Abstract
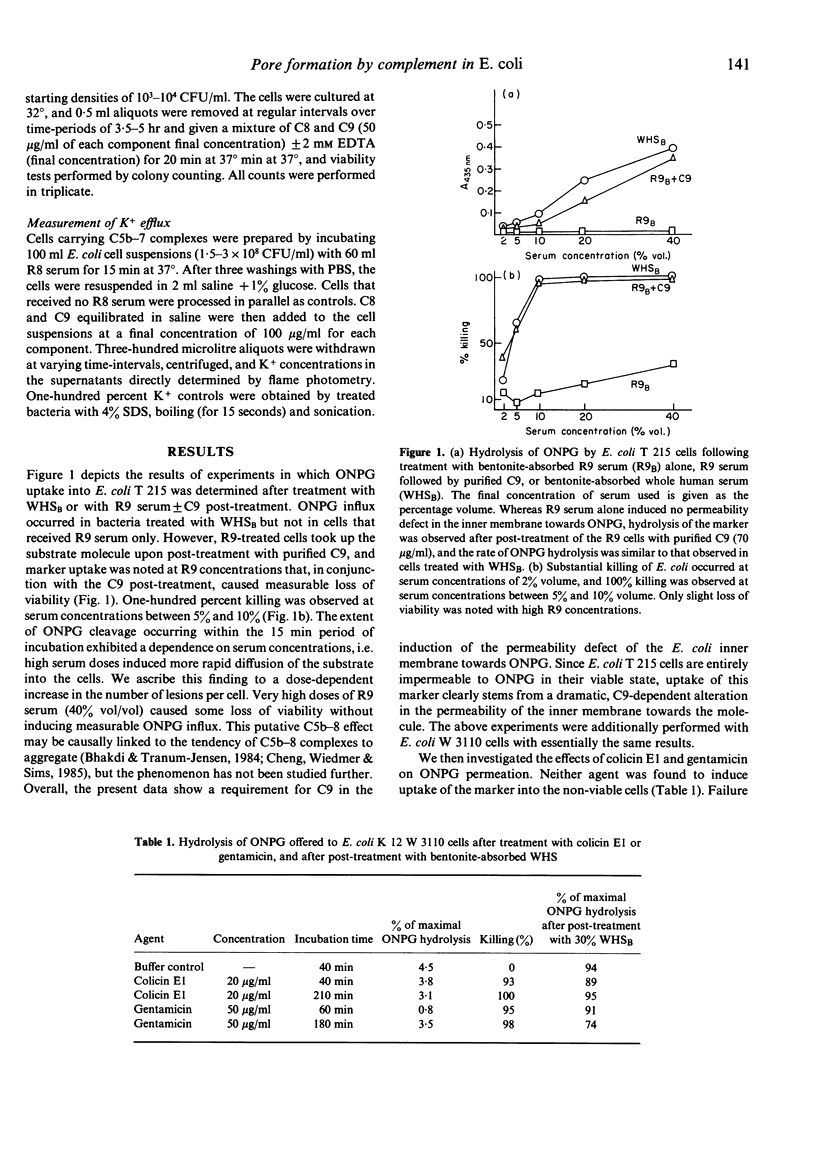
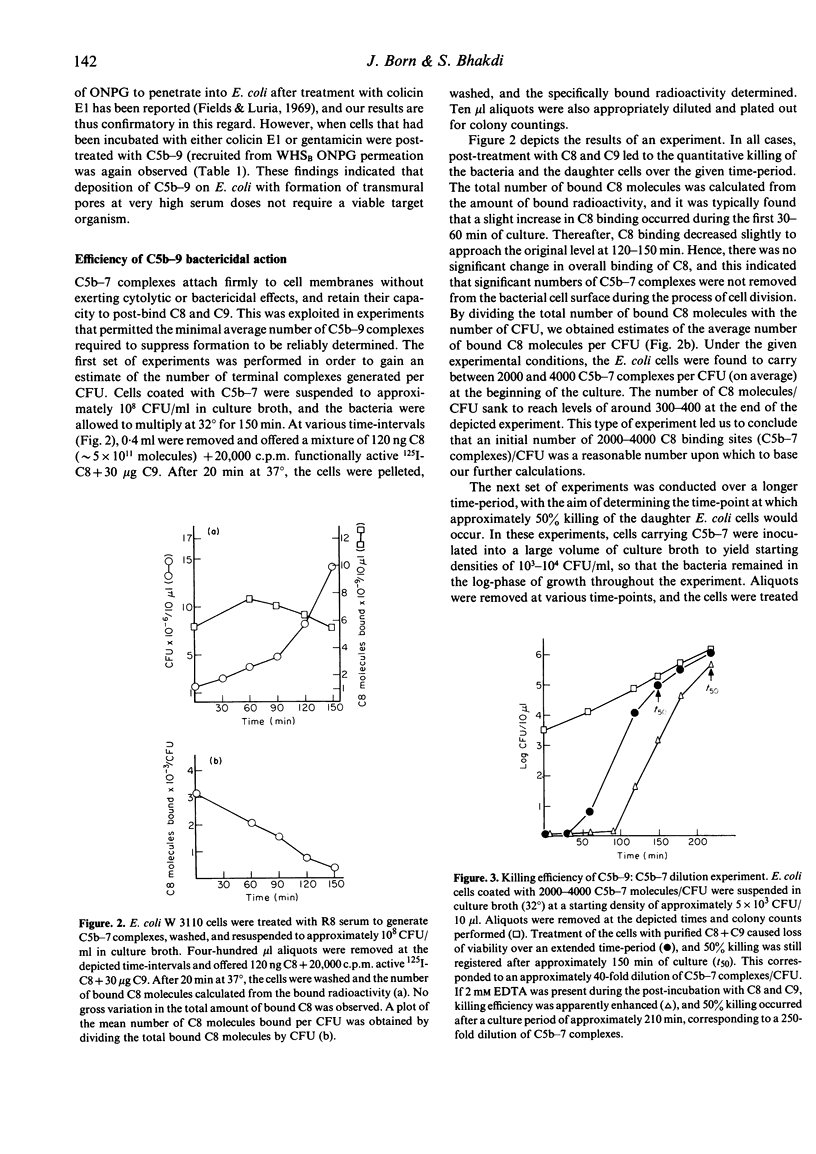
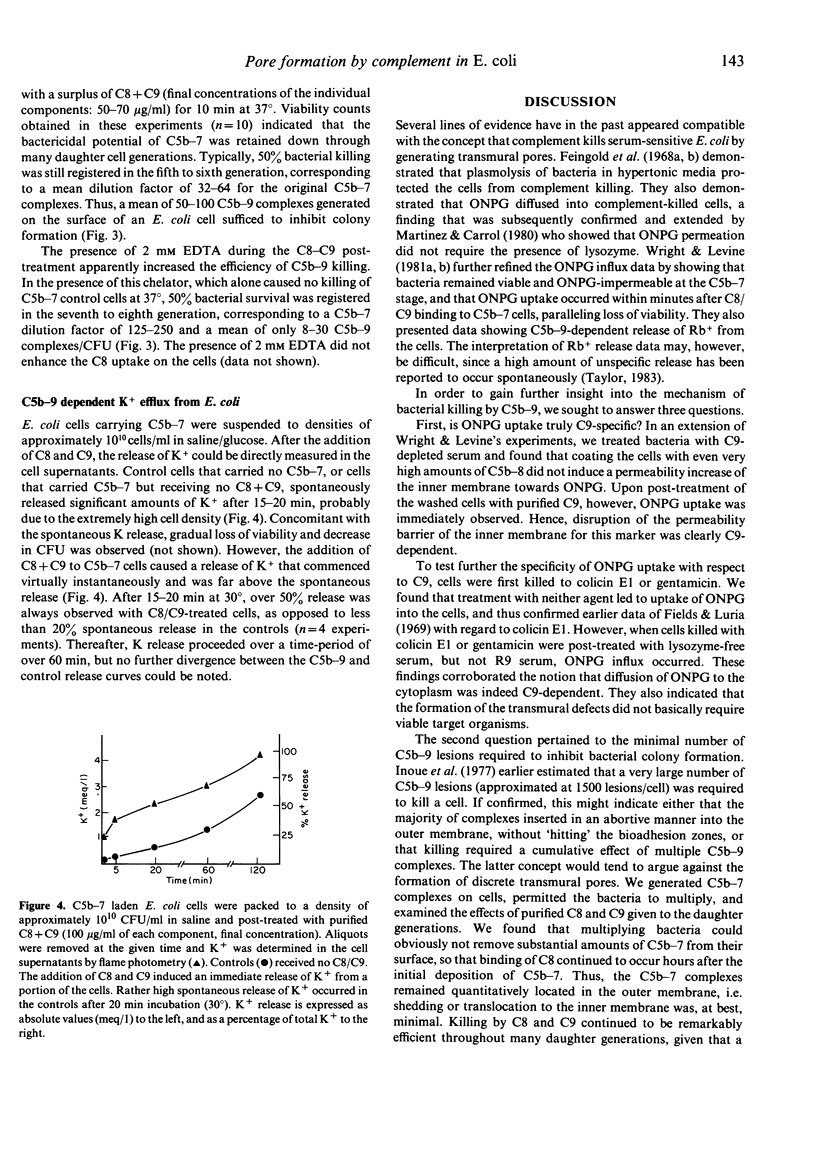
Three lines of evidence are presented to indicate that C5b-9 kills serum-sensitive E. coli K 12 cells by generating functional pores across the outer and inner bacterial membrane. First, viable cells carrying C5b-8 complexes are impermeable to o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactoside (ONPG), but lose viability and become permeable to this marker upon post-treatment with purified C9 in the absence of lysozyme. Cells killed with colicin E1 or gentamicin are also impermeable to ONPG but take up the marker if they are post-treated with lysozyme-free serum. Second, killing by C5b-9 is highly effective, deposition of only a small number of complexes being lethal. This has been demonstrated in experiments where viable cells carrying 2000-4000 C5b-7 complexes per CFU were permitted to multiply in broth culture, and the daughter generations subsequently treated with purified C8 and C9. Fifty percent killing was observed in the fifth to sixth generation, corresponding to a dilution of C5b-7 complexes to 50-100 molecules/CFU. In the presence of 2 mM EDTA, further dilution of C5b-7 down to 8-30 complexes/CFU still caused 50% killing of daughter cells. Third, treatment of C5b-7 cells with purified CC8 and C9 results in the release of intracellular K+, which commences immediately after addition of C8/C9. This was shown in experiments where C5b-7 cells were packed to high density in saline, post-treated with C8 + C9, and K+ directly measured in the cell supernatants. Based on these results, we propose that C5b-9 pores deposited in the outer bacterial membrane periodically fuse with the inner membrane, the transmural pores thus generated permitting rapid K+ efflux, with cell death ensuing through the collapse of membrane potential.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. C5b-9 assembly: average binding of one C9 molecule to C5b-8 without poly-C9 formation generates a stable transmembrane pore. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2999–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by complement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):343–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. On the cause and nature of C9-related heterogeneity of terminal complement complexes generated on target erythrocytes through the action of whole serum. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1453–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: purification and physicochemical characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1291–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. H., Wiedmer T., Sims P. J. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer study of the associative state of membrane-bound complexes of complement proteins C5b-8. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):459–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kinoshita T., Okada M., Akiyama Y. Release of phospholipids from complement-mediated lesions on the surface structure of Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Sanders M. E., Murray T. G., Hammer C. H., Dourmashkin R., Frank M. M. Multimeric complement component C9 is necessary for killing of Escherichia coli J5 by terminal attack complex C5b-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll H. P., Bhakdi S., Taylor P. W. Membrane changes induced by exposure of Escherichia coli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1055-1066.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Carroll S. F. Sequential metabolic expressions of the lethal process in human serum-treated Escherichia coli: role of lysozyme. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):735–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.735-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):93–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01893017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Normal serum cytotoxicity for P32-labeled smooth Enterobacteriaceae. II. Fate of macromolecular and lipid phosphorus of damaged cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):148–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.148-152.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Wilson L. A. Normal serum cytotoxicity for P32-labeled smooth Enterobacteriaceae. I. Loss of label, death, and ultrastructural damage. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):393–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.393-400.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Kroll H. P. Killing of an encapsulated strain of Escherichia coli by human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.122-131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levine R. P. How complement kills E. coli. I. Location of the lethal lesion. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levine R. P. How complement kills E. coli. II. The apparent two-hit nature of the lethal event. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1152–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


