Abstract
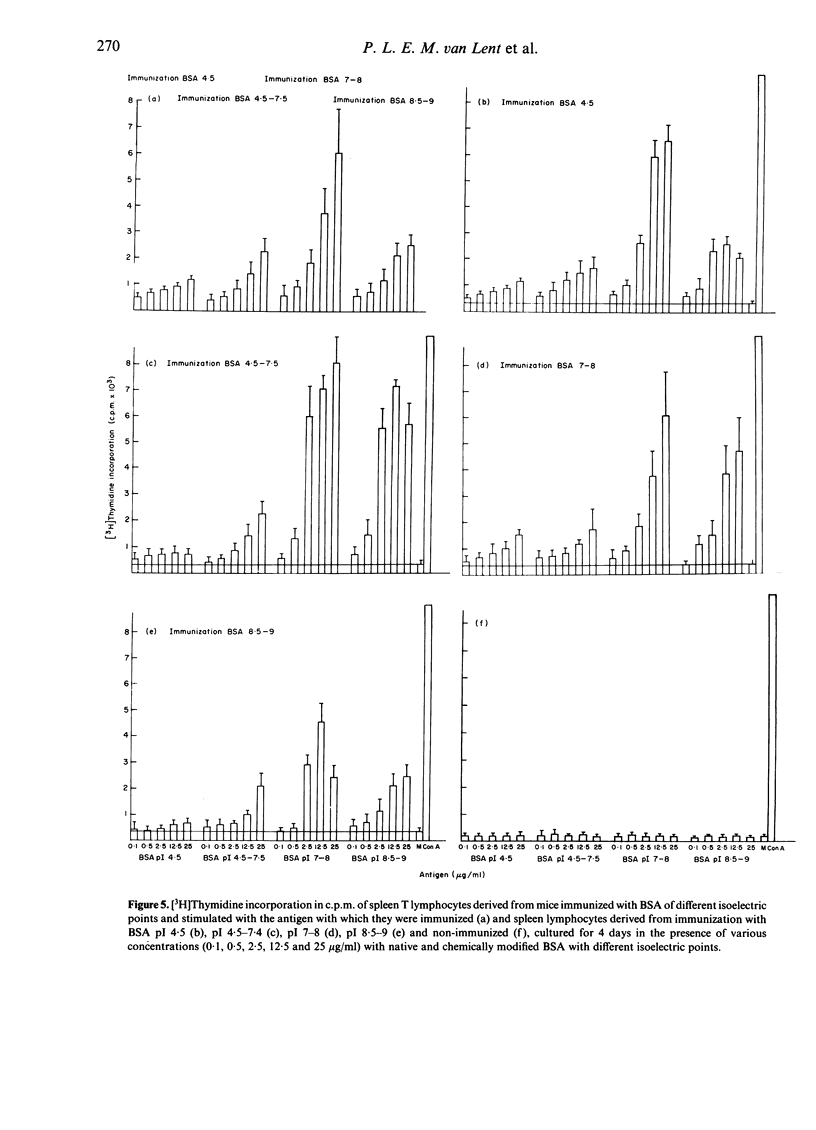
In order to define the antigenic properties necessary for sustained allergic arthritis, we prepared a range of differently charged bovine serum albumin (BSA) species with increasing isoelectric points (4.5, 4.5-7.4, 7-8, 8.5-9 and greater than 9). The highly cationic BSA greater than 9 appeared to be in a polymeric form. We investigated three properties of these proteins: (i) antigen retention, (ii) T-cell reactivity, and (iii) arthritis induction. Injection of the respective radiolabelled antigens in the knee-joints of immunized mice showed that antigen retention increased with cationicity of the proteins, with the best retention found for BSA with pI greater than 9. However, sustained joint inflammation was only found with BSA8.5-9, and not with a level BSA of lower or even higher pI. T-cell reactivity in vivo as measured by delayed-type hypersensitivity (skin testing) was similar for the tested antigens, with the exception of polymeric BSA (greater than 9). The latter appeared to be a poor antigen. In vitro, T-cell reactivity ([3H]-thymidine incorporation) against the cationized BSA species was slightly higher as compared to native BSA. The combination of excellent antigen retention and adequate T-cell reactivity appears to be optimal for the induction of chronic arthritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Unanue E. R. Differential requirements for antigen processing by macrophages for lysozyme-specific T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1077–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. I. The role of antigen on the local immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Patrucco A. Preferential development by mice of delayed hypersensitivity to purified basic proteins. J Allergy. 1968 Sep;42(3):140–156. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey M. O., Hunter R. L. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to chemically modified antigens in guinea pigs. I. Characterization of the immune response to lipid-conjugated protein antigens. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon D., Goldstein L., Marikovsky Y., Skutelsky E. Use of cationized ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. The chronicity of inflammation and its significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):105–121. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Flare-up of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after challenge with intravenous antigen: studies on the characteristics of and mechanisms involved in the reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muckerheide A., Apple R. J., Pesce A. J., Michael J. G. Cationization of protein antigens. I. Alteration of immunogenic properties. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):833–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renau-Piqueras J., Miragall F., Cervera J. Endocytosis of cationized ferritin in human peripheral blood by resting T-lymphocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;240(3):743–746. doi: 10.1007/BF00216363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenseth K., Hedin U., Thyberg J. Endocytosis, intracellular transport, and turnover of anionic and cationic proteins in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;31(1):15–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Vogt A. Mitogenic activity of extracellular cationic products produced by group A streptococci; analysis of the lymphocyte response. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):132–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Batsford S., Rodríguez-Iturbe B., García R. Cationic antigens in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Dec;20(6):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Joosten L. A., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A. Electrical charge and joint inflammation. Suppression of cationic aBSA-induced arthritis with a competitive polycation. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):15–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van Lent P. L., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A. Electrical charge of hyaline articular cartilage: its role in the retention of anionic and cationic proteins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 May;39(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Electrical charge of the antigen determines its localization in the mouse knee joint. Deep penetration of cationic BSA in hyaline articular cartilage. Am J Pathol. 1985 Nov;121(2):224–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]