Abstract
There is accumulating evidence concerning the possible importance of secretory IgA antibodies in defence mechanisms against infections of the gastrointestinal tract, including cholera. Intestinal IgA antibodies are also thought to play a major role in protection against the diarrhoeogenic effects of cholera toxin. We therefore attempted to induce secretory IgA antibodies towards a reactive synthetic peptide from the cholera toxin B subunit sequence. We report that rat biliary secretory IgA antibodies against the CTP3 peptide (residues 50-64 of the B subunit) were obtained by three intra-Peyer's patch immunizations, at 2-week intervals, with CTP3 conjugated to tetanus toxoid in complete Freund's adjuvant. Purified secretory IgA fractions from bile of such immunized rats reacted with the carrier toxoid, but also with the CTP3 peptide, and with the native cholera toxin, they also partially neutralized its biological activity, as assayed by inhibition of in vitro cholera toxin-induced cAMP production in mouse thymocytes.
Full text
PDF


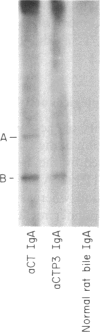
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew E., Hall J. G. IgA antibodies in the bile of rats. I. Some characteristics of the primary response. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):169–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew E., Hall J. G. IgA antibodies in the bile of rats. II. Evidence for immunological memory in secretory immunity. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):177–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Orlans E., Reynolds J., Dean C., Peppard J., Gyure L., Hobbs S. Occurrence of specific antibodies of the IgA class in the bile of rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;59(1):75–84. doi: 10.1159/000232242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ouchterlony O., Anderson A., Walletström G., Westerberg-Berndtsson U. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: protection, and serum and local antibody responses in rabbits after enteral and parenteral immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1331–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1331-1340.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Pines M., Arnon R. Neutralization of heat-labile toxin of E. coli by antibodies to synthetic peptides derived from the B subunit of cholera toxin. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2889–2893. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Sela M., Arnon R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides of the B subunit of cholera toxin: crossreaction and neutralization of the toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Sela M., Pines M., Hurwitz S., Arnon R. Both cholera toxin-induced adenylate cyclase activation and cholera toxin biological activity are inhibited by antibodies against related synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7893–7896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Clements J. D., Houghten R. A. Vaccine for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli based on synthetic heat-stable toxin crossed-linked to the B subunit of heat-labile toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):318–326. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Houghten R. A. Properties of cross-linked toxoid vaccines made with hyperantigenic forms of synthetic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):268–273. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.268-273.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Shearman D. J., Rowley D. Antibodies in serum and secretions 1 year after salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):551–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître-Coelho I., Jackson G. D., Vaerman J. P. Rat bile as a convenient source of secretory IgA and free secretory component. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sacci J. B., Jr Oral immunization of dogs with purified cholera toxin, crude cholera toxin, or B subunit: evidence for synergistic protection by antitoxic and antibacterial mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):687–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.687-694.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sircar B. K. Induction of a mucosal antitoxin response and its role in immunity to experimental canine cholera. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.185-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Gothefors L., Sack D. A., Bardhan P. K., Holmgren J. Local and systemic antibody responses and immunological memory in humans after immunization with cholera B subunit by different routes. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(6):909–918. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
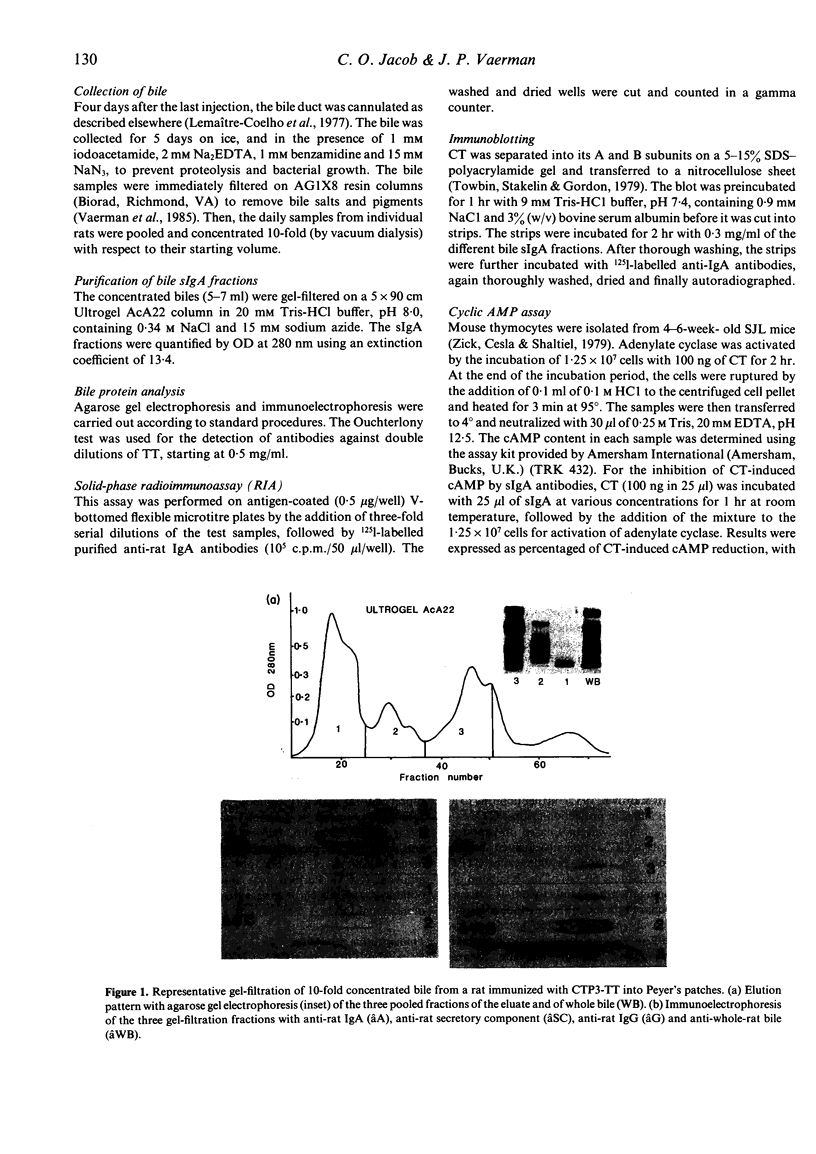
- Svennerholm A., Lange S., Holmgren J. Correlation between intestinal synthesis of specific immunoglobulin A and protection against experimental cholera in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.1-6.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaru T., Brown W. R. IgA antibodies in rat bile inhibit cholera toxin-induced secretion in ileal loops in situ. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):579–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Derijck-Langendries A., Rits M., Delacroix D. Neutralization of cholera toxin by rat bile secretory IgA antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):601–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F., Bazin H., Beckers A. Identification and some properties of rat secretory component. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):265–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Cesla R., Shaltiel S. cAMP-dependent protein kinase from mouse thymocytes. Localization, characterization, and evaluation of the physiological relevance of a massive cytosol to nucleus translocation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):879–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]