Abstract
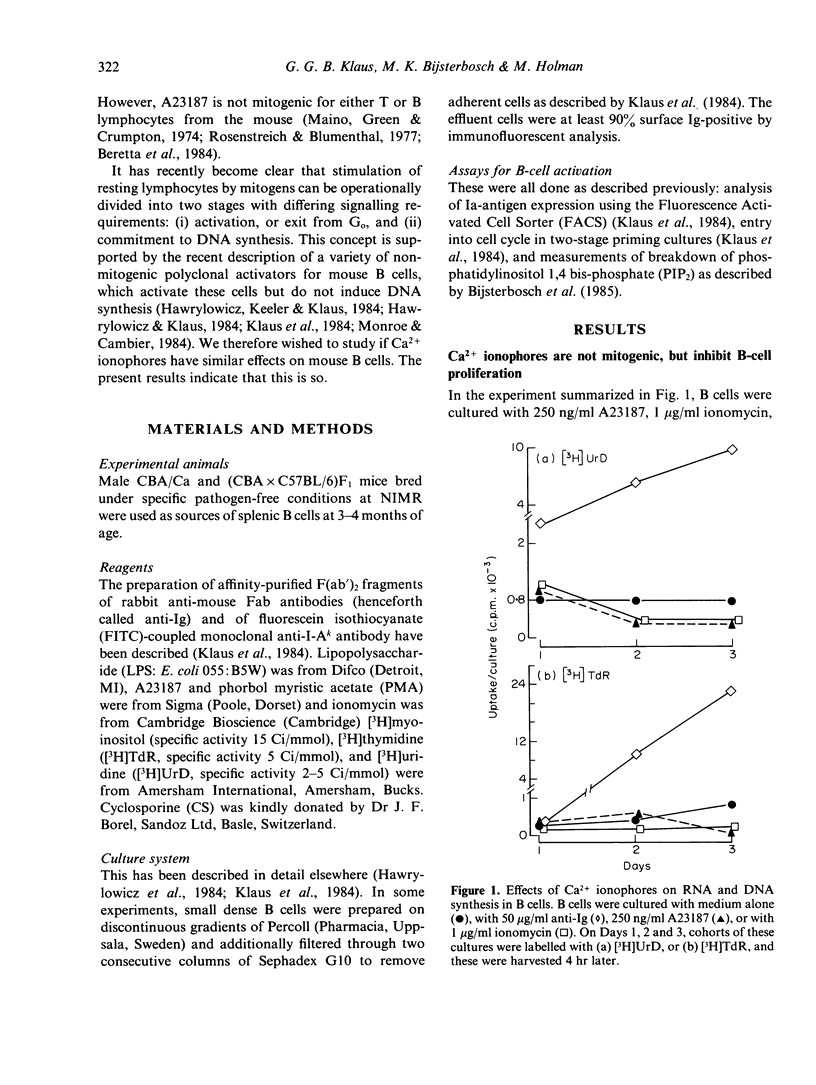
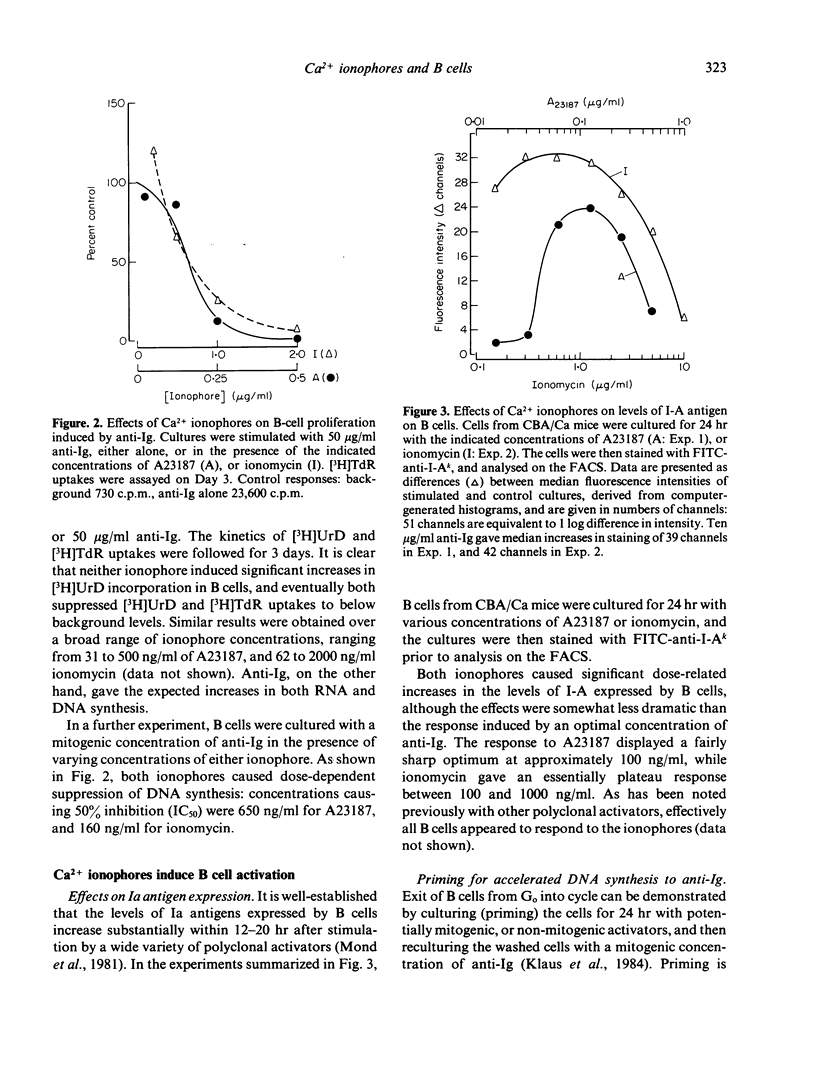
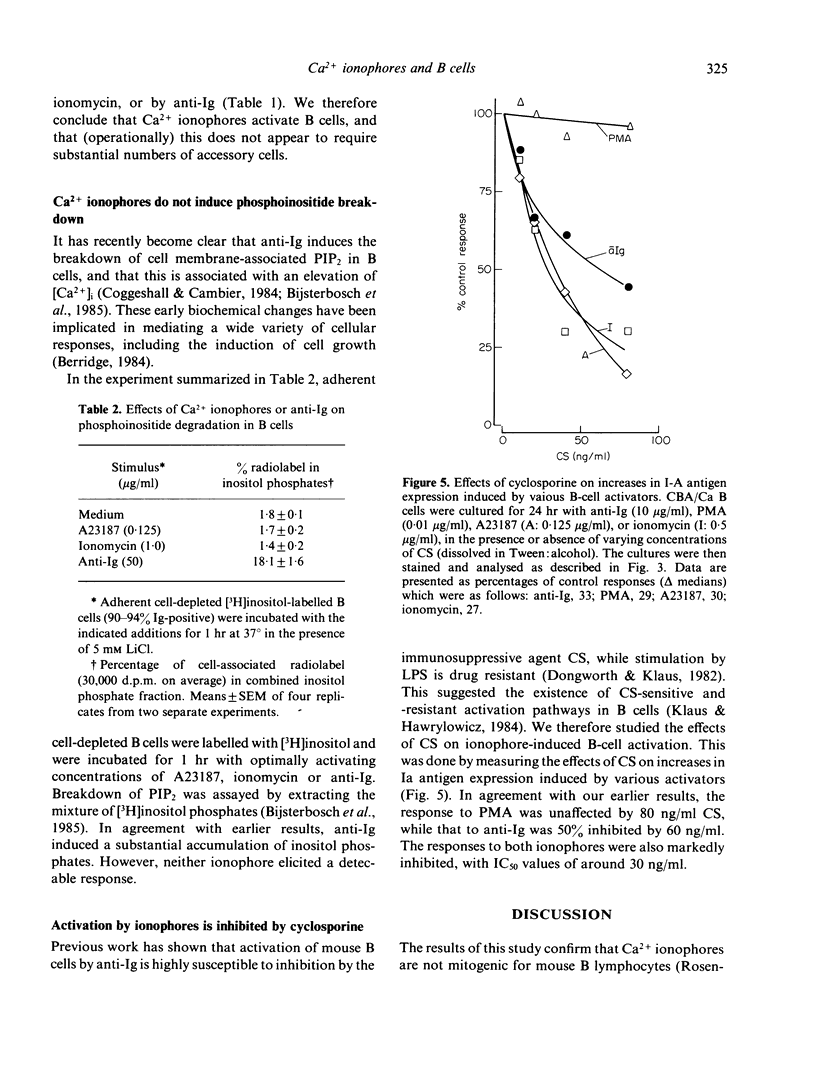
Calcium ionophores cause polyclonal proliferation of lymphocytes from man, rabbit and pig, but are not mitogenic for mouse T or B lymphocytes. We show here that two Ca2+ ionophores (A23187 and ionomycin) nonetheless activate a substantial proportion of mouse B lymphocytes at concentrations which effectively inhibit DNA synthesis induced by conventional mitogens, such as anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. Activation of B cells was detected by (i) increased expression of Ia antigen after 24 hr culture with ionophores, and (ii) the accelerated onset of DNA synthesis in B cells primed with ionophores for 24 hr, washed and then rechallenged with anti-Ig. Unlike anti-Ig, the ionophores did not induce either the breakdown of inositol phospholipids, or RNA synthesis in B cells. Finally, activation of B cells by ionophores is highly susceptible to inhibition by cyclosporine. These results therefore suggest that elevation of intracellular Ca2+ induced by these ionophores is sufficient to cause B cells to leave Go, but not to enter the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Clearly, additional signals are required for B cells to progress further into cycle and eventually become committed to DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford R. H. Metal cation requirements for phytohemagglutinin-induced transformation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):698–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beretta A., Gullberg M., Larsson E. L., Möller G. Ionophore A23-187 induces responses to TCGF in mouse lymphocytes. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 May-Jun;135C(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(84)80966-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. VIII. Membrane immunoglobulins transduce signals via activation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3382–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dongworth D. W., Klaus G. G. Effects of cyclosporin A on the immune system of the mouse. I. Evidence for a direct selective effect of cyclosporin A on B cells responding to anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1018–1022. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Khan N. R., Trew-Marshall B. J., Cupples C. G., Mély-Goubert B. Early biochemical events in lymphocyte activation. II. Selectivity of A23187 for T lymphocytes and the use of an apolar fluorescent probe (1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene) to monitor ionophore- and lectin-induced lymphocyte activation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Feb;58(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawrylowicz C. M., Keeler K. D., Klaus G. G. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. I. A comparison of the capacity of anti-Ig antibodies or phorbol myristic acetate to activate B cells from CBA/N or normal mice into G1. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):244–250. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawrylowicz C. M., Klaus G. G. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. IV. Concanavalin A stimulates B cells to leave G0, but not to proliferate. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):703–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Allison A. C., Williams S. C. Proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes induced by A23187, a streptomyces antibiotic. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:92–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90658-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. E., Benzie C. R., Borghetti A. F. Effect of cyclosporin A on lymphocyte activation by the calcium ionophore A23187. Immunology. 1983 Nov;50(3):441–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Hawrylowicz C. M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. II. Evidence for activation (G0 to G1) signals differing in sensitivity to cyclosporine. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):250–254. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Hawrylowicz C. M., Holman M., Keeler K. D. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. III. Intact (IGG) anti-immunoglobulin antibodies activate B cells but inhibit induction of DNA synthesis. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):693–701. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Segel G. B., Lichtman M. A. The role of calcium in lymphocyte proliferation. (An interpretive review). Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):413–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckasen J. R., White J. G., Kersey J. H. Mitogenic properties of a calcium ionophore, A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maino V. C., Green N. M., Crumpton M. J. The role of calcium ions in initiating transformation of lymphocytes. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):324–327. doi: 10.1038/251324b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe S. Cyclosporine does not prevent cytoplasmic calcium changes associated with lymphocyte activation. Transplantation. 1984 Aug;38(2):161–164. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198408000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Seghal E., Kung J., Finkelman F. D. Increased expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) on B cells after cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. III. B cell plasma membrane depolarization and hyper-Ia antigen expression induced by receptor immunoglobulin cross-linking are coupled. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1589–1599. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Niedel J. E., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. IV. Induction of cell membrane depolarization and hyper-I-A expression by phorbol diesters suggests a role for protein kinase C in murine B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1472–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resch K., Bouillon D., Gemsa D. The activation of lymphocytes by the ionophore A 23 187. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1514–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Blumenthal R. Ionophorous activity and murine B lymphocyte mitogens. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P. Mitogens increase phosphorylation of phosphoinositides in thymocytes. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):462–465. doi: 10.1038/312462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney R. B., Sutherland R. M. Requirement for calcium ions in lymphocyte transformation stimulated by phytohemagglutinin. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Dec;80(3):329–337. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040800303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


