Abstract
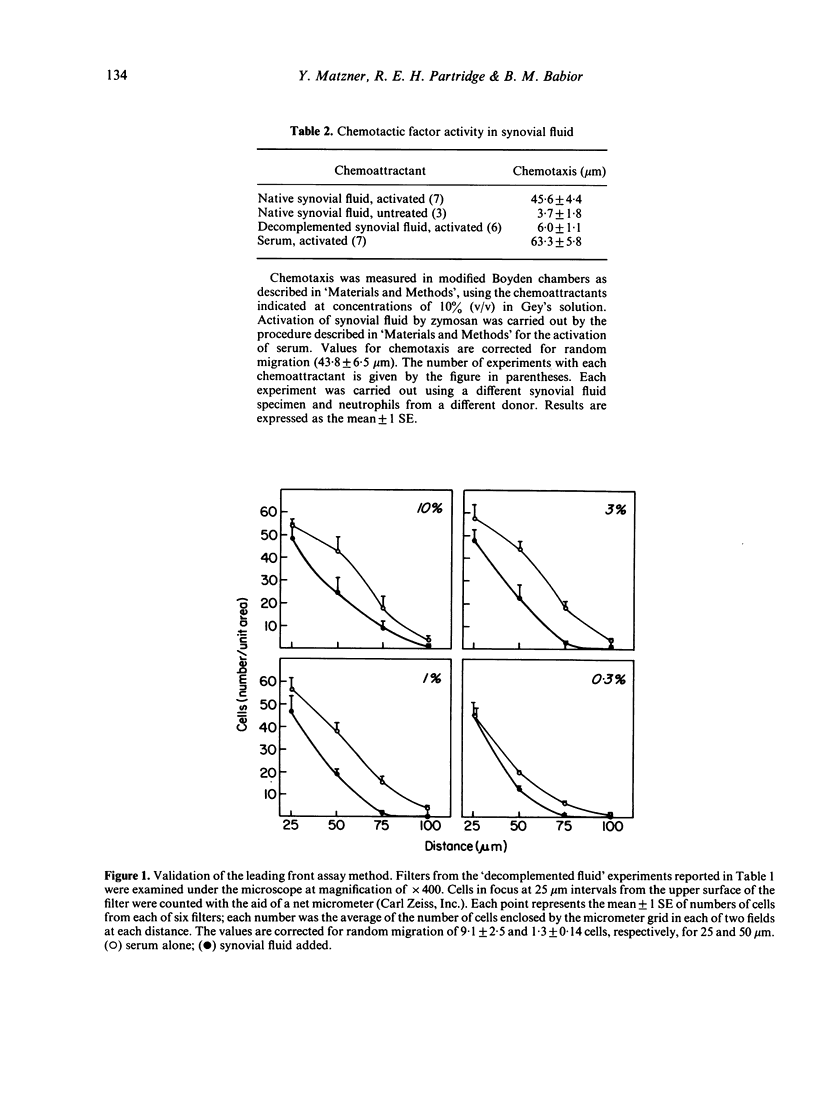
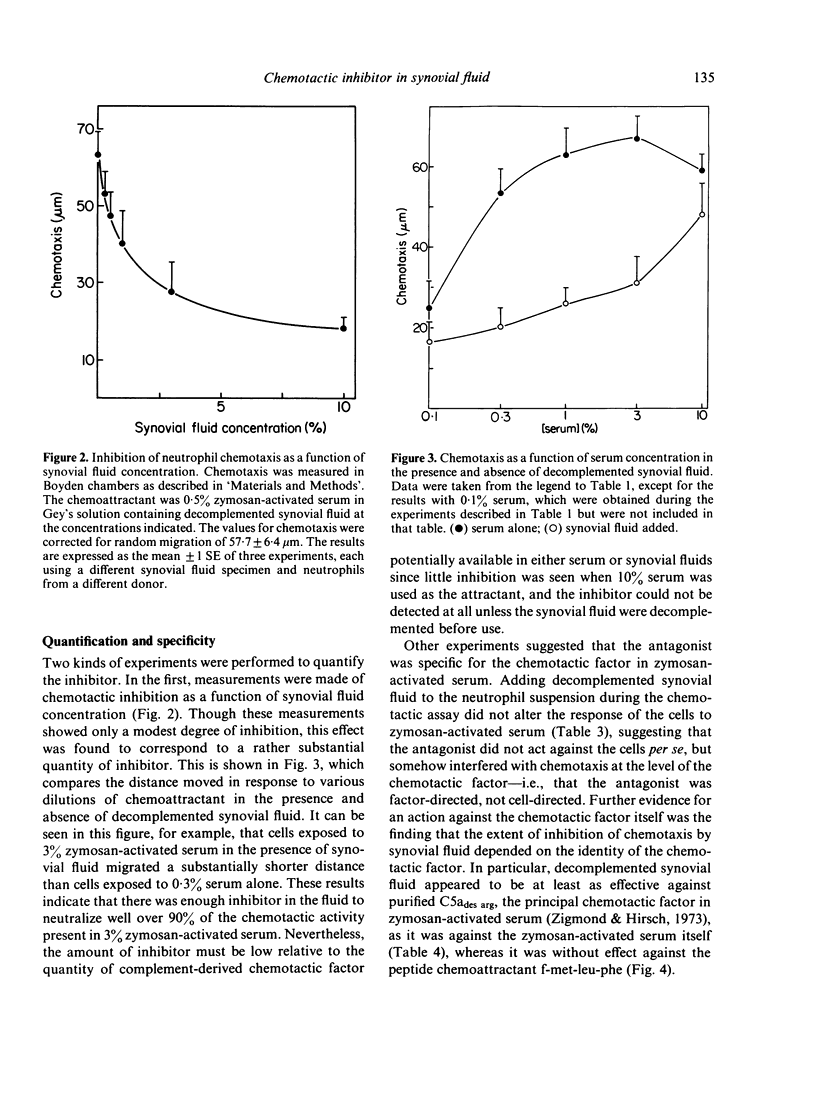
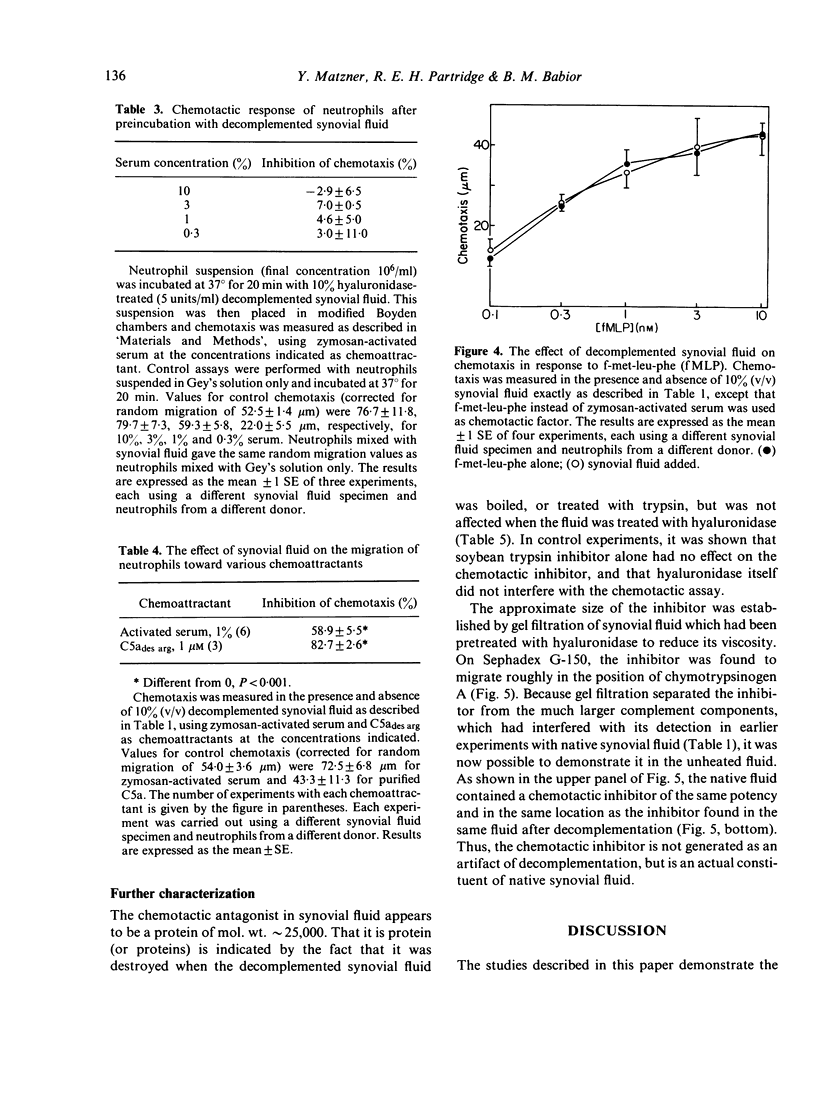
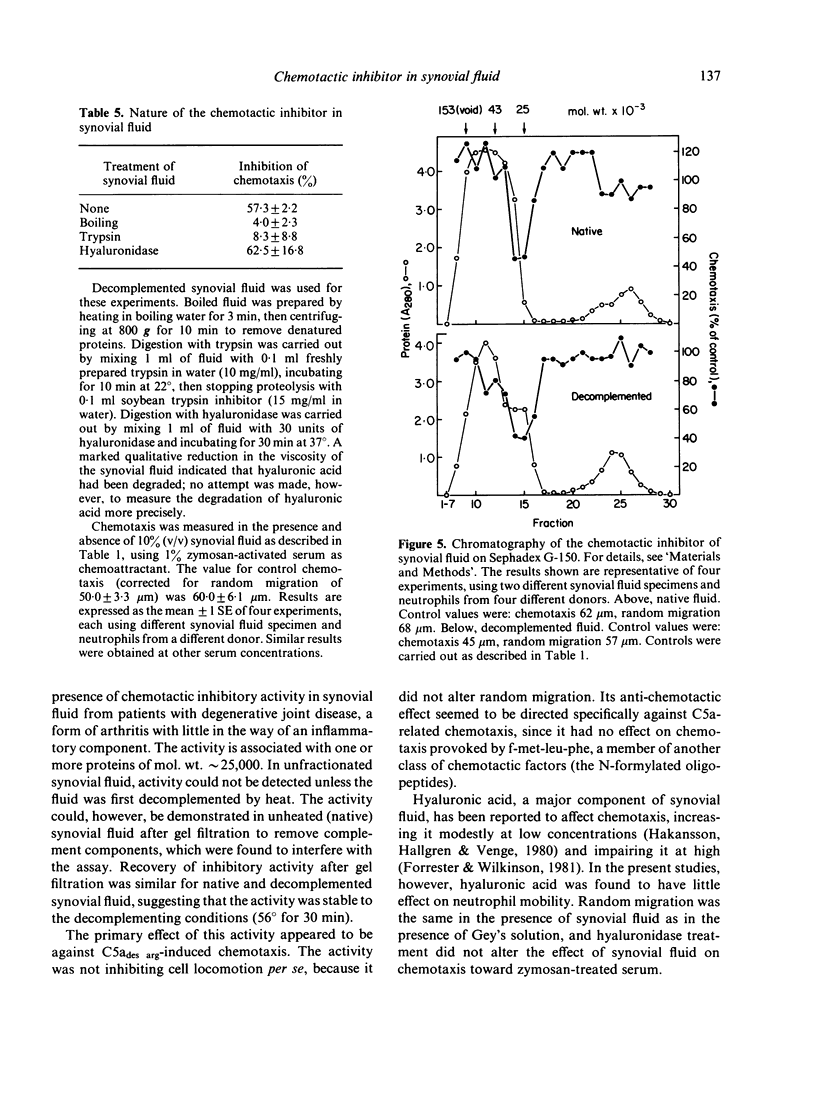
Synovial fluid was found to contain an inhibitor of neutrophil chemotaxis. The activity of this inhibitor was masked in native synovial fluid, but could be detected in fluid in which complement had been deactivated by mild heating. The inhibitor was most effective against the chemotactic activity of zymosan-activated serum (C5ades arg). It had little effect when N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine served as chemoattractant. Inhibition was not the result of a direct effect on the neutrophils, since incubation of cells with synovial fluid did not alter their chemotactic response. The inhibitory activity was destroyed by boiling the synovial fluid or treating it with trypsin, suggesting that it is a protein (or proteins); it was not affected by hyaluronidase treatment. Gel filtration revealed that the inhibitor was present in native as well as decomplemented synovial fluid, and that its molecular weight was in the vicinity of 25,000. It is proposed that this inhibitory activity plays a role in the regulation of the inflammatory response in joints.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brozna J. P., Ward P. A. Antileukotactic properties of tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):616–623. doi: 10.1172/JCI108131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C. A., Curnutte J. T., Rosin R. E., André-Schwartz J., Gallin J. I., Klempner M., Snyderman R., Southwick F. S., Stossel T. P., Babior B. M. An inherited abnormality of neutrophil adhesion. Its genetic transmission and its association with a missing protein. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1163–1168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester J. V., Wilkinson P. C. Inhibition of leukocyte locomotion by hyaluronic acid. J Cell Sci. 1981 Apr;48:315–331. doi: 10.1242/jcs.48.1.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Weissmann G. Generation of C5-derived lysosomal enzyme-releasing activity (C5a) by lysates of leukocyte lysosomes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1583–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson L., Hällgren R., Venge P. Regulation of granulocyte function by hyaluronic acid. In vitro and in vivo effects on phagocytosis, locomotion, and metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):298–305. doi: 10.1172/JCI109857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Weksler B. B., Goldstein I. M. Generation of a chemotactic lipid from a arachidonic acid by exposure to a superoxide-generating system. Inflammation. 1980 Sep;4(3):313–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00915032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrone W. F., English D. K., Wong K., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: superoxide-dependent activation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Partial characterization of leukocyte inhibitory factor by concanavalin A-stimulated human lymphocytes (LIF Con A). J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1161–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Products of activated lymphocytes: leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) distinct from migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1461–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G., Ward P. A. Two distinct chemotactic factor inactivators in human serum. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):843–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Strickland R. G., Williams R. C., Jr Inhibitors of leukocyte chemotaxis in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Hill J. H. C5 chemotactic fragments produced by an enzyme in lysosomal granules of neutrophils. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Ozols J. Characterization of the protease activity in the chemotactic factor inactivator. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):123–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI108440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M. Release of inflammatory mediators from stimulated neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):27–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Gallin J. I. A functional differentiation of human neutrophil granules: generation of C5a by a specific (secondary) granule product and inactivation of C5a by azurophil (primary) granule products. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1068–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


