Abstract
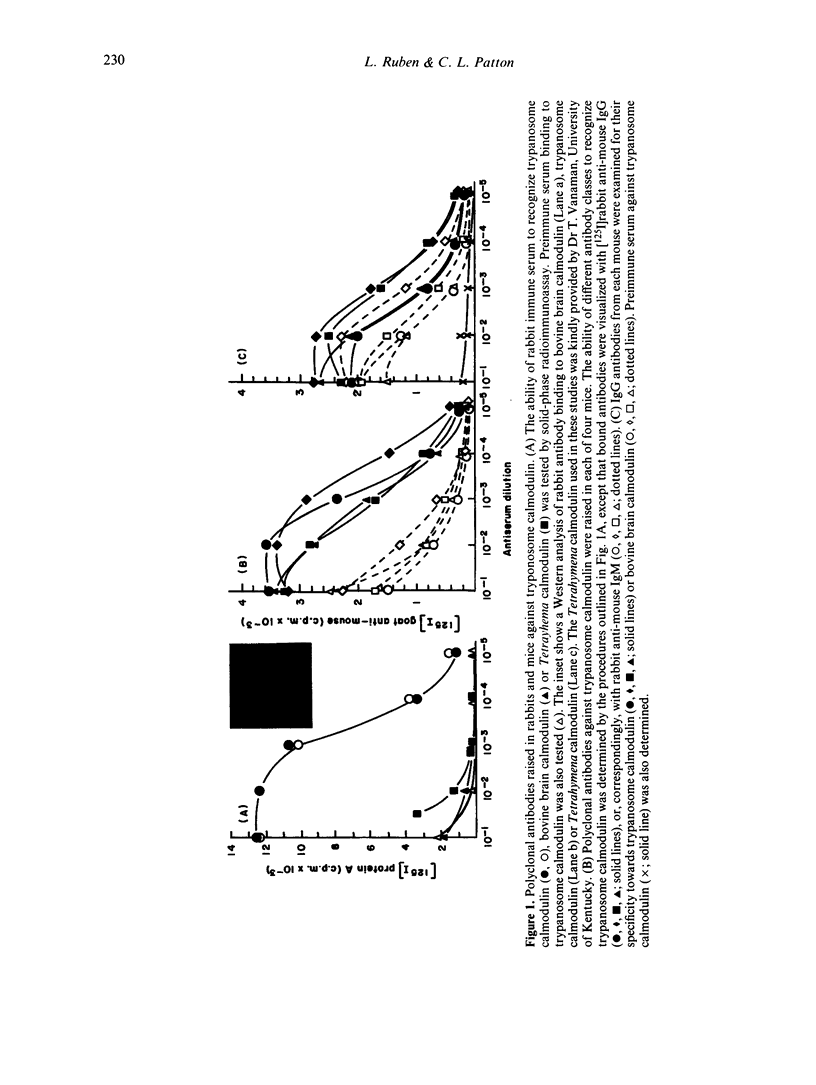
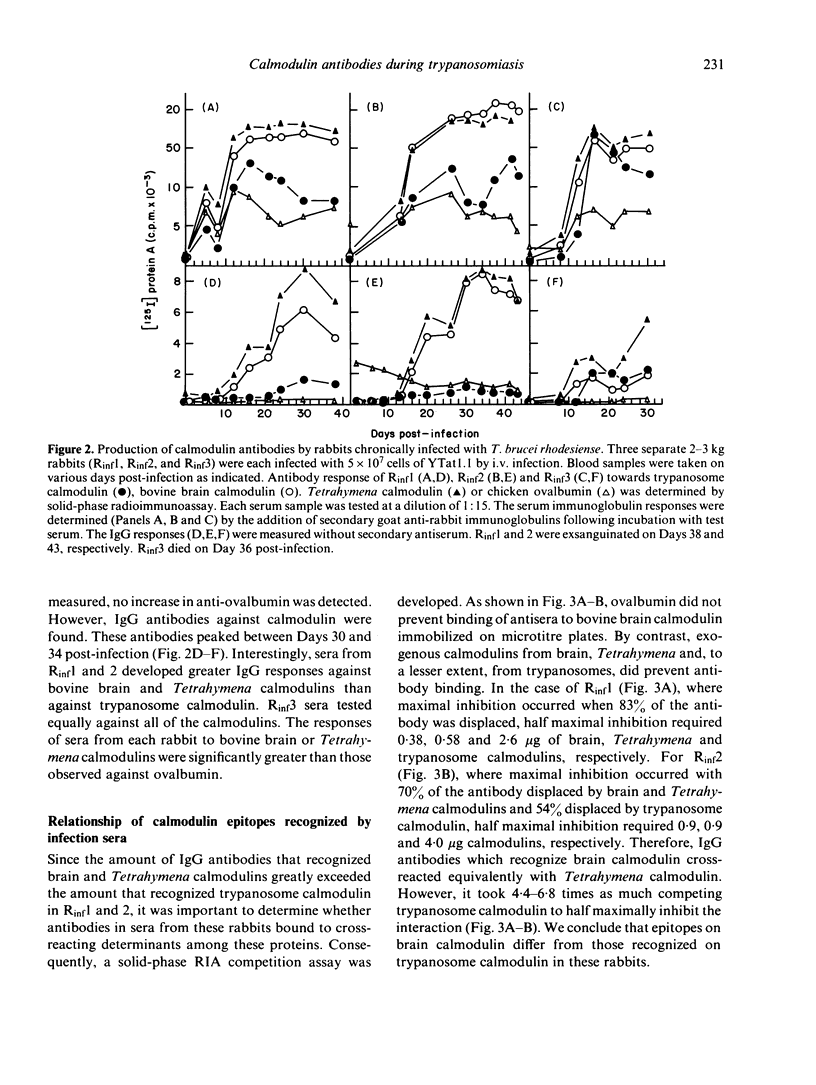
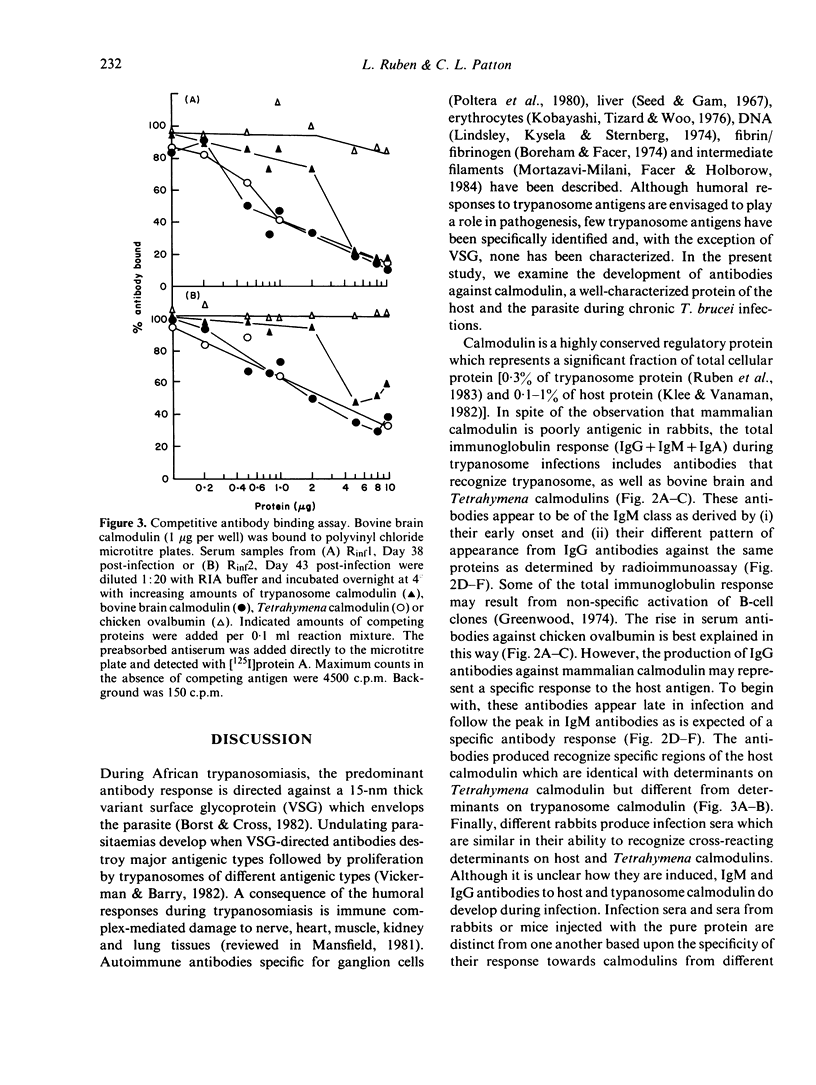
Calmodulin is an intracellular Ca2+ receptor protein which regulates a wide variety of enzymatic processes in eukaryotic cells examined in detail. Native calmodulin is not antigenic in rabbits because of its small size, high degree of amino acid sequence conservation and hydrophobicity. African trypanosomes contain a novel calmodulin which is structurally distinct from bovine brain and Tetrahymena calmodulins. In the present study, we examine the antibody response towards these calmodulins during chronic Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense infections. Injection of purified trypanosome calmodulin into rabbits stimulates the production of specific IgG antibodies which recognize trypanosome, but not bovine brain or Tetrahymena calmodulins. By contrast, during chronic T. brucei infections in rabbits, antibodies (IgG + IgM + IgA) that recognize trypanosome, Tetrahymena and mammalian calmodulins arise. When only IgG antibodies are evaluated from infection sera, the major response is against mammalian and Tetrahymena calmodulins. Significantly fewer IgG antibodies are measured in the infection sera which recognize trypanosome calmodulin, while the non-specific control protein, chicken ovalbumin, is not recognized. Peak IgG antibody responses against calmodulin occur between Days 30-34 post-infection. Competition assays indicate that Tetrahymena and mammalian calmodulins are recognized at identical epitopes which are distinct from epitopes on trypanosome calmodulin. We conclude that, in the context of chronic T. brucei infections in rabbits, antibodies arise which are able to recognize mammalian host calmodulin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Rieber M. Antibodies to laminin in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.402-406.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boreham P. F., Facer C. A. Autoimmunity in trypanosome infections. II. Anti-fibrin-fibrinogen (anti-F) autoantibody in Trypanosoma (Trypanozoon) brucei infections of the rabbit. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Dec;4(6):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Cross G. A. Molecular basis for trypanosome antigenic variation. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A., Jr, Frazier W. A. Dictyostelium calmodulin: affinity isolation and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90490-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi A., Tizard I. R., Woo P. T. Studies on the anemia in experimental African trypanosomiasis. II. The pathogenesis of the anemia in calves infected with Trypanosoma congolense. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 May;25(3):401–406. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley H. B., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Nucleic acid antibodies in African trypanosomiasis: studies in Rhesus monkeys and man. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1921–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortazavi-Milani S. M., Facer C. A., Holborow E. J. Induction of anti-intermediate filament antibody in rabbits experimentally infected with Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):423–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal muscle calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 27;167(2):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltera A. A., Hochmann A., Rudin W., Lambert P. H. Trypanosoma brucei brucei: a model for cerebral trypanosomiasis in mice--an immunological, histological and electronmicroscopic study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jun;40(3):496–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben L., Egwuagu C., Patton C. L. African trypanosomes contain calmodulin which is distinct from host calmodulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 29;758(2):104–113. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed J. R., Gam A. A. The presence of antibody to a normal rabbit liver antigen in rabbits infected with Trypanosoma gambiense. J Parasitol. 1967 Oct;53(5):946–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Ohnishi K., Hirabayashi T., Watanabe Y. Tetrahymena calmodulin. Characterization of an anti-tetrahymena calmodulin and the immunofluorescent localization in Tetrahymena. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Watterson D. M. Reproducible production of antiserum against vertebrate calmodulin and determination of the immunoreactive site. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4205–4210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin. Production of an antibody in rabbit and development of a radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6564–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



