Abstract
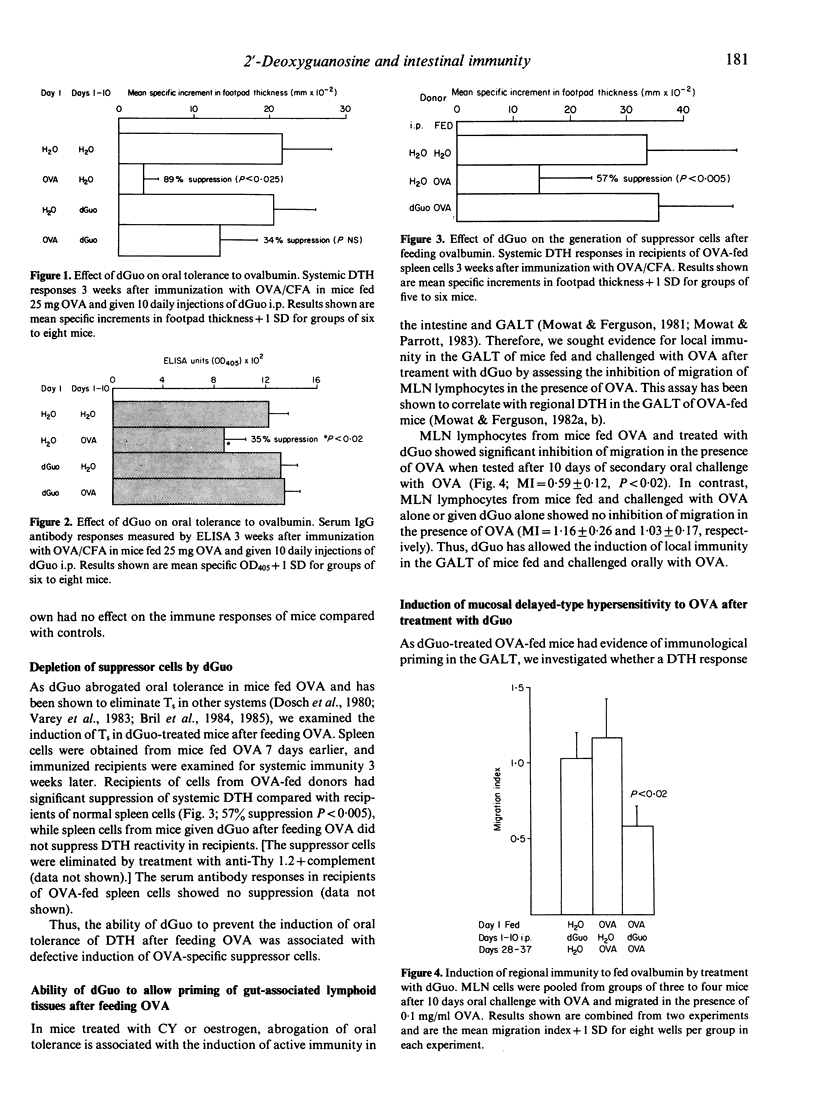
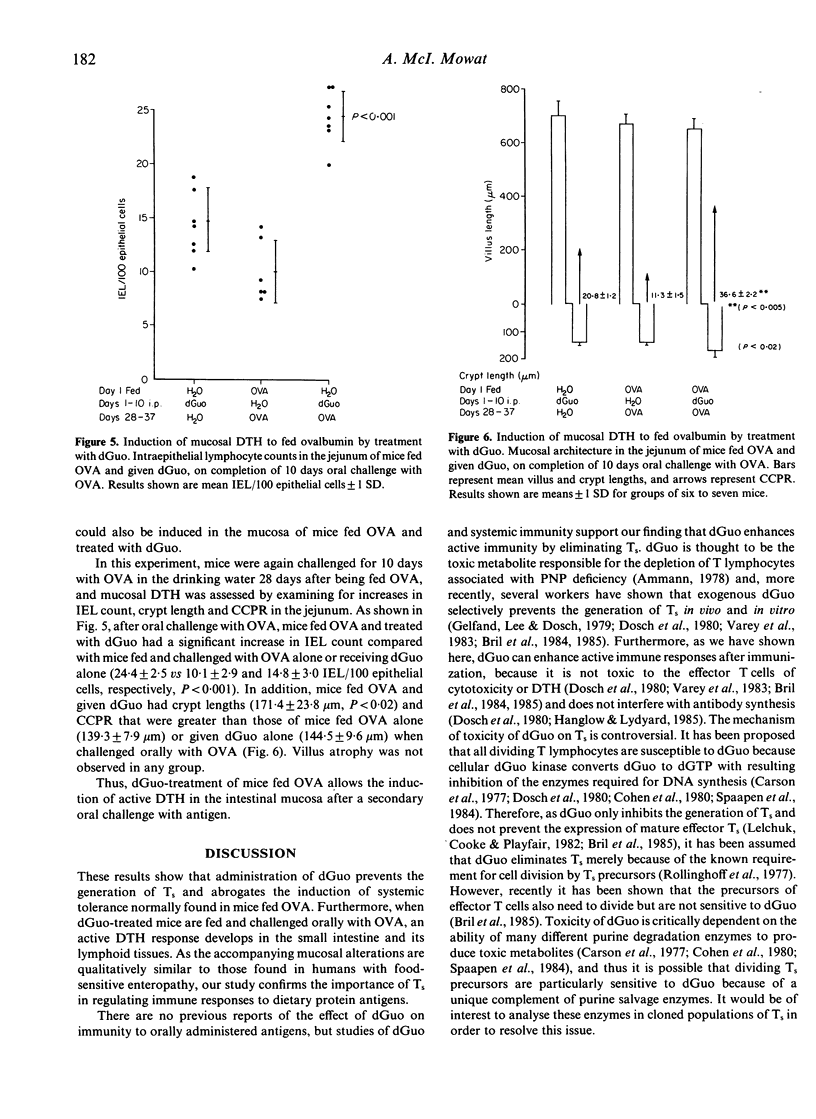
We have re-examined the role of suppressor T cells (Ts) in regulating immune responses to fed proteins by investigating the effect of 2'-deoxyguanosine (dGuo) on systemic and intestinal immunity in mice fed ovalbumin (OVA). Administration of dGuo for 10 days abrogated the suppression of systemic delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) and antibody responses normally found after feeding OVA, and also prevented the generation of OVA-specific Ts. In parallel, mice given dGuo and fed OVA developed sensitization to OVA in the gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) after oral challenge with OVA and had increased intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) counts and crypt cell production rates (CCPR) in the jejunal mucosa, indicating the presence of a local DTH response. These findings confirm the importance of Ts in preventing hypersensitivity to dietary protein antigens and suggest that enteropathies associated with food hypersensitivity are due to a defect in Ts activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann A. J. Immunological aberrations in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiencies. Ciba Found Symp. 1978;(68):55–75. doi: 10.1002/9780470720516.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bril H., van den Akker T. W., Hussaarts-Odijk L. M., Benner R. Differential influence of 2'-deoxyguanosine on the induction and expression of suppressor T lymphocytes in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1985 Feb;90(2):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90217-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bril H., van den Akker T. W., Molendijk-Lok B. D., Bianchi A. T., Benner R. Influence of 2'-deoxyguanosine upon the development of DTH effector T cells and suppressor T cells in vivo. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):599–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Lymphospecific toxicity in adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency: possible role of nucleoside kinase(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Systemic tolerance and secretory immunity after oral immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1459–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Lee J. W., Dosch H. M., Gelfand E. W. The expression of deoxyguanosine toxicity in T lymphocytes at different stages of maturation. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1578–1582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch H. M., Mansour A., Cohen A., Shore A., Gelfand E. W. Inhibition of suppressor T-cell development following deoxyguanosine administration. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):494–496. doi: 10.1038/285494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Murray D. Quantitation of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human jejunum. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):988–994. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Lee J. J., Dosch H. M. Selective toxicity of purine deoxynucleosides for human lymphocyte growth and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanglow A. C., Lydyard P. M. The effect of 2'deoxyguanosine on human lymphocyte responses. I. 2'deoxyguanosine enhances T lymphocyte responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):653–658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson D. G., Miller S. D. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. V. Induction of the tolerant state in the absence of specific suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2378–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelchuk R., Cooke A., Playfair J. H. Differential sensitivity to 2'-deoxyguanosine of antigen-specific and nonspecific suppressor T cells in delayed hypersensitivity. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. G., Newby T. J., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Influence of diet on postweaning malabsorption and diarrhoea in the pig. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Mar;36(2):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Hanson D. G. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. IV. Evidence for tolerance and specific active suppression of cell-mediated immune responses to ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2344–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity in the small intestinal mucosa. V. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to a dietary antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):574–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Migration inhibition of lymph node lymphocytes as an assay for regional cell-mediated immunity in the intestinal lymphoid tissues of mice immunized orally with ovalbumin. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):365–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Migration inhibition of lymph node lymphocytes as an in vitro assay for cell-mediated immunity in the draining lymph nodes of parenterally immunized mice. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):357–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Parrot D. M. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. IV. Effects of stimulating the reticuloendothelial system on oral tolerance and intestinal immunity to ovalbumin. Immunology. 1983 Dec;50(4):547–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Strobel S., Drummond H. E., Ferguson A. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. I. Reversal of oral tolerance to ovalbumin by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):105–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M. The role of antigen recognition and suppressor cells in mice with oral tolerance to ovalbumin. Immunology. 1985 Oct;56(2):253–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Chiller J. M., Brown W. R., Hanson D. G., Vaz N. M. Enterically induced immunologic tolerance. I. Induction of suppressor T lymphoyctes by intragastric administration of soluble proteins. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2429–2434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röllinghoff M., Starzinski-Powitz A., Pfizenmaier K., Wagner H. Cyclophosphamide-sensitive T lymphocytes suppress the in vivo generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):455–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobhon P., Wanichanon C., Sretarugsa P. Morphological changes induced by cyclophosphamide in crypt epithelium of the small intestine in mice: light and electron microscopic studies. Am J Anat. 1977 Aug;149(4):563–583. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001490409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaapen L. J., Rijkers G. T., Staal G. E., Rijksen G., Wadman S. K., Stoop J. W., Zegers B. J. The effect of deoxyguanosine on human lymphocyte function. I. Analysis of the interference with lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2311–2317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Ferguson A. Immune responses to fed protein antigens in mice. 3. Systemic tolerance or priming is related to age at which antigen is first encountered. Pediatr Res. 1984 Jul;18(7):588–594. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198407000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Mowat A. M., Drummond H. E., Pickering M. G., Ferguson A. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. II. Oral tolerance for CMI is due to activation of cyclophosphamide-sensitive cells by gut-processed antigen. Immunology. 1983 Jul;49(3):451–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Chiller J. M. A simple and effective method to assess murine delayed type hypersensitivity to proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1981;45(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varey A. M., Lelchuk R., Hutchings P., Cooke A. The differential effect of 2-deoxyguanosine on concanavalin A-induced suppressor and cytotoxic activity. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 1;81(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


