Abstract
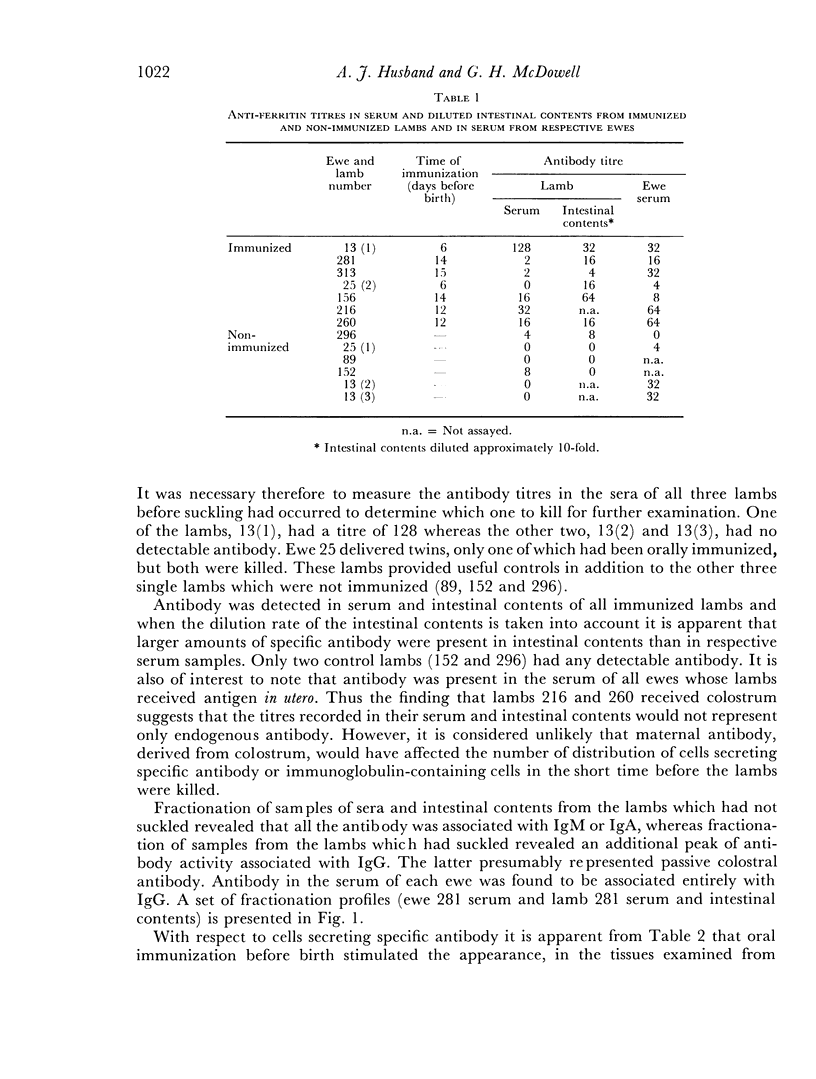
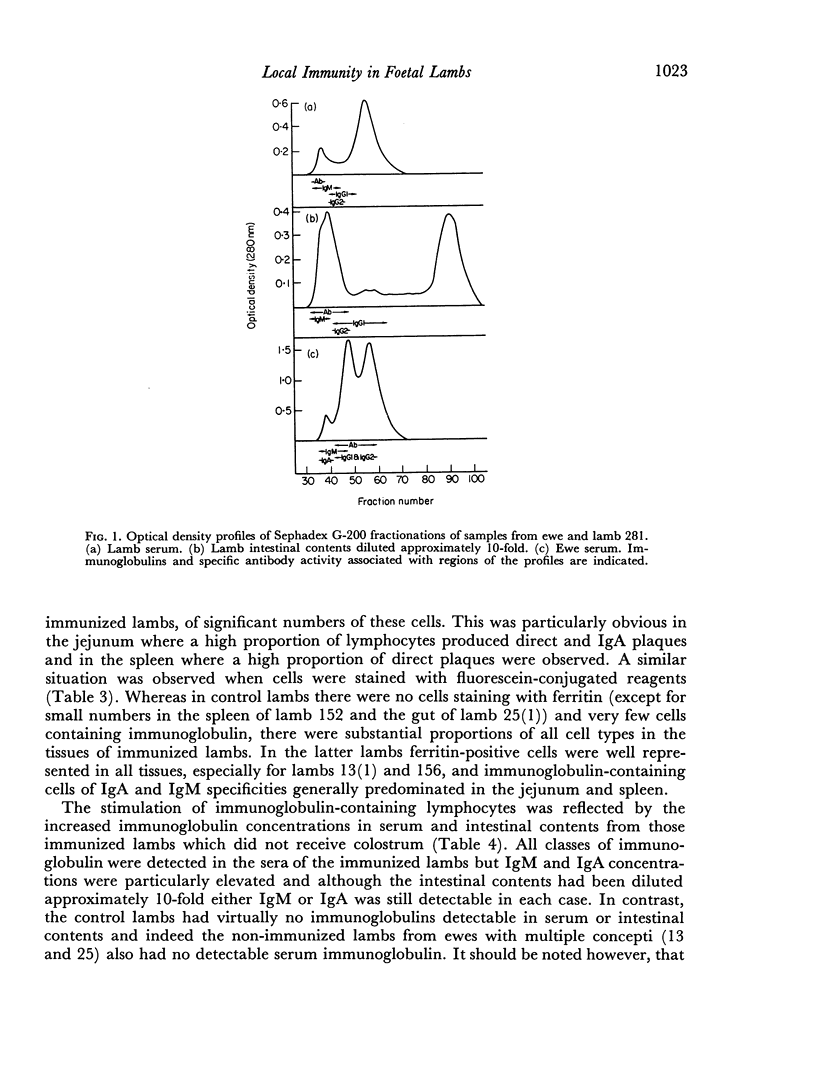
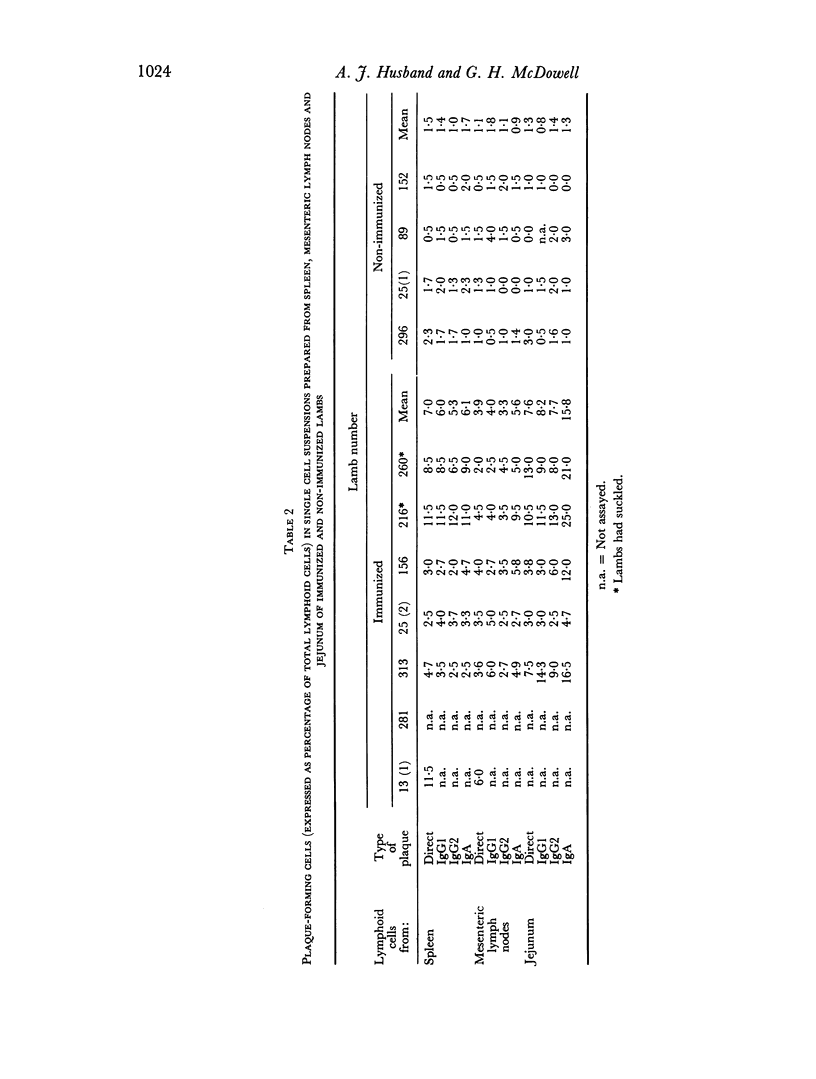
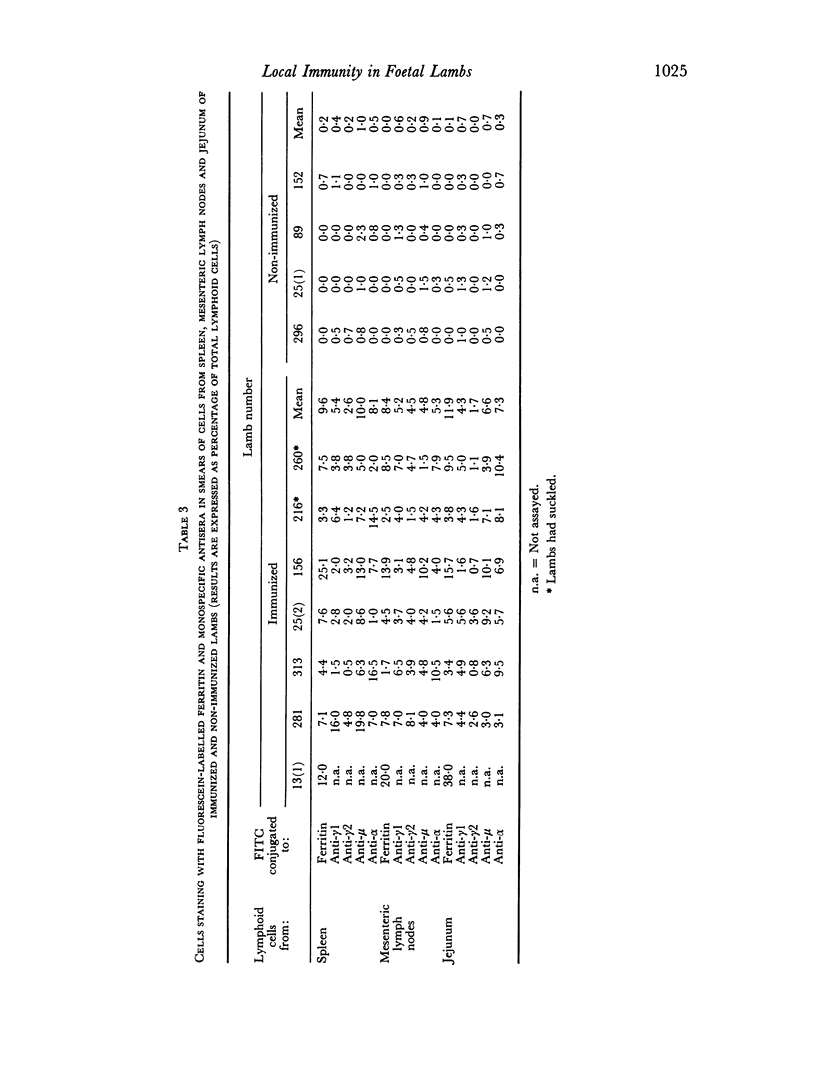
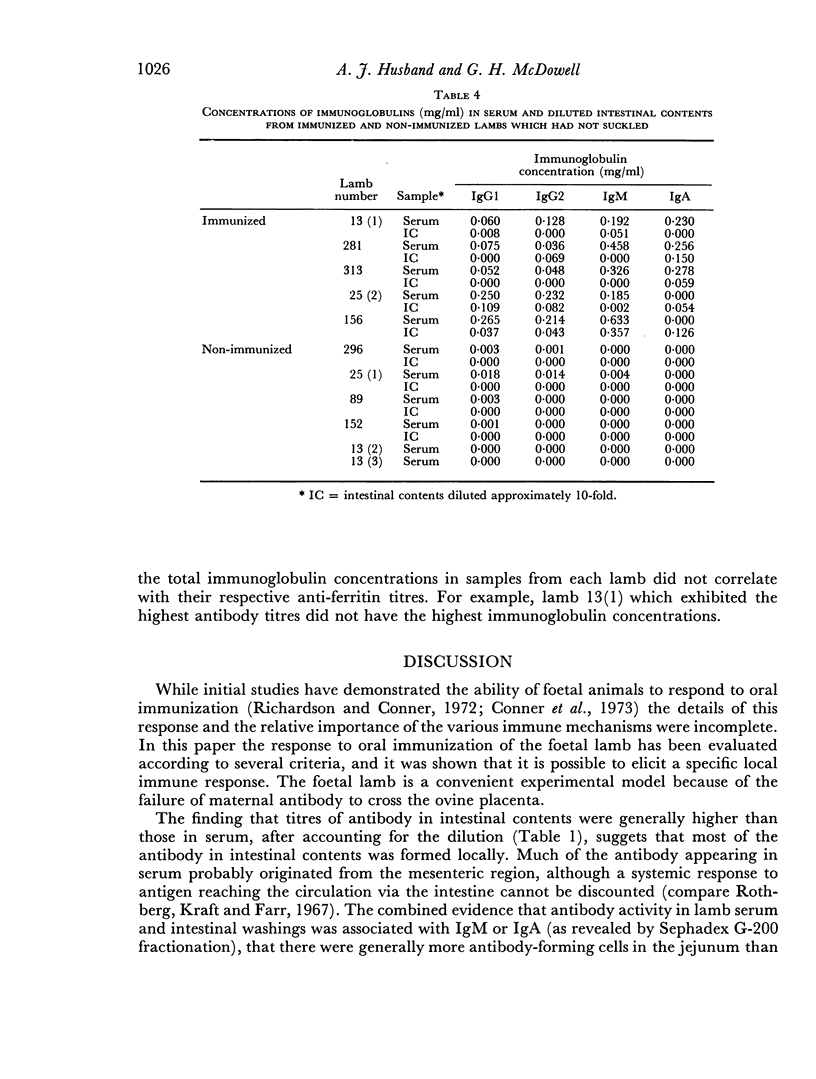
Foetal lambs were immunized orally 6-15 days before birth by introducing horse spleen ferritin into the amniotic fluid. Immunized and non-immunized lambs were killed at birth, usually before they had suckled, blood and intestinal contents were collected and single cell suspensions were prepared from spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes and jejunum. Specific antibody was detected in serum and intestinal contents of all immunized lambs which had not suckled. Specific antibody was usually not detected in samples from non-immunized lambs. In immunized lambs antibody activity in serum was associated with IgM and in intestinal contents with IgA and IgM. In agreement with these findings, the levels of IgM and IgA in serum and intestinal contents of immunized lambs were relatively high. Generally, immunoglobulins were not detected in samples from non-immunized lambs. Relatively high proportions of cells secreting specific antibody were present in the tissues of immunized but not non-immunized lambs. In the spleen most of the cells were secreting IgM antibody, in mesenteris lymph nodes IgM cells predominated and small numbers of IgA cells were detected, and in the jejunum approximately equal numbers of IgA and IgM cells were secreting specific antibody.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beh K. J., Lascelles A. K. Class specificity of intracellular and surface immunoglobulin of cells in popliteal and intestinal lymph from sheep. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1974 Jun;52(Pt 3):505–514. doi: 10.1038/icb.1974.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandon M. R., Watson D. L., Lascelles A. K. The mechanism of transfer of immunoglobulin into mammary secretion of cows. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Dec;49(6):613–623. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J. Immunoglobulins and immunocytes. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):159–171. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.159-171.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. J., Morris B. The growth and development of lambs thymectomized in utero. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Feb;49(1):33–53. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. H., Richardson M., Carter G. R. Prenatal immunization and protection of the newborn: ovine and bovine fetuses vaccinated with Escherichia coli antigen by the oral route and exposed to challenge inoculum at birth. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Jun;34(6):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doré C. F., Balfour B. M. A device for preparing cell spreads. Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):403–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM D. G., SMITH A. N. IMMUNOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF YOUNG ANIMALS. I. REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE. Can Vet J. 1965 Aug;6:194–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton A. R., 3rd, Asofsky R., Hylton M. B., Cooper M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin class synthesis in mice. I. Effects of treatment with antibody to -chain. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):277–297. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Synthesis of antibody and immunoglobulins without detectable antibody function in cells responding to horseradish peroxidase. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):626–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucca P. J., Faulk W. P., Fudenberg H. H. Passive immune lysis with chromic chloride-treated erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):812–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Kenworthy R., Allen W. D. Effect of oral immunisation with E coli antigens on post weaning enteric infection in the young pig. Vet Rec. 1974 Aug 3;95(5):99–104. doi: 10.1136/vr.95.5.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Kenworthy R., Holme D. W., Horsfield S. Escherichia coli antigens as dietary additives for oral immunisation of pigs: trials with pig creep feeds. Vet Rec. 1973 Jun 16;92(24):630–636. doi: 10.1136/vr.92.24.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Kenworthy R., Noakes D. E., Allen W. D. Intestinal antibody secretion in the young pig in response to oral immunization with Escherichia coli. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):841–853. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Noakes D. E., Allen W. D. Intestinal secretion of immunoglobulins in the preruminant calf. Immunology. 1972 Sep;23(3):299–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M., Beck C. C., Clark D. T. Prenatal immunization of the lamb to Brucella: Dissociation of immunocompetence and reactivity. J Immunol. 1968 Dec;101(6):1363–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M., Conner G. H., Beck C. C., Clark D. T. Prenatal immunization of the lamb to brucella; secondary antibody response in utero and at birth. Immunology. 1971 Nov;21(5):795–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M., Conner G. H. Prenatal immunization by the oral route: stimulation of Brucella antibody in fetal lambs. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):454–460. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.454-460.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M., Kraft S. C., Farr R. S. Similarities between rabbit antibodies produced following ingestion of bovine serum albumin and following parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):386–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. M., UHR J. W., KRANER K. L., LUKES R. J. Fetal response to antigenic stimulus. II. Antibody production by the fetal lamb. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:799–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schipper I. A., Kelling C. L. O agglutinin response of Eshcerichia coli in mature and neonatal pigs given heat-killed bacterin. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Oct;35(10):1365–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L., Brandon M. R., Lascelles A. K. Concentrations of immunoglobulin in mammary secretion of ruminants during involution with particular reference to selective transfer of IgG. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1972 Aug;50(4):535–539. doi: 10.1038/icb.1972.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. R. Vaccination against Escherichia coli enteritis in pigs. Vet Rec. 1972 Apr 1;90(14):400–401. doi: 10.1136/vr.90.14.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


