Abstract
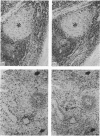
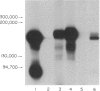
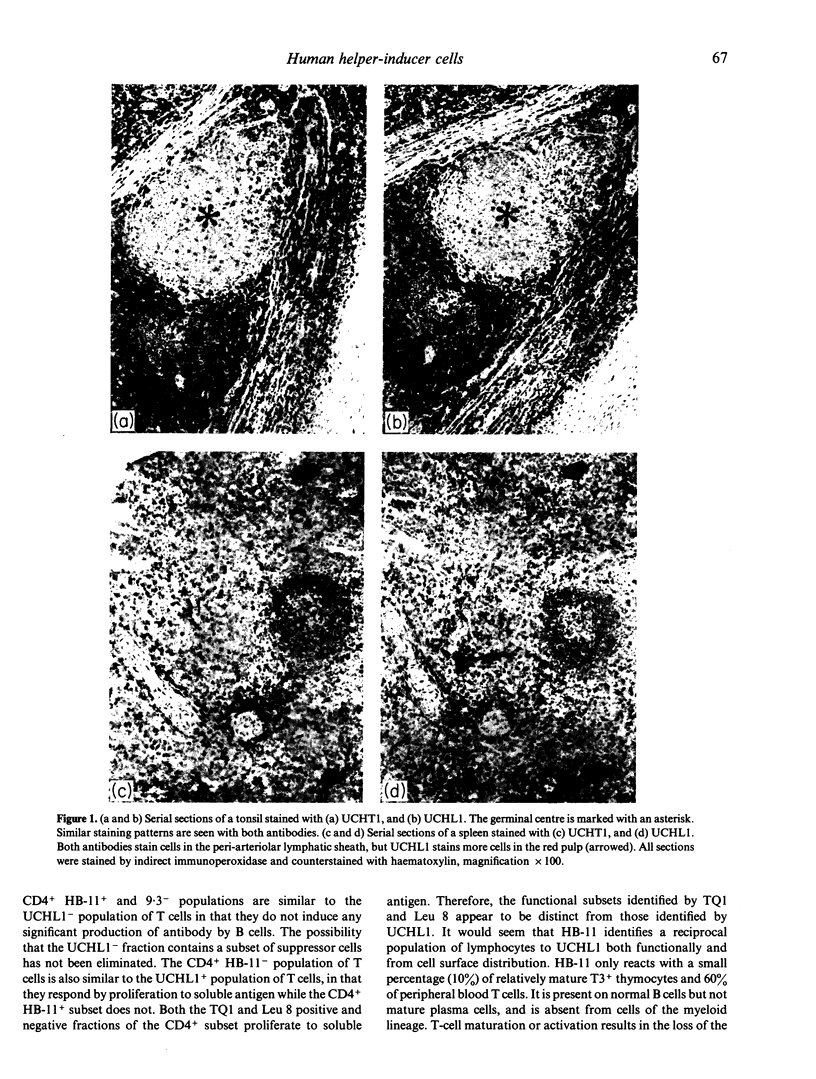
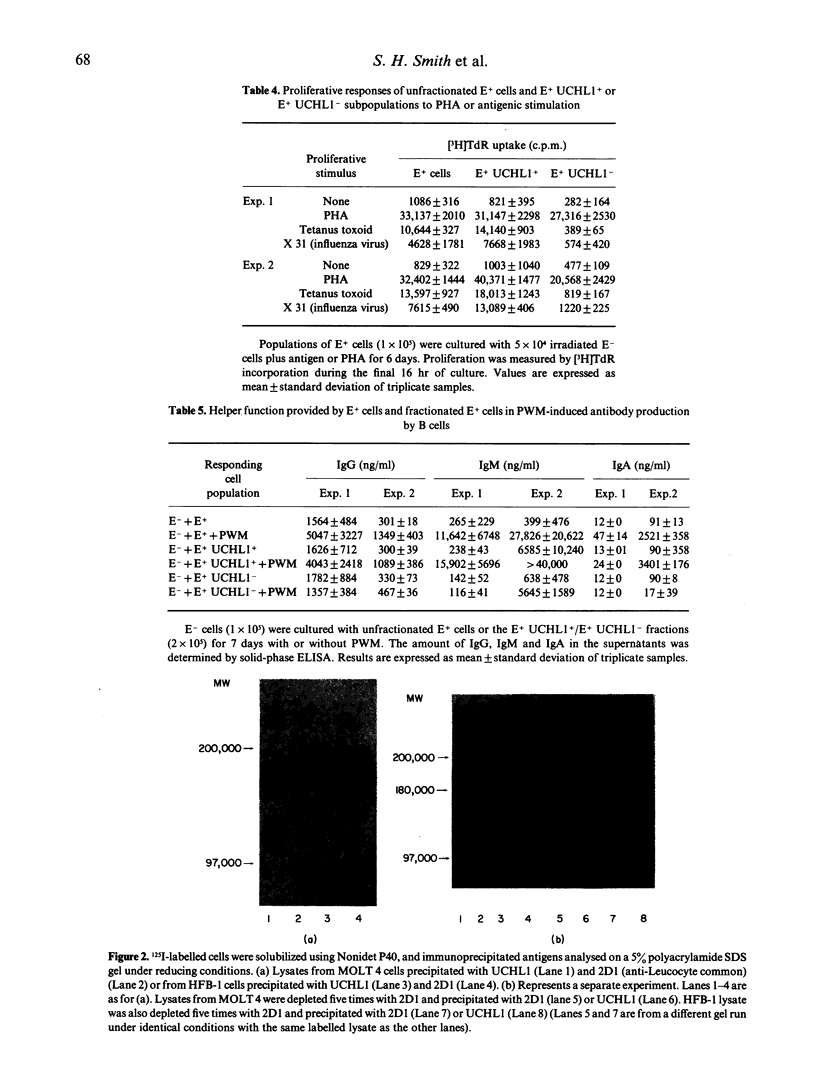
The monoclonal antibody UCHL1 identified an antigen present on most thymocytes, a subpopulation of resting T cells within both the CD4 and CD8 subsets, and on mature activated T cells. The UCHL1 determinant is also present on cells of the myeloid lineage, but not normal B cells or NK cells. Functionally, UCHL1 identifies a subpopulation of T cells which proliferates maximally to soluble antigen and provides maximum help for PWM-stimulated immunoglobulin synthesis. In contrast, the UCHL1- cells do not induce immunoglobulin synthesis and do not proliferate in the presence of soluble antigen, although both the UCHL1- and the UCHL1+ fractions of T cells proliferate well in the presence of PHA. By standard immunoprecipitation techniques and SDS page, the antigen recognized by UCHL1 was found to have a molecular weight of 180,000-185,000. Preclearing experiments using antibodies identifying the leucocyte common antigen, LCA, and the lymphocyte function-associated antigen, LFA-1, which have similar molecular weights to UCHL1, showed that the UCHL1 determinant is not biochemically related to these antigens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on microexudate-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1372–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C., Callard R. E. Distinctive functional characteristics of human "T" lymphocytes defined by E rosetting or a monoclonal anti-T cell antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):329–334. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradstock K. F., Janossy G., Pizzolo G., Hoffbrand A. V., McMichael A., Pilch J. R., Milstein C., Beverley P., Bollum F. J. Subpopulations of normal and leukemic human thymocytes: an analysis with the use of monoclonal antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jul;65(1):33–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Dagg M. K., Landay A. Characterization of human lymphocyte subpopulations: alloreactive cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursor and effector cells are phenotypically distinct from Leu 2+ suppressor cells. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;4(5):395–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00917143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dongworth D. W., Gotch F. M., Hildreth J. E., Morris A., McMichael A. J. Effects of monoclonal antibodies to the alpha and beta chains of the human lymphocyte function-associated (H-LFA-1) antigen on T lymphocyte functions. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Sep;15(9):888–892. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Beverley P. C., Feldmann M. Long-term human T-helper lines producing specific helper factor reactive to influenza virus. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):166–168. doi: 10.1038/294166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., MacDonald S., Slusarenko M., Beverley P. C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for human monocytes, granulocytes and endothelium. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):753–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Wood G. S., Fishwild D. M., Engleman E. G. Functional characterization of human T lymphocyte subsets distinguished by monoclonal anti-leu-8. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2995–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum L. G., Orcutt-Thordarson N., Seigneuret M. C., Hansen J. A. In vitro regulation of immunoglobulin synthesis by T-cell subpopulations defined by a new human T-cell antigen (9.3). Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Sammons R. Alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase for double immunoenzymatic labelling of cellular constituents. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):454–460. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. K., McDougal J. S., Spira T. J., Cross G. D., Jones B. M., Reinherz E. L. Immunoregulatory subsets of the T helper and T suppressor cell populations in homosexual men with chronic unexplained lymphadenopathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):191–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI111190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F. Biosynthesis of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9678–9684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Morimoto C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F. Heterogeneity of human T4+ inducer T cells defined by a monoclonal antibody that delineates two functional subpopulations. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Nagy J. A., Robbins E., Simon P., Springer T. A. A human leukocyte differentiation antigen family with distinct alpha-subunits and a common beta-subunit: the lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1), the C3bi complement receptor (OKM1/Mac-1), and the p150,95 molecule. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1785–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigfusson A., Babbage J. W., Souhami R. L. Defective in vitro antibody production in response to pokeweed mitogen and influenza antigen in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):396–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stashenko P., Nadler L. M., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1678–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Cooper M. D., Clement L. T. Human lymphocyte differentiation antigens HB-10 and HB-11. II. Differential production of B cell growth and differentiation factors by distinct helper T cell subpopulations. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2989–2994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Orientation of cell-surface antigens in the lipid bilayer of lymphocyte plasma membrane. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):307–311. doi: 10.1038/269307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]