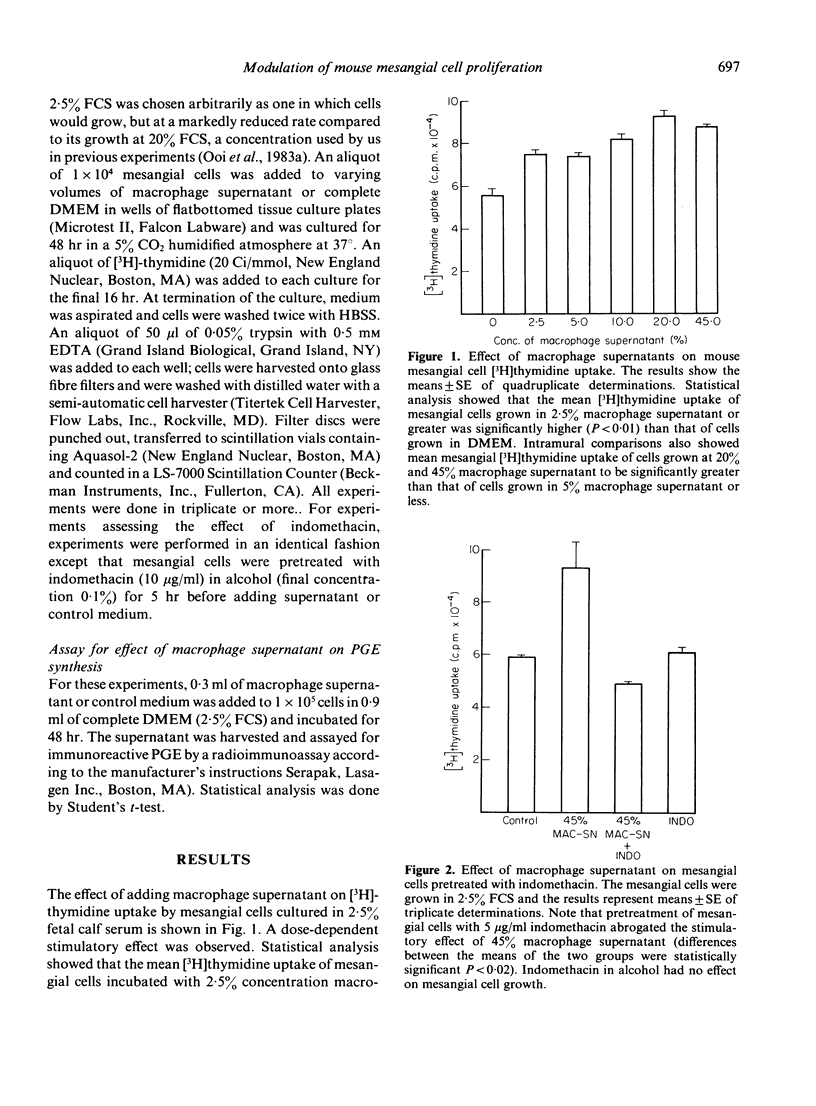
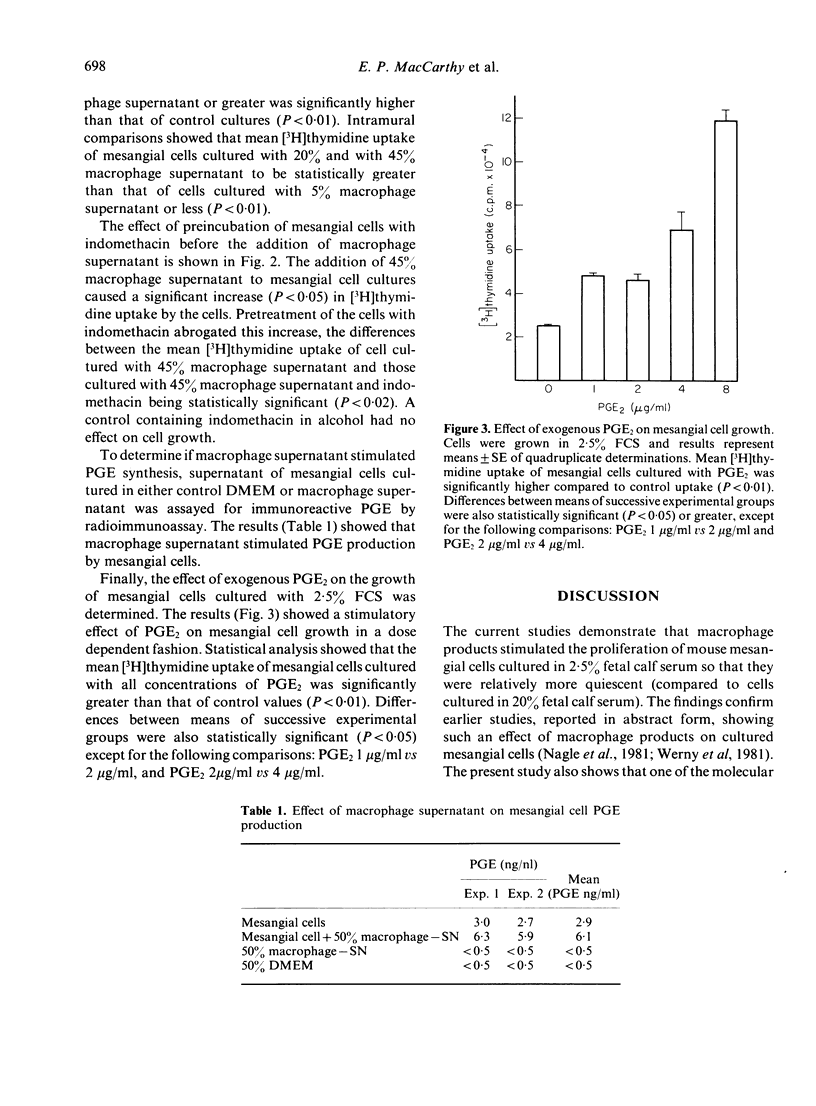
Abstract
Mesangial hypercellularity is usually found in many models of nephritis characterized by monocyte/macrophage infiltration of the glomerulus. In order to examine the mechanism mediating these events, an in vitro model was used to study the effects of macrophage products on mouse mesangial cells, cultured under conditions which would render them relatively quiescent. Under these conditions, macrophage supernatants stimulated the proliferation of the mesangial cells. The stimulatory effect could be shown to be due in part to enhancement of endogenous mesangial cell PGE production. This was demonstrated by experiments which showed that macrophage supernatants stimulated mesangial cell PGE production, that the stimulatory effect of macrophage products was abrogated by pretreatment of mesangial cells with indomethacin, and finally that exogenous PGE2 stimulated mesangial cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcelli U., Rademacher R., Ooi Y. M., Ooi B. S. Modification of glomerular immune complex deposition in mice by activation of the reticuloendothelial system. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):20–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI110013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 65th annual meeting, Atlanta, Georgia, April 12-17, 1981. Abstracts. Fed Proc. 1981 Mar 1;40(3 Pt 2):805–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B. Abrogation of macrophage-dependent injury in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rabbit. Use of an antimacrophage serum. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):686–698. doi: 10.1172/JCI110304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Shearer T. P., Plattner S. B., Weisenburger D. The role of monocytes in serum sickness nephritis. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):413–425. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn J. H., Halushka P. V., LeRoy E. C. Mononuclear cell modulation of connective tissue function: suppression of fibroblast growth by stimulation of endogenous prostaglandin production. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):543–554. doi: 10.1172/JCI109698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. A thymocyte-activating factor derived from glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1796–1801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. Stimulation of rat mesangial cell proliferation by macrophage interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. S., MacCarthy E. P., Hsu A., Ooi Y. M. Human mononuclear cell modulation of endothelial cell proliferation. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Sep;102(3):428–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi Y. M., Weiss M. A., Hsu A., Ooi B. S. Mechanisms of suppression of mouse mesangial cell proliferation by macrophage supernatants. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1790–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Mizel S. B., Cohen D., Green I. Interleukin 1, a potential regulator of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Pardo V., Unanue E. R. A mononuclear cell component in experimental immunological glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):369–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


