Abstract
IgM rheumatoid factors (RF) were isolated from the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a serologically active Fabmicron RF fragment prepared by papain digestion. A radioimmunoassay was developed for the determination of interaction of 19S IgM RF and Fabmicron RF with human 7S IgG, heat-aggregated IgG, rabbit 7S IgG, and human pFc'. RF isolated under neutral conditions had a very low binding constant for human 7S IgG (of the order of 10(2) to 10(3) 1 mole-1) and a considerably higher value (ca. 10(5)) for the aggregated protein and monomeric rabbit IgG. RF obtained under acid conditions which dissociate the complexes with endogenous Ig, had a higher avidity for human IgG monomer as expected and also a comparable reactivity with rabbit IgG. Monovalent Fabmicron fragments of 'acid' RF had closely similar affinities for 7S and aggregated IgG suggesting that the enhanced binding with the aggregated protein is essentially dependent on its multivalency rather than the exposure of a new determinant lacking in the native molecule.
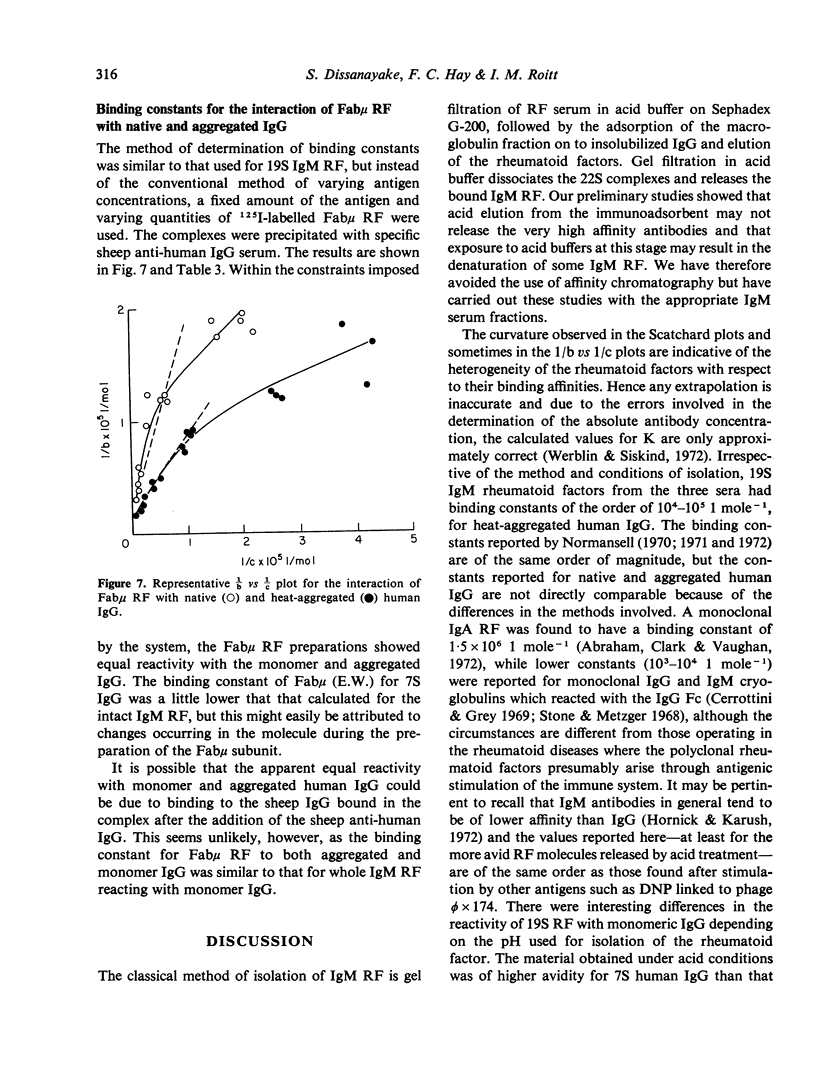
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G. N., Clark R. A., Vaughan J. H. Characterization of an IgA rheumatoid factor: finding properties and reactivity with the subclasses of human G globulin. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Grey H. M. Binding properties of monoclonal gammaG-antiglobulin factors with human gamma G. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):76–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaarder P. I., Natvig J. B. Hidden rheumatoid factors reacting with "non a" and other antigens of native autologous IgG. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):928–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIROSE S. I., OSLER A. G. INTERACTION OF RHEUMATOID FACTORS WITH AGGREGATED SUBUNITS OF HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:927–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. Hidden' IgG antiglobulins in normal human serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):185–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. Structural and conformational specificity of the antigen for rheumatoid factor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):52–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S. I., Osler A. G. Interaction of rheumatoid factors with urea-denatured human gamma-globulin and its subunits. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick C. L., Karuch F. Antibody affinity. 3. The role of multivalance. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. 3. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with heterologous G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jul;9(7):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. II. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with altered G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jul;8(7):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti-gamma-globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. I. Studies on the 22S complex. Immunochemistry. 1970 Sep;7(9):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E., Stanworth D. R. Interactions between rheumatoid factor and native gamma-G-globulins studied in the ultracentrifuge. Immunology. 1968 Oct;15(4):549–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E., Stanworth D. R. Ultracentrifugal studies of the reactions of rheumatoid factor with native human gamma-G-globulin. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):527–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoue K., Kishimoto T., Yamamura Y. Structure of human immunoglobuli M. II. Isolation of a high molecular weight Fc fragment of IgM composed of several Fc subunits. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Petty R. E. The use of ammonium sulphate globulin precipitation for determination of affinity of anti-protein antibodies in mouse serum. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):747–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Turner M. W., Natvig J. B., Gaarder P. I. The binding affinities of rheumatoid factors interacting with the C gamma 3 homology region of human IgG. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):145–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Metzger H. Binding properties of a Waldenström macroglobulin antibody. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5977–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. Subfragments from the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G. Isolation and physicochemical charaterization. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1070171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Distribution of antibody affinities: technique of measurement. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


