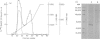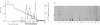Abstract
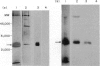
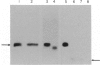
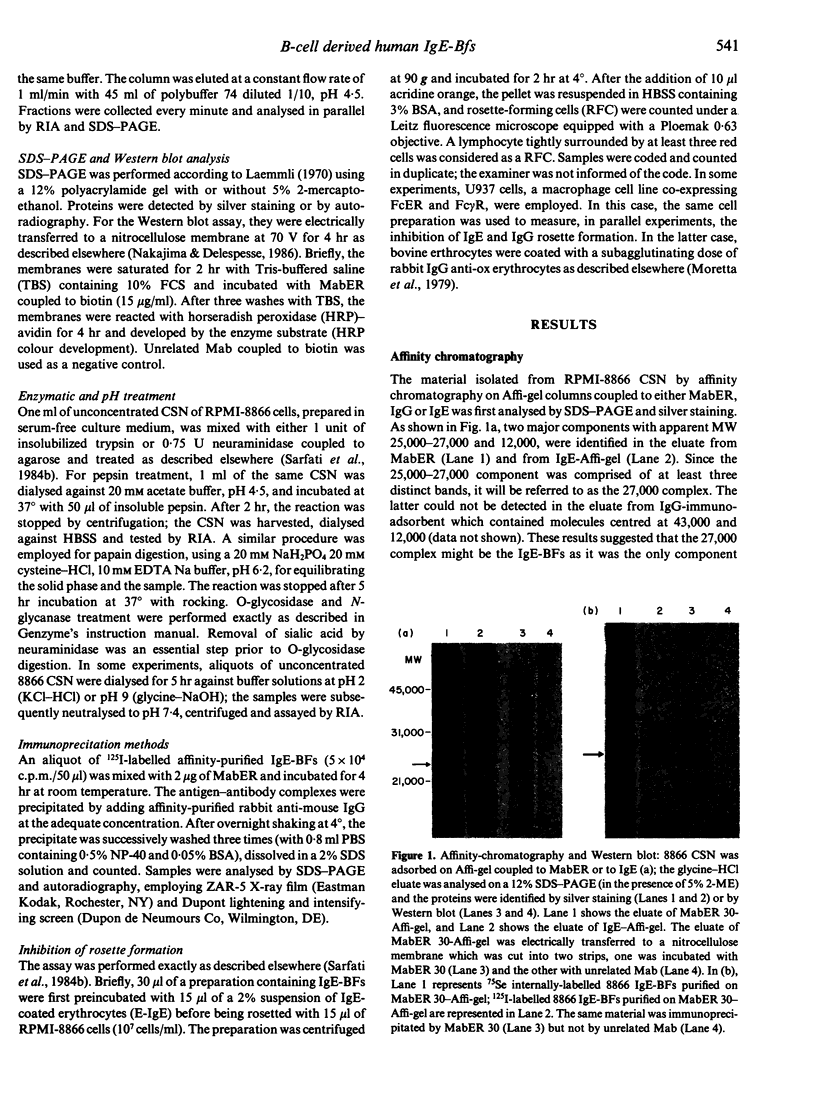
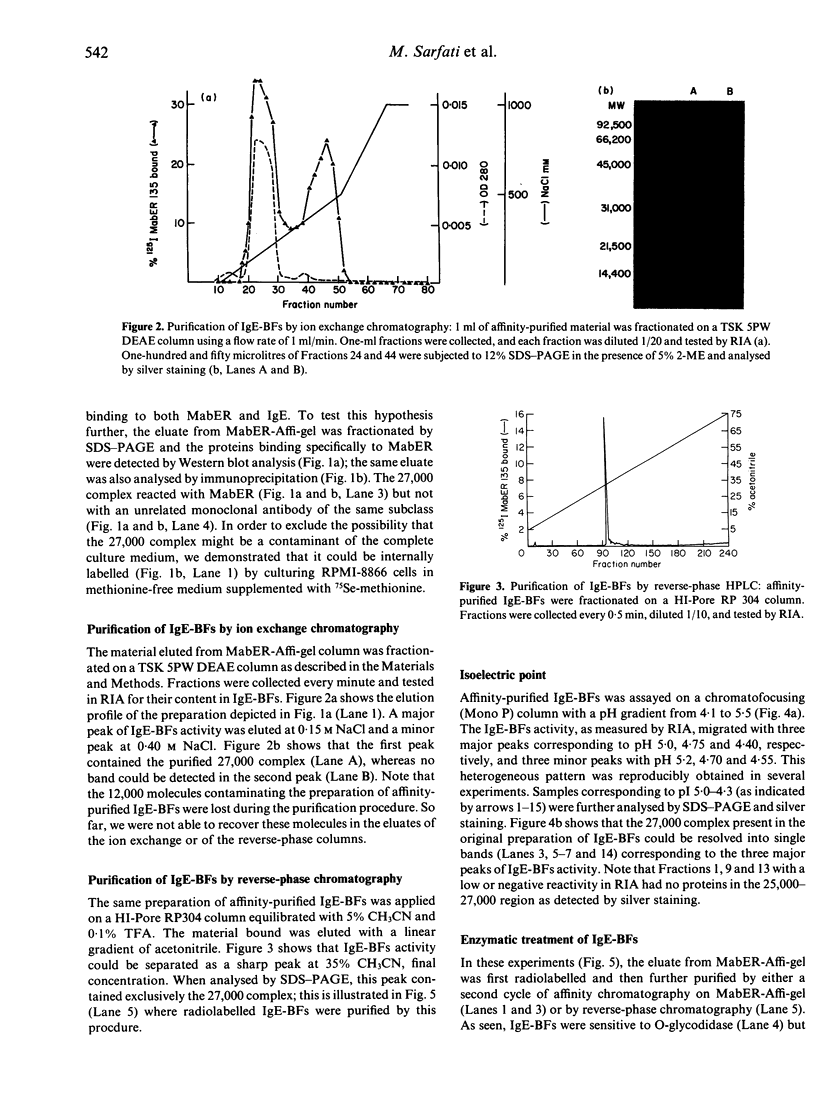
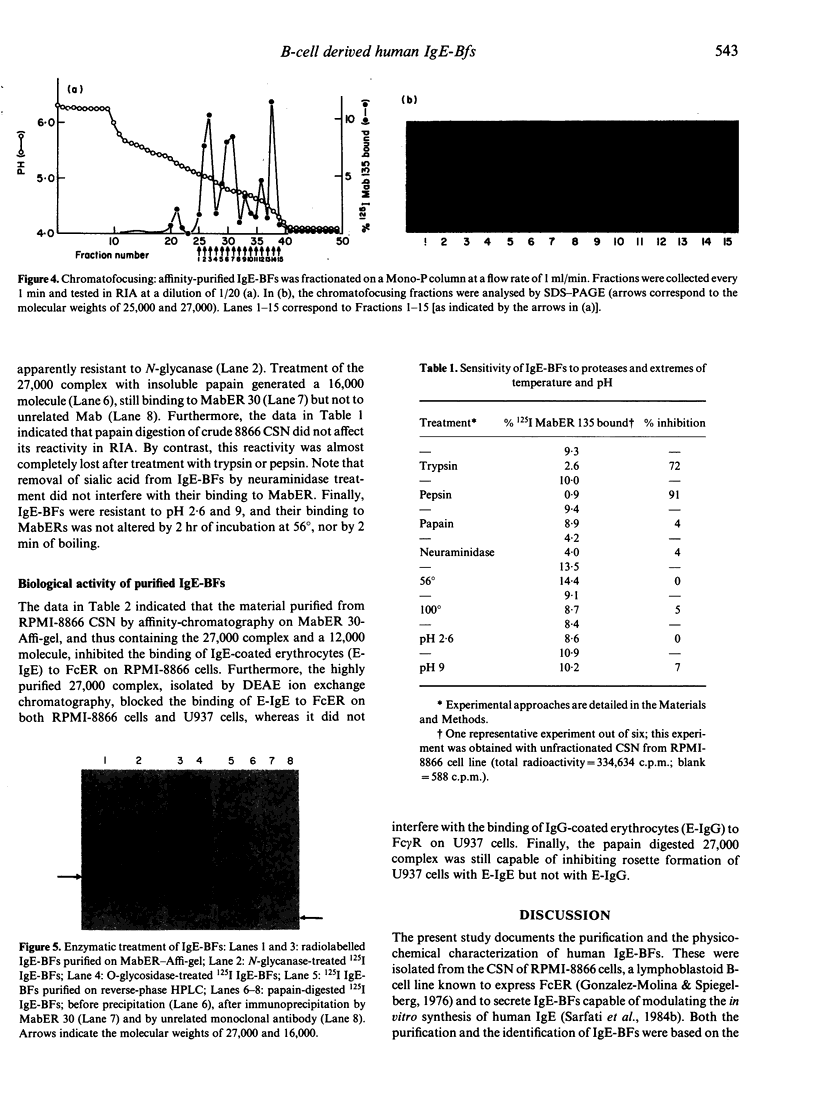
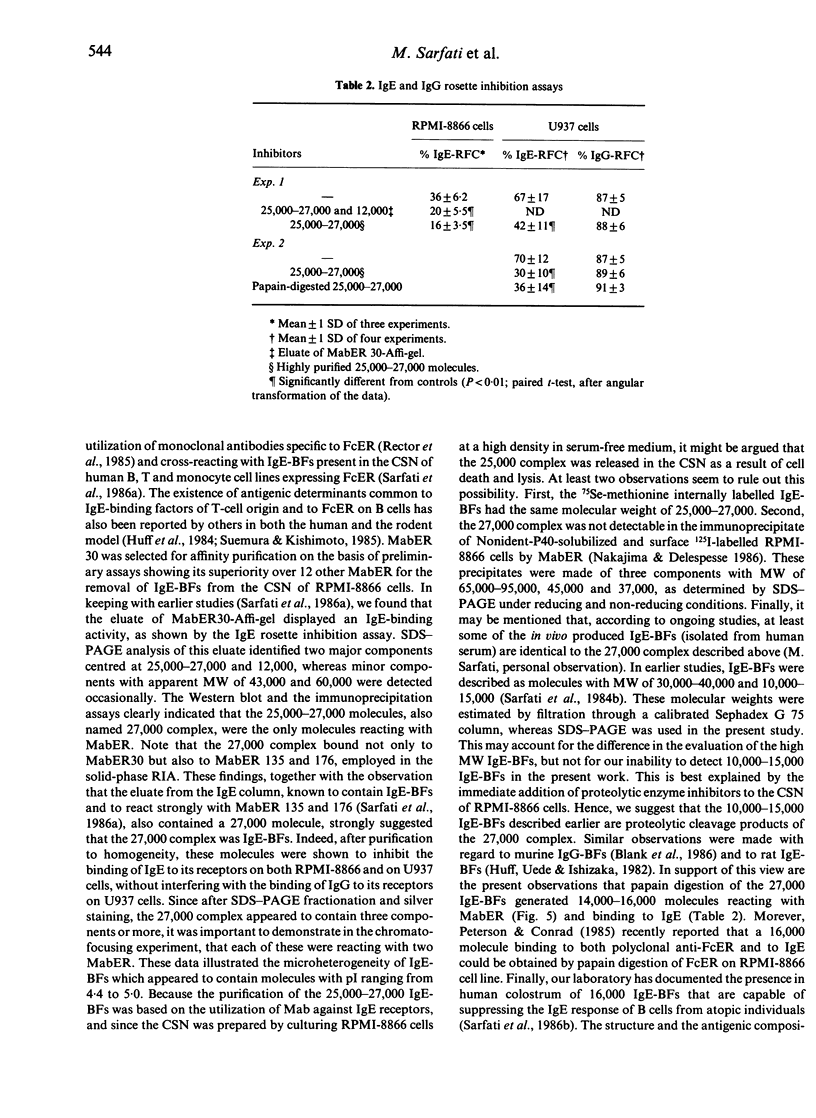
IgE-binding factors (IgE-BFs) were purified from the culture supernatant of RPMI-8866 cells, a human lymphoblastoid B-cell line expressing IgE receptors. The material, purified by affinity-chromatography on immunoadsorbents coupled to IgE or to monoclonal antibody against IgE receptor, was comprised of two major components with apparent molecular weight (MW) of 25,000-27,000 and 12,000, as determined by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Only the 25,000-27,000 MW molecules were identified as IgE-BFs, as demonstrated by their reactivity with MabER in the Western blot and the immunoprecipitation assays, and their ability to inhibit rosette formation of U937 cells with IgE- but not with IgG-coated erythrocytes. IgE-BFs were purified to homogeneity by combining affinity-chromatography and either DEAE-ion exchange or reverse-phase chromatography on an HPLC system. Chromatofocusing analysis demonstrated the microheterogeneity of IgE-BFs that were comprised of molecules with isoelectric points ranging from 5.0 to 4.4. IgE-BFs were sensitive to treatment with O-glycosidase but not with N-glycanase. These molecules were resistant to heat and to pH ranging from 2 to 9; their immunoreactivity was lost after treatment with trypsin and pepsin. Papain digestion of purified IgE-BFs generated 14,000-16,000 MW molecules that were still binding to IgE and to MabER.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blank U., Fridman W. H., Daëron M., Galinha A., Moncuit J., Néauport-Sautès C. Size and charge heterogeneity of murine IgG-binding factors (IgG-BF). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2975–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caraux J., Chichehian B., Serrou B., Weigle W. O. Human soluble Fc gamma-binding material. I. Immunochemical properties of the material produced by the T cell line KE37. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2295–2301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K. Requirements of cleavage of high mannose oligosaccharides in glycoproteins by peptide N-glycosidase F. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Molina A., Spiegelberg H. L. Binding of IgE myeloma proteins to human cultured lymphoblastoid cells. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1838–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Ishizaka K. Formation of IgE-binding factors by human T-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Regulatory effects of human IgE-binding factors on the IgE response of rat lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):955–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Formation of rat IgE-binding factors by rat-mouse T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Yodoi J., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Presence of an antigenic determinant common to rat IgE-potentiating factor, IgE-suppressive factor, and Fc epsilon receptors on T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Huff T. F., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factor. V. The role of glycosylation-enhancing factor and glycosylation-inhibiting factor in determining the nature of IgE-binding factors. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Moore K., Martens C., Ishizaka K. Relationship among IgE-binding factors with various molecular weights. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2727–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H. The IgE antibody system is coordinately regulated by FcR epsilon-positive lymphoid cells and IgE-selective soluble factors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):21–25. doi: 10.1159/000233747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens C. L., Huff T. F., Jardieu P., Trounstine M. L., Coffman R. L., Ishizaka K., Moore K. W. cDNA clones encoding IgE-binding factors from a rat-mouse T-cell hybridoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Cooper M. D. Human T lymphocyte subpopulations: studies of the mechanism by which T cells bearing Fc receptors for IgG suppress T-dependent B cell differentiation induced by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):984–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Delespesse G. IgE receptors on human lymphocytes. I. Identification of the molecules binding to monoclonal anti-Fc epsilon receptor antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jul;16(7):809–814. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. H., Conrad D. H. Fine specificity, structure, and proteolytic susceptibility of the human lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2654–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijkers G. T., Mosier D. E. Pneumococcal polysaccharides induce antibody formation by human B lymphocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Nutman T., Fonteyn C., Delespesse G. Presence of antigenic determinants common to Fc IgE receptors on human macrophages, T and B lymphocytes and IgE-binding factors. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):569–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Rector E., Rubio-Trujillo M., Wong K., Sehon A. H., Delespesse G. In vitro synthesis of IgE by human lymphocytes. III. IgE-potentiating activity of culture supernatants from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transformed B cells. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):207–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Rector E., Wong K., Rubio-Trujillo M., Sehon A. H., Delespesse G. In vitro synthesis of IgE by human lymphocytes. II. Enhancement of the spontaneous IgE synthesis by IgE-binding factors secreted by RPMI 8866 lymphoblastoid B cells. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):197–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Vanderbeeken Y., Rubio-Trujillo M., Duncan D., Delespesse G. Presence of IgE suppressor factors in human colostrum. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):1005–1008. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemura M., Kishimoto T. Regulation of human IgE response by T cells and their products. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):26–31. doi: 10.1159/000233748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Production of IgE-potentiating factor in man by T cell lines bearing Fc receptors for IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):871–878. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]