Abstract
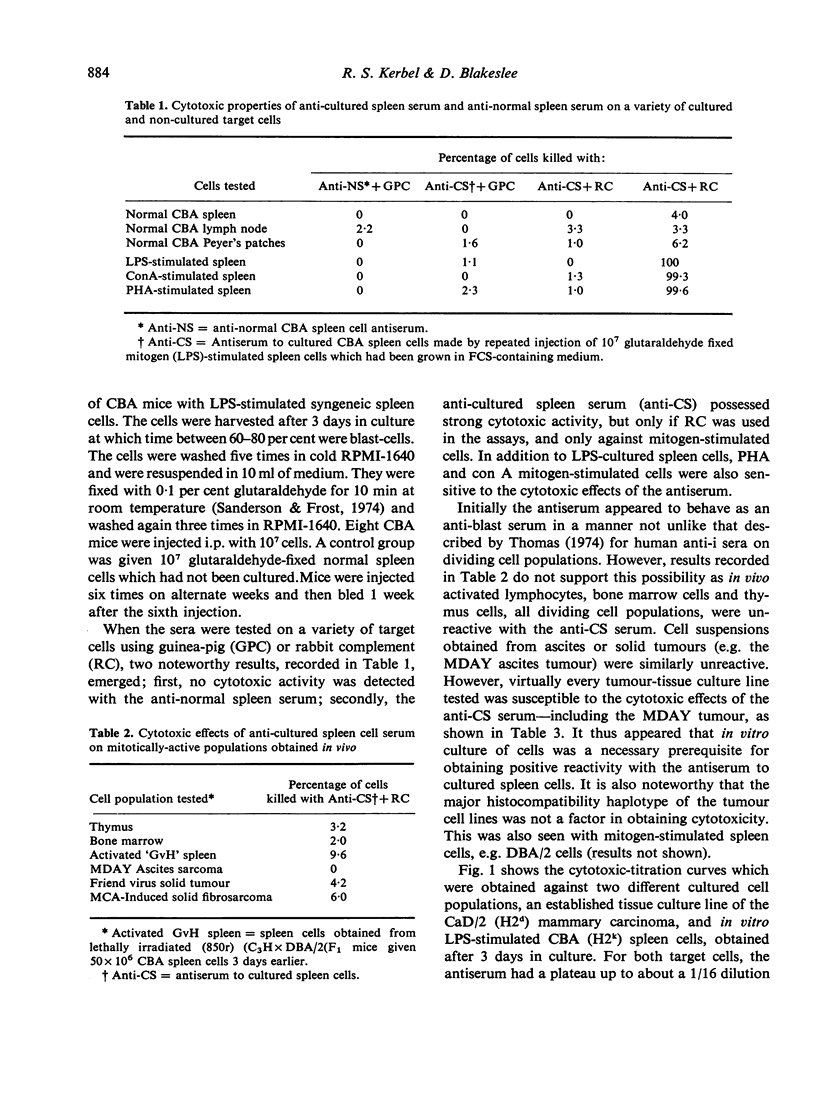
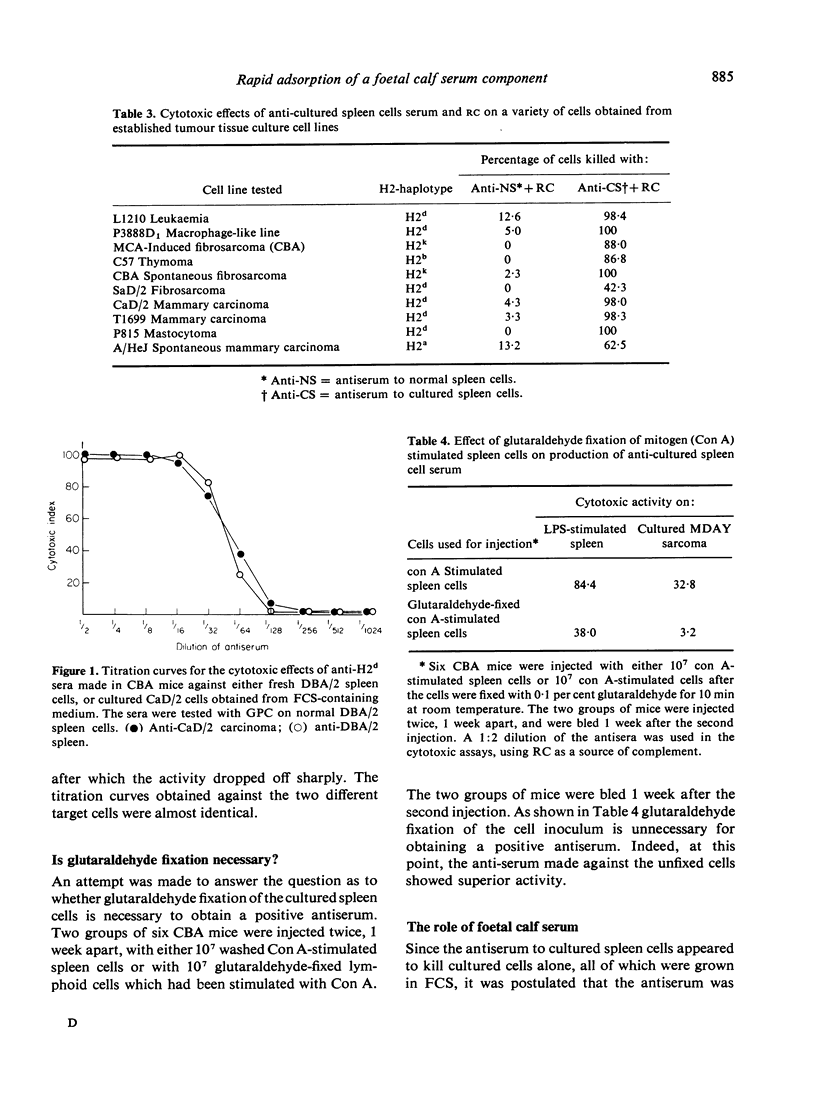
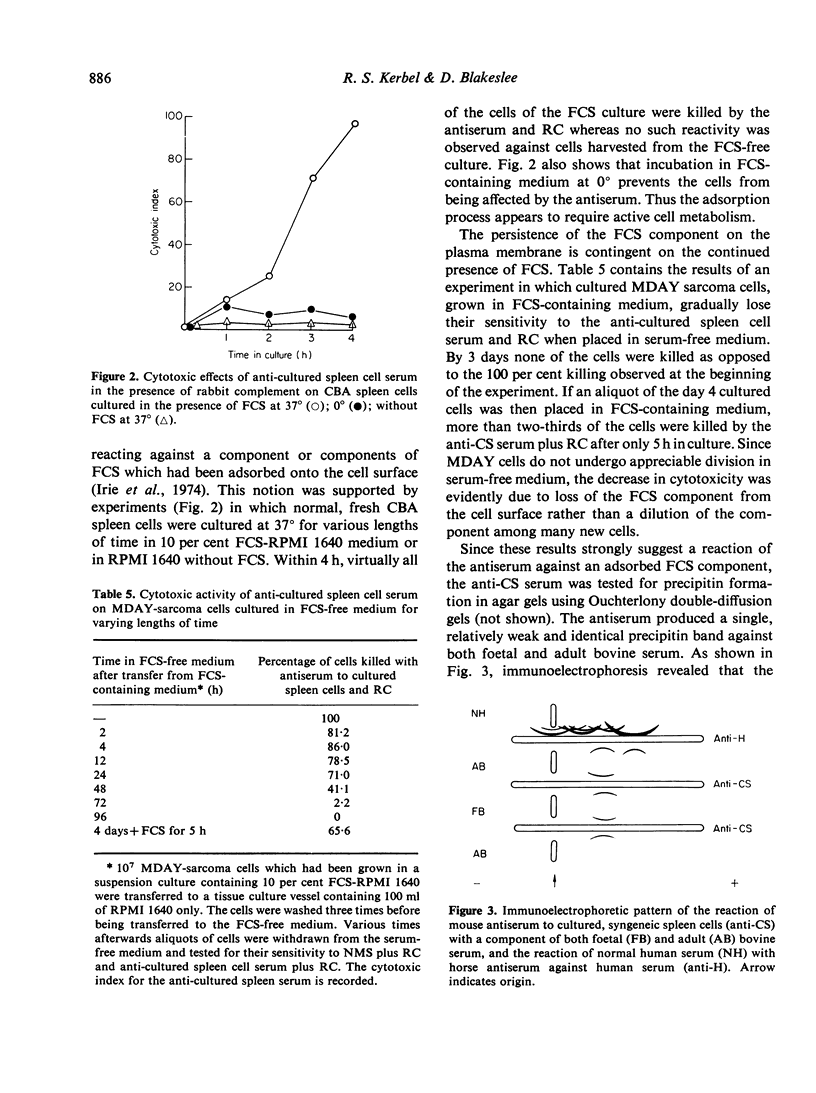
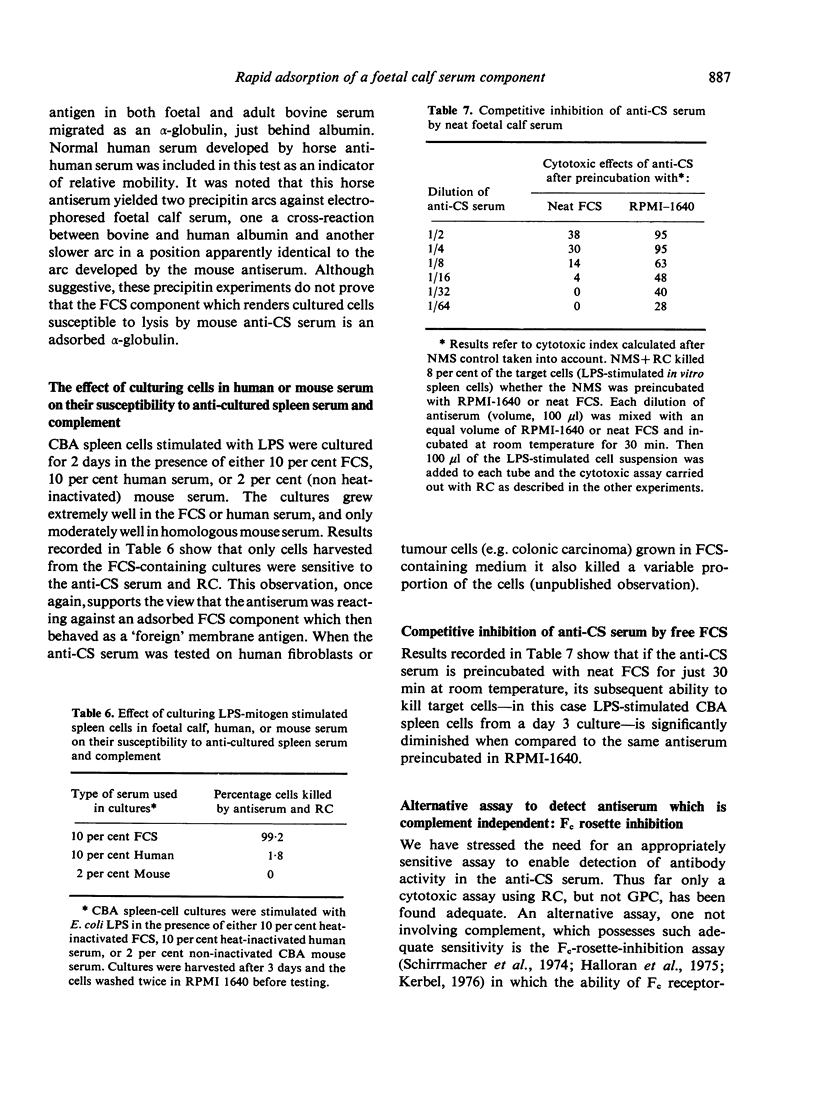
Injection of CBA mice the either mitogen-stimulated (LPS or con A) CBA lymphocytes which had been cultured for 3 days in the presence of foetal calf serum (FCS) led to the production of antisera which reacted strongly with virtually all types of mammalian cells, including human, whether normal or malignant, provided they had been cultured in FCS-containing media. Reactivity was detected by sensitive immunological assays such as complement-dependent cytoxocity using rabbit complement (but not using guinea-pig complement), or EA-rosette inhibition of Fc receptor-bearing cells. The antisera did not react with fresh normal lymphoid cells or ascites tumour cells; however, these same cell populations became fully susceptible to the cytotoxic effects of the antisera after as little as 4 h incubation at 37 degrees in the presence of FCS. Cells incubated without FCS or with FCS at 0 degrees were not affected. The antisera reacted with FCS to form a single band on Ouchterlony double-diffusion plates. On immunoelectrophoresis the reactive antigen appeared to migrate in the alpha-globulin region of serum proteins. These observations suggest that FCS may be a source of potentially serious misinterpretations in immunological studies of cell-associated antigens using antisera produced by the injection of cells grown in FCS-containing cultures. Examples of artifcats arising from the use of FCS in certain systems, e.g. the preparation of alloantisera using cultured tumour cells vs fresh non-cultured lymphoid cells, are described.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fritze D., Kern D. H., Drogemuller C. R., Pilch Y. H. Production of antisera with specificity for malignant melanoma and human fetal skin. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 1):458–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEY G. O., KENT H. N. Changes in serum proteins during growth of malignant cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):205–208. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B. Studies on the specificity of human cytotoxic antibody reactive with cultures of lymphoid cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Jan;42(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie R. F., Irie K., Morton D. L. Natural antibody in human serum to a neoantigen in human cultured cells grown in fetal bovine serum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1051–1058. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT H. N., GEY G. O. Selective uptake of serum globulins and glycoproteins by cells growing in vitro. Science. 1960 Mar 4;131(3401):666–668. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3401.666-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbel R. S., Birbeck M. S., Robertson D., Cartwright P. Ultrastructural and serological studies on the resistance of activated B cells to the cytotoxic effects of anti-immunoglobulin serum. Patch and cap formation of surface immunoglobulin on mitotic B lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Apr;20(1):161–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbel R. S., Davies A. J. The possible biological significance of Fc receptors on mammalian lymphocytes and tumor cells. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbel R. S., Pross H. F., Elliott E. V. Origin and partial characterization of Fc receptor-bearing cells found within experimental carcinomas and sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jun 15;15(6):918–932. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbel R. S. Resistance of activated macrophages to H-2 antibody-mediated cytotoxicity and Fc rosette inhibition. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):226–228. doi: 10.1038/259226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. A. Anomalous reactions of mouse alloantisera with cultured tumor cells. I. Demonstration of widespread occurrence using reference typing sera. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1254–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koene R. A., McKenzie I. F. A comparison of the cytolytic action of guinea pig and rabbit complement on sensitized nucleated mouse cells. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1894–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanakumar T., Metzgar R. S., Miller D. S. Human leukemia cell antigens: serologic characterization with xenoantisera. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 May;52(5):1435–1444. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.5.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Klein P. A. Anomalous reactions of mouse alloantisera with cultured tumor cells. II. Cytotoxicity is caused by antibodies to leukemia viruses. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1261–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Frost P. The induction of tumour immunity in mice using glutaraldehyde-treated tumor cells. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):690–691. doi: 10.1038/248690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmacher V., Halloran P., David C. S. Interactions of Fc receptors with antibodies against Ia antigens and other cell surface components. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1201–1209. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


