Abstract
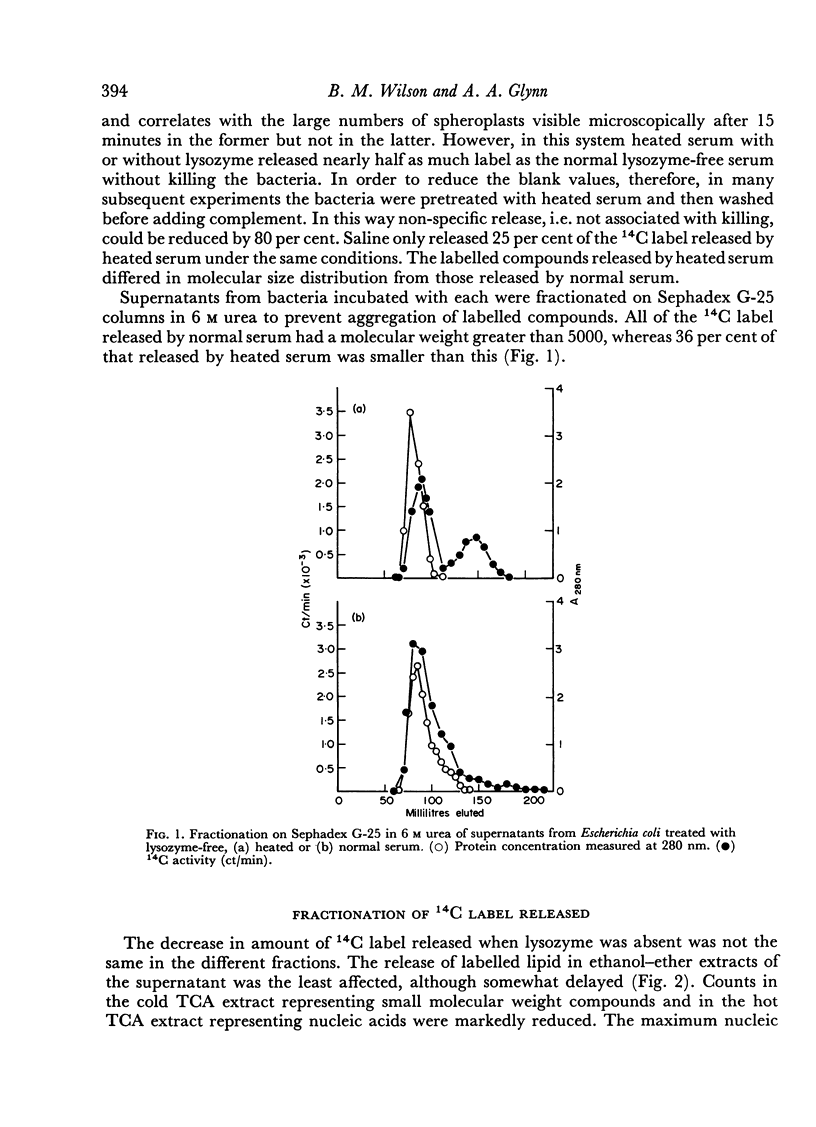
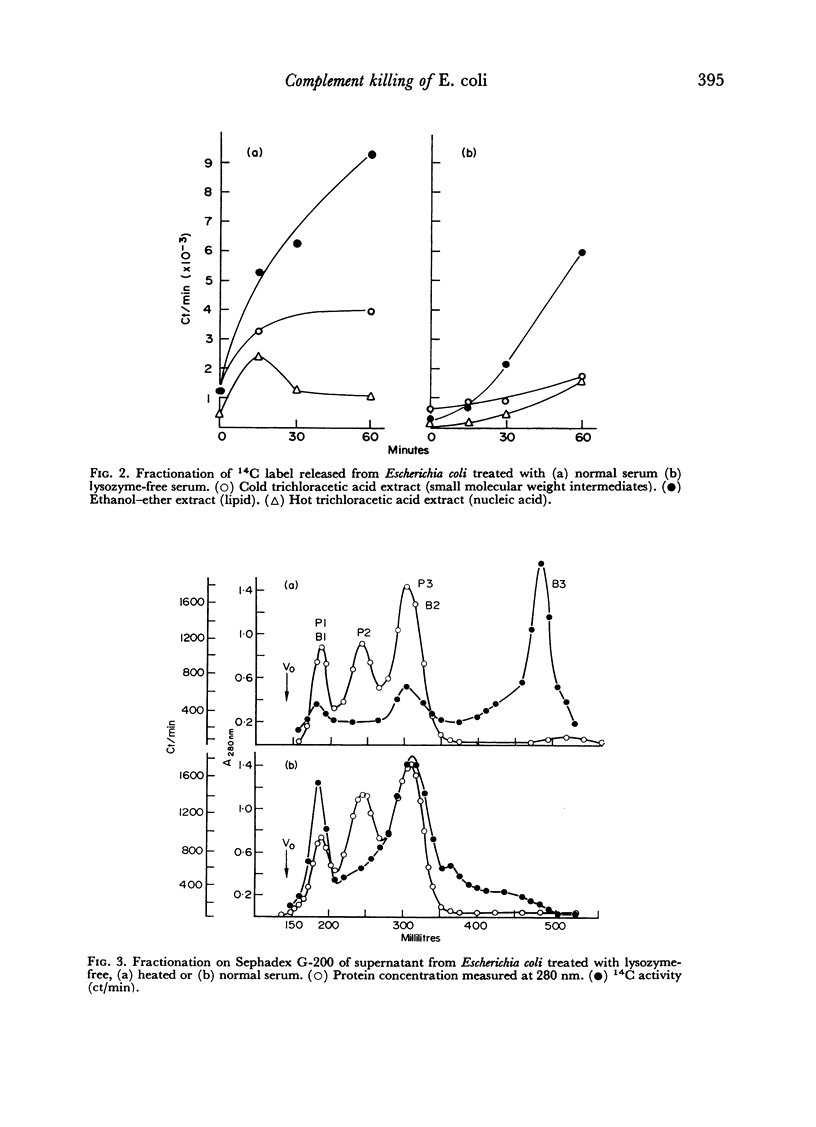
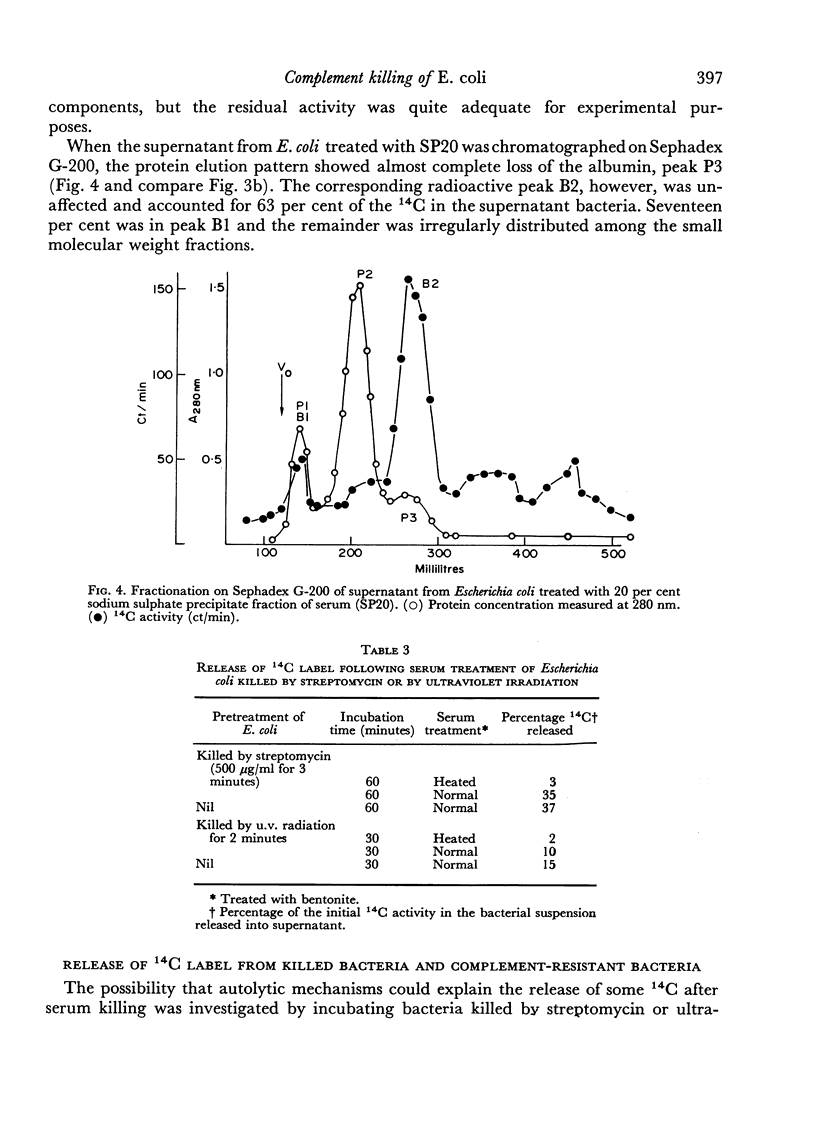
When Escherichia coli labelled with 14C were killed by complement, characteristic 14C compounds were released even when complete cell disintegration was prevented or delayed by removal of lysozyme. Treatment with heated serum only resulted in the loss of small molecular weight compounds. Separation of the products was made easier if whole serum was replaced by a salt-precipitated fraction which contained no albumin or lysozyme but retained antibody and complement. Fractionation of the bacterial products on Sephadex G-200 showed two radioactive peaks containing lipids and proteins of which a preliminary examination was made. The release of these compounds was related to complement action, since they were not found when bacteria were killed by streptomycin or ultra-violet light in the absence of complement. Nor were they found when resistant bacteria were treated with complement and survived. The possible modes of action of complement on bacterial cell walls are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. Electrokinetic requirements for the reaction between Cl. perfringens alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) and phospholipid substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:103–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. The fate of bacteria within phagocytic cells. I. The degradation of isotopically labeled bacteria by polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:27–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON J. N., SMELLIE R. M. S. Phosphorus compounds in the cell. III. The incorporation of radioactive phosphorus into the ribonucleotide fraction of liver tissue. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):599–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0520599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Milne C. M. A kinetic study of the bacteriolytic and bactericidal action of human serum. Immunology. 1967 Jun;12(6):639–653. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Payne S. N., Humphrey J. H. Complement and phospholipase C lysis of lipid membranes. Immunology. 1972 Nov;23(5):705–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILLANDER J. SEPARATION OF HUMAN HEME- AND HEMOGLOBIN-BINDING PLASMA PROTEINS, CERULOPLASMIN AND ALBUMIN BY GEL FILTRATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:1–14. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., JACKSON J. E. ACTIVITY OF THE ANTIBODY-COMPLEMENT SYSTEM AND LYSOZYME AGAINST ROUGH GRAM NEGATIVE ORGANISMS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:881–884. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The molecular basis of the biological activities of complement. Harvey Lect. 1971;66:75–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen B., Zwaal R. F., Comfurius P., Woodward C. B., van Deenen L. L. Action of pure phospholipase A 2 and phospholipase C on human erythrocytes and ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):925–929. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. K., Becker E. L. Serum complement and the enzymatic degradation of erythrocyte phospholipid. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):459–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARDLAW A. C. The complement-dependent bacteriolytic activity of normal human serum. I. The effect of pH and ionic strength and the role of lysozyme. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1231–1249. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Spitznagel J. K. Characteristics of complement-dependent release of phospholipid from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1971 Jul;4(1):23–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.1.23-28.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Spitznagel J. K. Molecular and structural damage to Escherichia coli produced by antibody, complement, and lysozyme systems. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1339–1348. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1339-1348.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


