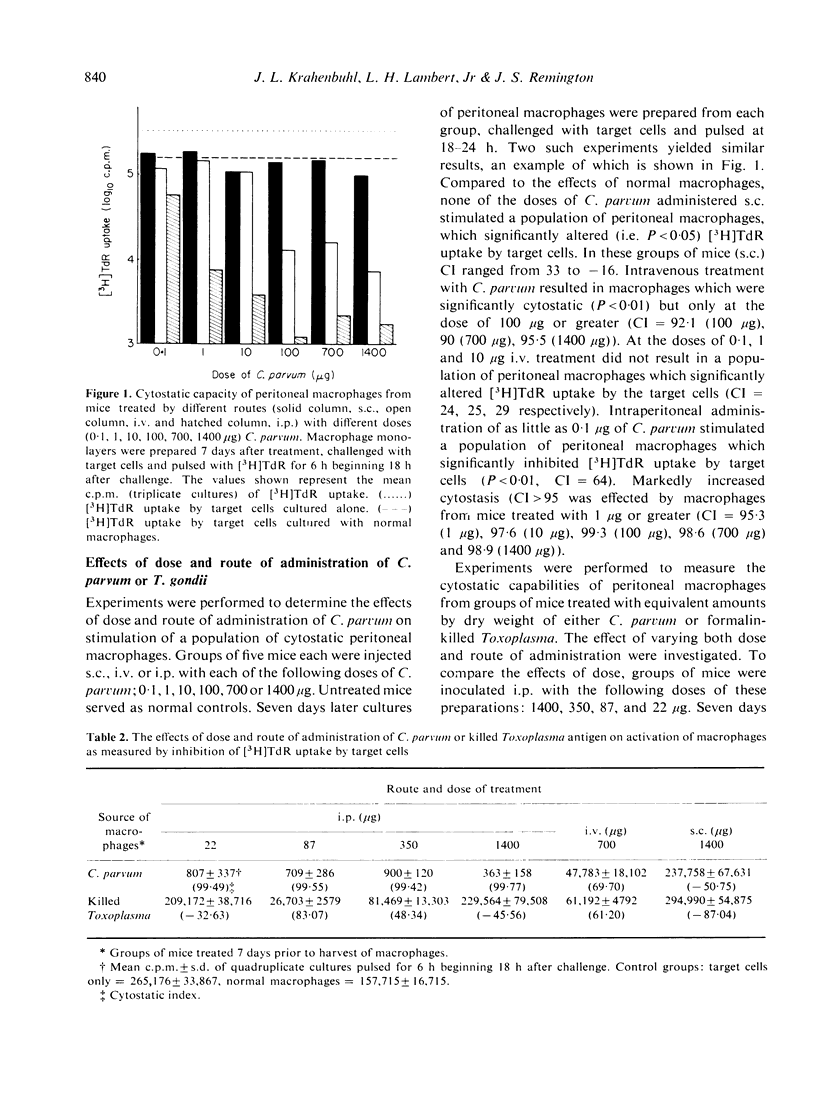
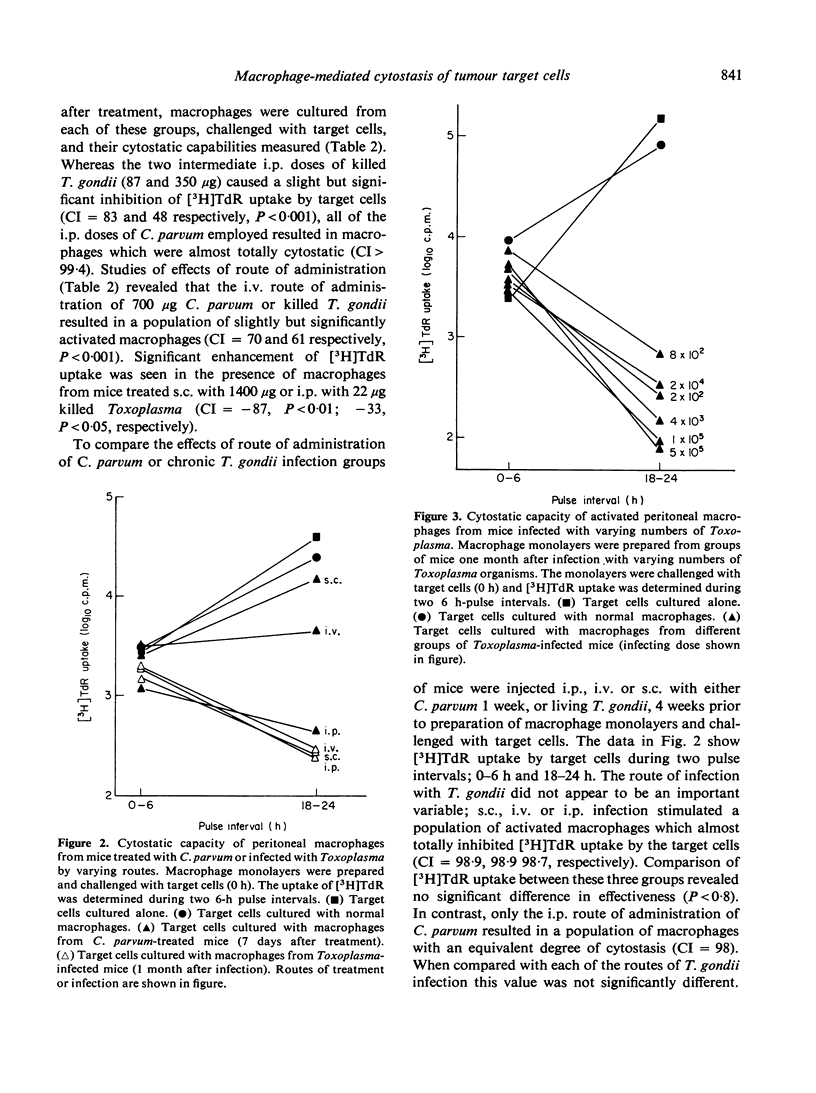
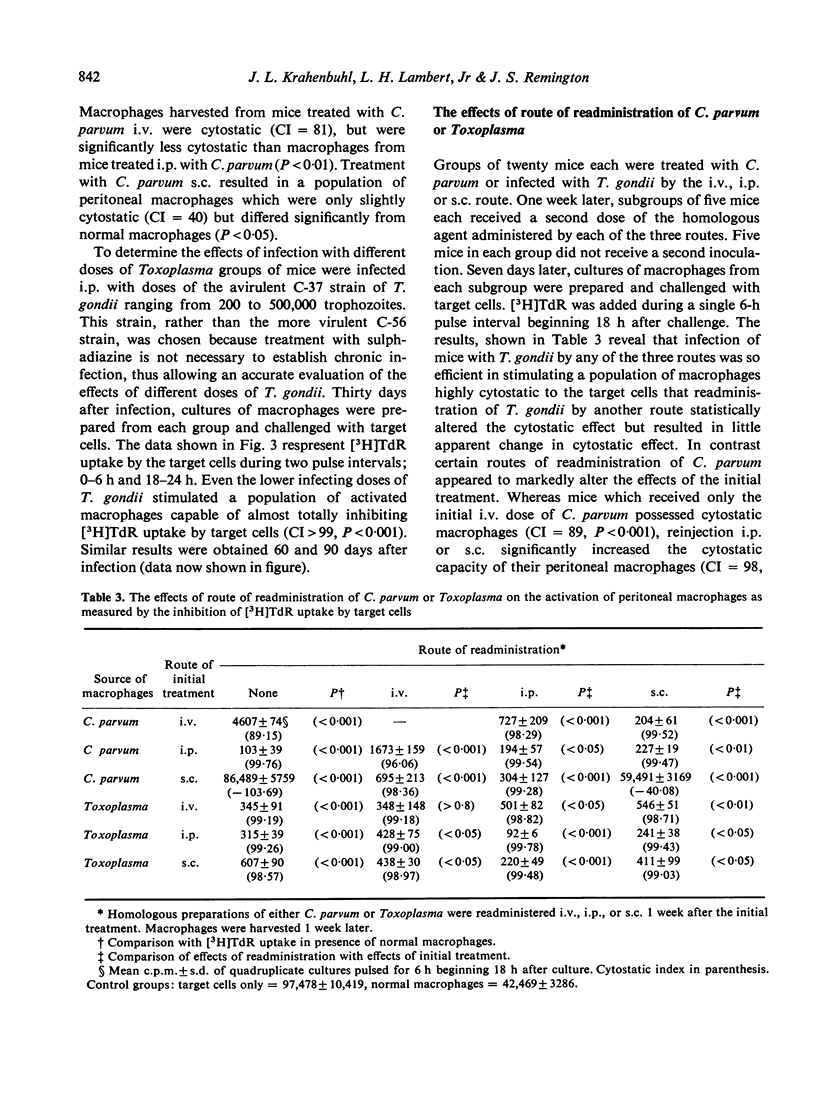
Injection of mice with Corynebacterium parvum or living or killed Toxoplasma gondii was studied to determine the efficacy of these treatments in activating peritoneal macrophages to inhibit the uptake of [3H]TdR (cytostasis) by tumour target cells in vitro. In the presence of activated macrophages from mice treated i.p. with a wide dose range of either C. parvum or living Toxoplasma, cytostasis was usually greater than 99%. This population of activated macrophages was transient in C. parvum-treated mice, but persists, probably for life, in Toxoplasma-infected mice. Whereas the i.p. route of administration of C. parvum was more efficient in activating macrophages than the i.v. route, the s.c. route appeared to be relatively ineffective. Treatment with killed Toxoplasma by any route was also relatively ineffective in activating macrophages. In contrast Toxoplasma infection resulted in highly activated peritoneal macrophages, regardless of the route of administration. Depending upon the route of initial treatment, the route of readministration of C. parvum had either no appreciable effect or resulted in a marked alteration in the cytostatic capacity of peritoneal macrophages.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Scott M. T. Lympho-reticular stimulatory properties of Corynebacterium parvum and related bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):261–274. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast R. C., Jr, Zbar B., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. BCG and cancer. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 27;290(26):1458–1469. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406272902605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford R., Christie G. H. Mechanisms of macrophage activation by corynebacterium parvum. II. In vivo experiments. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. H., Bomford R. Mechanisms of macrophage activation by Corynebacterium parvum. I. In vitro experiments. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Wolmark N., Saffer E., Fisher E. R. Inhibitory effect of prolonged Corynebacterium parvum and cyclophosphamide administration on the growth of established tumors. Cancer. 1975 Jan;35(1):134–143. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197501)35:1<134::aid-cncr2820350119>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar A., Cullen R. T., Dunbar N., Woodruff M. F. Anti-tumour effect in vitro of lymphocytes and macrophages from mice treated with Corynebacterium parvum. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):199–205. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., PREVOT A. R., BIOZZI G., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D., MORARD J. C., BOUTHILLIER Y., DECREUSEFOND C. STIMULATION DE L'ACTIVIT'E PHAGOCYTAIRE DU SYST'EME R'ETICULOENDOTH'ELIAL PROVOQU'EE PAR CORYNEBACTERIUM PARVUM. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1964 Jan;1:77–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern B. N., Biozzi G., Stiffel C., Mouton D. Inhibition of tumour growth by administration of killed corynebacterium parvum. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):853–854. doi: 10.1038/212853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Resistance to murine tumors conferred by chronic infection with intracellular protozoa, Toxoplasma gondii and Besnoitia jellisoni. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):587–592. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Gaines J. D., Remington J. S. Lymphocyte transformation in human toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):283–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Lambert L. H., Jr Cytokinetic studies of the effects of activated macrophages on tumor target cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1433–1437. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. In vitro induction of nonspecific resistance in macrophages by specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.337-343.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. The role of activated macrophages in specific and nonspecific cytostasis of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Ruskin J., Remington J. S. The use of killed vaccines in immunization against an intracellular parasite: Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likhite V. V., Halpern B. N. Lasting rejection of mammary adenocarcinoma cell tumors in DBA-2 mice with intratumor injection of killed Corynebacterium parvum. Cancer Res. 1974 Feb;34(2):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likhite V. V., Halpern B. N. The delayed rejection of tumors formed from the administration of tumor cells mixed with killed Corynebacterium parvum. Int J Cancer. 1973 Nov 15;12(3):699–704. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Schipper H., Fischer H. Macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity against allogeneic target cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann C. F., Hendrickson C. G., Spitler L. E., Gunnarsson A., Banerjee D., Nelson W. R. Immunotherapy of melanoma with BCG: two fatalities following intralesional injection. Cancer. 1975 Feb;35(2):514–520. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197502)35:2<514::aid-cncr2820350233>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milas L., Hunter N., Withers H. R. Corynebacterium-induced protection against artificial pulmonary metastases of a syngeneic fibrosarcoma in mice. Cancer Res. 1974 Mar;34(3):613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milas L., Mujagić H. Protection by Corynebacterium parvum against tumour cells injected intravenously. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1972 May;17(5):498–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON D. S., BOYDEN S. V. The loss of macrophages from peritoneal exudates following the injection of antigens into guinea-pigs with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Immunology. 1963 May;6:264–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivotto M., Bomford R. In vitro inhibition of tumour cell growth and DNA synthesis by peritoneal and lung macrophages from mice injected with Corynebacterium parvum. Int J Cancer. 1974 Apr 15;13(4):478–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Bloomfield M. M., Russell E., Jr, Robinson W. S. The RNA of toxoplasma gondii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):623–626. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Corynebacterium parvum as a therapeutic antitumor agent in mice. I. Systemic effects from intravenous injection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Sep;53(3):855–860. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.3.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Corynebacterium parvum as a therapeutic antitumor agent in mice. II. Local injection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Sep;53(3):861–865. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.3.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolmark N., Fisher B. The effect of a single and repeated administration of Corynebacterium parvum on bone marrow macrophage colony production in syngeneic tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2869–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Boak J. L. Inhibitory effect of injection of Corynebacterium parvum on the growth of tumour transplants in isogenic hosts. Br J Cancer. 1966 Jun;20(2):345–355. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1966.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


