Abstract
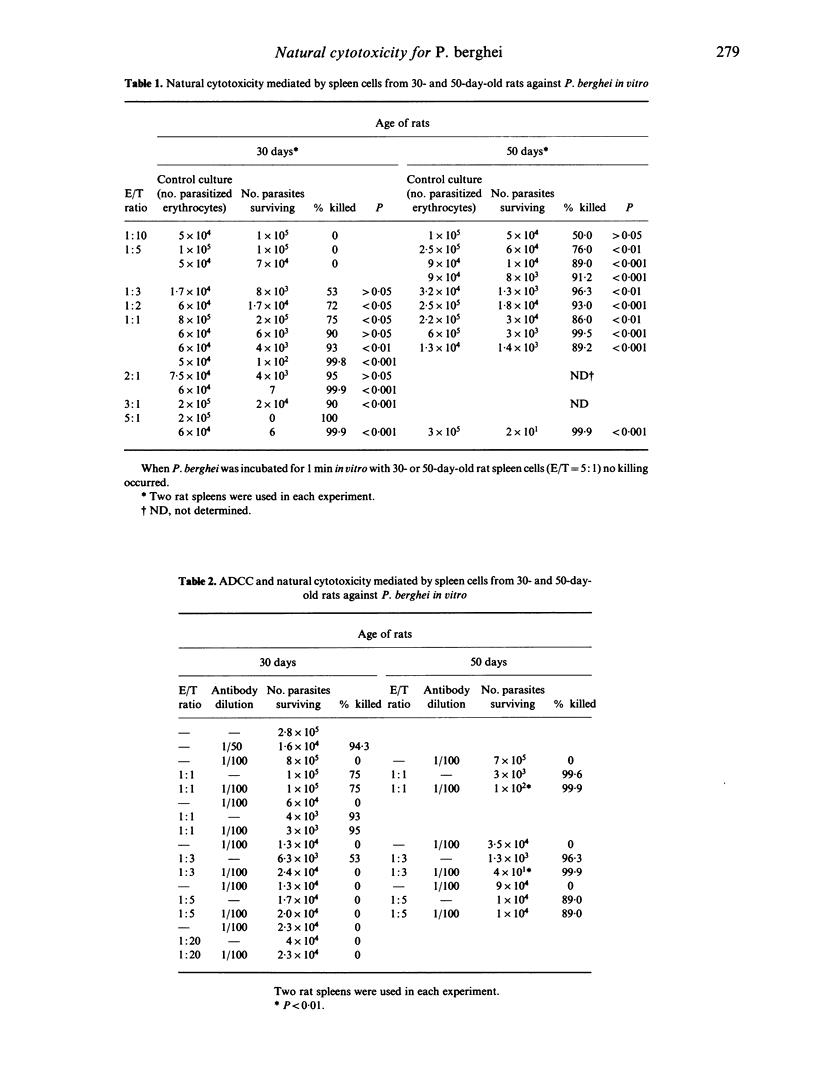
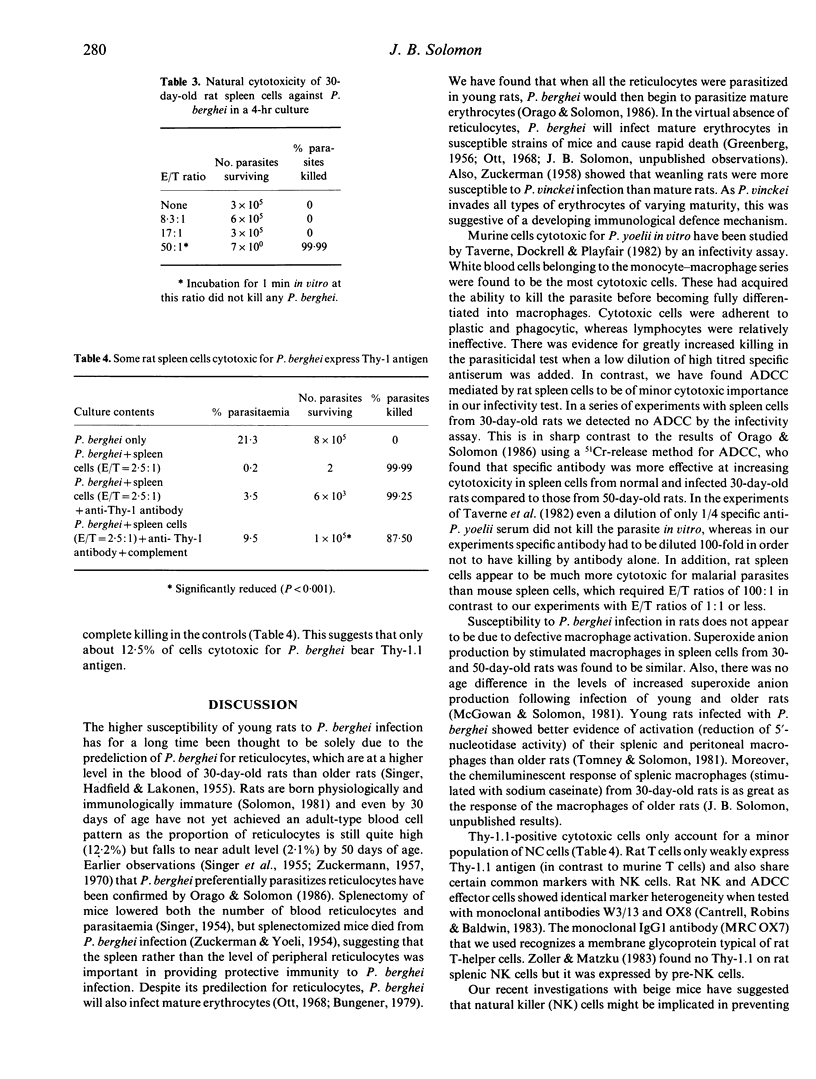
The susceptibility of 30-day-old rats to Plasmodium berghei infection has traditionally been ascribed to the higher levels of circulating blood reticulocytes for which P. berghei has a predilection. However, spleen cells soon develop natural cytotoxicity for P. berghei which may account, in part, for the increased natural resistance of older rats. Spleen cells from normal 30- or 50-day-old rats were cultured overnight with erythrocytes parasitized by P. berghei and then injected into MF1 mice. Six days later, the percentage parasitaemia was determined and the extent of killing by the spleen cells in vitro determined. Spleen cells from 50-day-old resistant rats were found to be four times better at killing P. berghei in vitro than those from 30-day-old susceptible rats. Antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) was, at best, only a minor component. About 12% of total cytotoxicity was destroyed by pretreatment of spleen cells with monoclonal anti-Thy-1.1 antibody and complement. The possibility that natural cytotoxicity in these experiments is mediated by natural killer cells is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büngener W. Weitere Beobachtungen über den Verlauf der Plasmodium berghei-Infektion in der Maus. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1979 Mar;30(1):24–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Robins R. A., Baldwin R. W. A comparison of membrane markers on rat cytotoxic cells. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):139–146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG J. Differences in the course of Plasmodium berghei infections in some hybrid and backcross mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Jan;5(1):19–28. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1956.5.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop B. F., McNeilage L. J. Natural cytotoxicity: early killing of allogeneic lymphocytes in rats. Immunol Rev. 1983;73:35–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITCHFIELD J. T., Jr A method for rapid graphic solution of time-per cent effect curves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Dec;97(4):399-408, 3 tab. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orago A. S., Solomon J. B. Antibody-dependent and -independent cytotoxic activity of spleen cells for Plasmodium berghei from susceptible and resistant rats. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):283–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott K. J. Influence of reticulocytosis on the course of infection of Plasmodium chabaudi and P. berghei. J Protozool. 1968 May;15(2):365–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER I., HADFIELD R., LAKONEN M. The influence of age on the intensity of infection with Plasmodium berghei in the rat. J Infect Dis. 1955 Jul-Aug;97(1):15–21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/97.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER I. The effect of splenectomy or phenylhydrazine on infections with Plasmodium berghei in the white mouse. J Infect Dis. 1954 Mar-Apr;94(2):159–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/94.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. B., Forbes M. G., Solomon G. R. A possible role for natural killer cells in providing protection against Plasmodium berghei in early stages of infection. Immunol Lett. 1985;9(6):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Dockrell H. M., Playfair J. H. Killing of the malarial parasite Plasmodium yoelii in vitro by cells of myeloid origin. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Mar;4(2):77–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKERMAN A. Blood loss and replacement in plasmodial infections. I. Plasmodium berghei in untreated rats of varying age and in adult rats with erythropoietic mechanisms manipulated before inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1957 Mar-Apr;100(2):172–206. doi: 10.1093/infdis/100.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKERMAN A. Blood loss and replacement in plasmodial infections. II. Plasmodium vinckel in untreated weanling and mature rats. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):205–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKERMAN A., YOELI M. Age and sex as factors influencing Plasmodium berghei infections in intact and splenectomized rats. J Infect Dis. 1954 May-Jun;94(3):225–236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/94.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


