Abstract
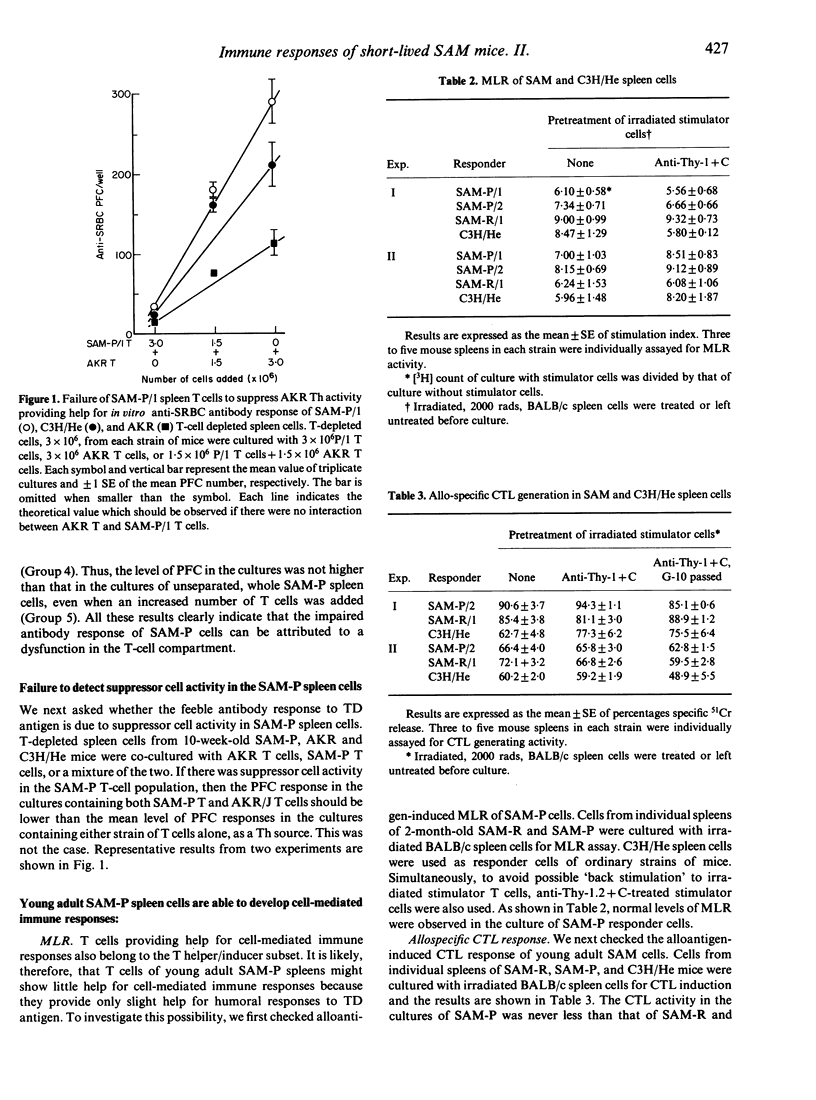
New short-lived strains of mice (SAM-P), which have been developed by Takeda et al. (1981), shows a defective antibody response to T dependent (TD) antigen in vitro, as demonstrated in the accompanying paper (see page 419). In the present study, we investigated the cellular site of the defect, using a cell culture system. In this paper, it is demonstrated that T-helper (Th) cell activity for the antibody response to TD antigen is impaired, while other cellular immune responses, e.g. mixed leucocyte reaction, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response, and delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, are normal. These results suggest that the defect in T-helper subset is limited in helper function for the antibody response, and that the helper function for the cell-mediated immune responses is intact. These two functions of the T-helper subset are apparently regulated in a different manner. The SAM-P strains of mice may thus serve as an appropriate model for studying functional heterogeneity in T-helper/inducer cell subsets.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur R. P., Mason D. T cells that help B cell responses to soluble antigen are distinguishable from those producing interleukin 2 on mitogenic or allogeneic stimulation. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):774–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa T., Hosono M., Higuchi K., Aoike A., Kawai K., Takeda T. Immune responses in newly developed short-lived SAM mice. I. Age-associated early decline in immune activities of cultured spleen cells. Immunology. 1987 Nov;62(3):419–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings J. J., Rittenberg M. B. Evidence for separate subpopulations of B cells responding to T-independent and T-dependent immunogens. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1749–1752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura I., Cudkowicz G. Requirement of parental T lymphocytes for the in vitro induction of F1 hybrid anti-parent cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1979 May;9(5):371–379. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Purves E. C. Separate thymus dependent and thymus independent antibody forming cell precursors. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):149–151. doi: 10.1038/newbio231149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki O., Shimizu M., Saeki Y., Kishimoto S., Kishimoto T. Dissociation in the production of B cell-stimulating factors (BCGF and BCDF) and interleukin 2 by T cells from a common variable immunodeficient patient. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1920–1924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Hosokawa M., Takeshita S., Irino M., Higuchi K., Matsushita T., Tomita Y., Yasuhira K., Hamamoto H., Shimizu K. A new murine model of accelerated senescence. Mech Ageing Dev. 1981 Oct;17(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(81)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


