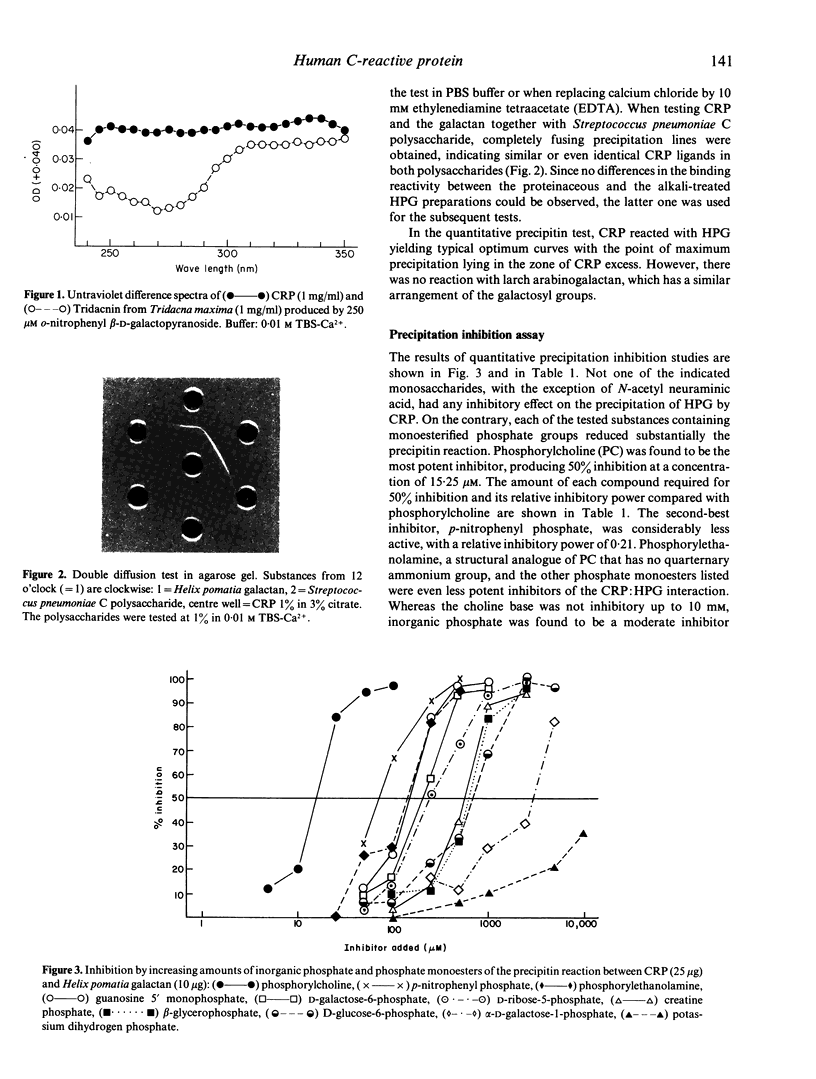
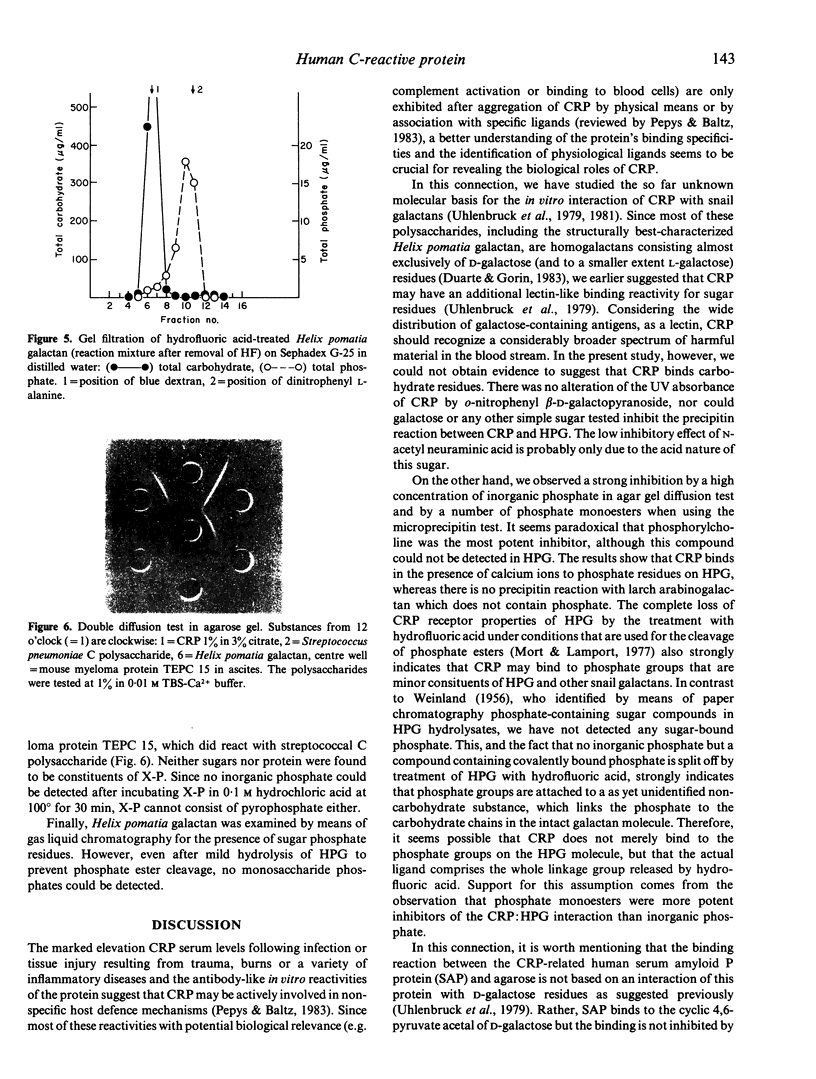
Abstract
Human C-reactive protein (CRP) shows binding specificities for phosphate monoesters, polycations and for several other biological macromolecules lacking these ligands. We report here that the formerly observed interaction of CRP with snail galactans, as exemplified by Helix pomatia galactan, is not due to a lectin-like carbohydrate-binding reactivity, but, instead that CRP obviously binds to phosphate groups that are minor constituents of these polysaccharides. Structural analysis of the galactan revealed that the phosphate groups are attached by a, as yet unidentified, linkage group to the carbohydrate backbone. Thus, the anti-galactan reactivity of CRP can be attributed to the protein's classical anti-phosphate/anti-phosphorylcholine specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldo B. A., Sawyer W. H., Stick R. V., Uhlenbruck G. Purification and characterization of a galactan-reactive agglutinin from the clam Tridacna maxima (Röding) and a study of its combining site. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):467–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1750467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak A. J., Tuma D. J. Determination of choline, phosphorylcholine, and betaine. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:287–292. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H. Lectins: their multiple endogenous cellular functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:207–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler W., Shafer J. A., Goldstein I. J. A spectrophotometric study of the carbohydrate binding site of concanavalina. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2819–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin M. F. A rapid and sensitive method for the analysis of carbohydrate components in glycoproteins using gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCamelli R., Potempa L. A., Siegel J., Suyehira L., Petras K., Gewurz H. Binding reactivity of C-reactive protein for polycations. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):1933–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Simpson R. M., Gewurz H. Activation of platelets by modified C-reactive protein. Immunology. 1982 Mar;45(3):439–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAL K., MILTENYI M. Haemagglutination test for the demonstration of C-reactive protein. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):41–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson P. A., Jermyn M. A., Clarke A. E. Isolation of an arabinogalactan protein by lectin affinity chromatography on tridacnin-sepharose 4B. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90622-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Edelman G. M. Binding properties and specificity of C-reactive protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):706–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Gotschlich E. C., Higginbotham J. D. Inhibition experiments with pneumococcal C and depyruvylated type-IV polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1972 Apr;22(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85719-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Collins P. M., Renn D., Cook R. B., Caspi D., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. Binding specificity of serum amyloid P component for the pyruvate acetal of galactose. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1058–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D. J., Ball A. J. A fast one-step method for the silylation of sugars and sugar phosphates. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):574–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mold C., Du Clos T. W., Nakayama S., Edwards K. M., Gewurz H. C-reactive protein reactivity with complement and effects on phagocytosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:251–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Ashley M. J. Isolation of C-reactive protein by affinity chromatography. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Jones K. D., Tanaka T., Liu T. Y. Binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin and nucleosome core particles. A possible physiological role of C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7311–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vartio T., Hedman K., Vaheri A. Binding of fibronectin by the acute phase reactant C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1496–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbruck G., Karduck D., Haupt H., Schwick H. G. C-reactive protein (CRP), 9.5 salpha1-glycoprotein and C1q: serum proteins with lectin properties? Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1979 Feb;155(3):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbruck G., Sölter J., Janssen E., Haupt H. Two new, additional "combining sites" of C-reactive protein: lectin specificity of the anti-galactan type and anti-haemocyanin reactivity. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Aug;362(8):1167–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Gewurz H., Hansen B., James K., Baum L. L. Effects of C-reactive protein on human lymphocyte responsiveness. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Kaplan M. H. Specificity of C-reactive protein for choline phosphate residues of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):612–614. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Narkates A. J. Interaction of C-reactive protein with artificial phosphatidylcholine bilayers and complement. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1820–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINLAND H. Beobachtungen bei der Säurehydrolyse des Galaktogens. V. Die säurestabilen Phosphorsäureester. Galaktose-6-phosphorsäure, frei, und als Bestandteil einer Trisaccharid-monophosphorsäure. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1956 Dec 10;306(2-3):56–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer F. C., Soutar A. K., Baltz M. L., Trayner I. M., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein are selectively bound by aggregated C-reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):230–242. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]