Abstract
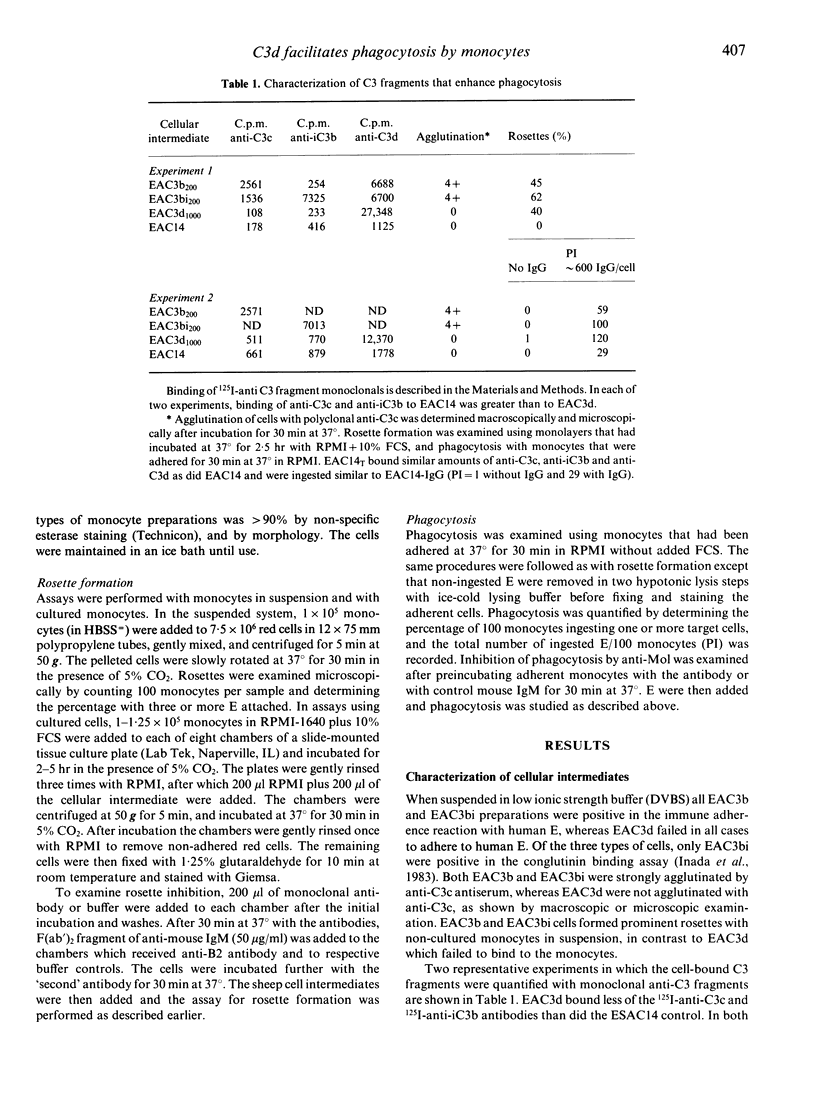
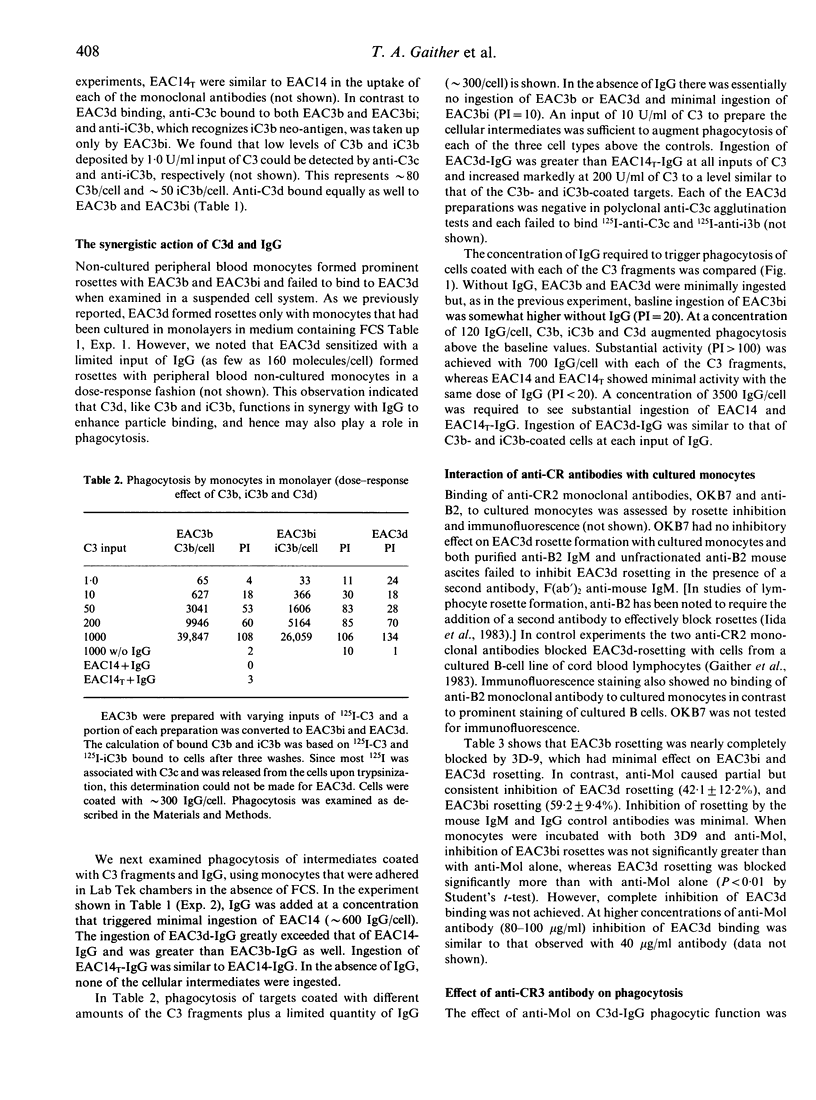
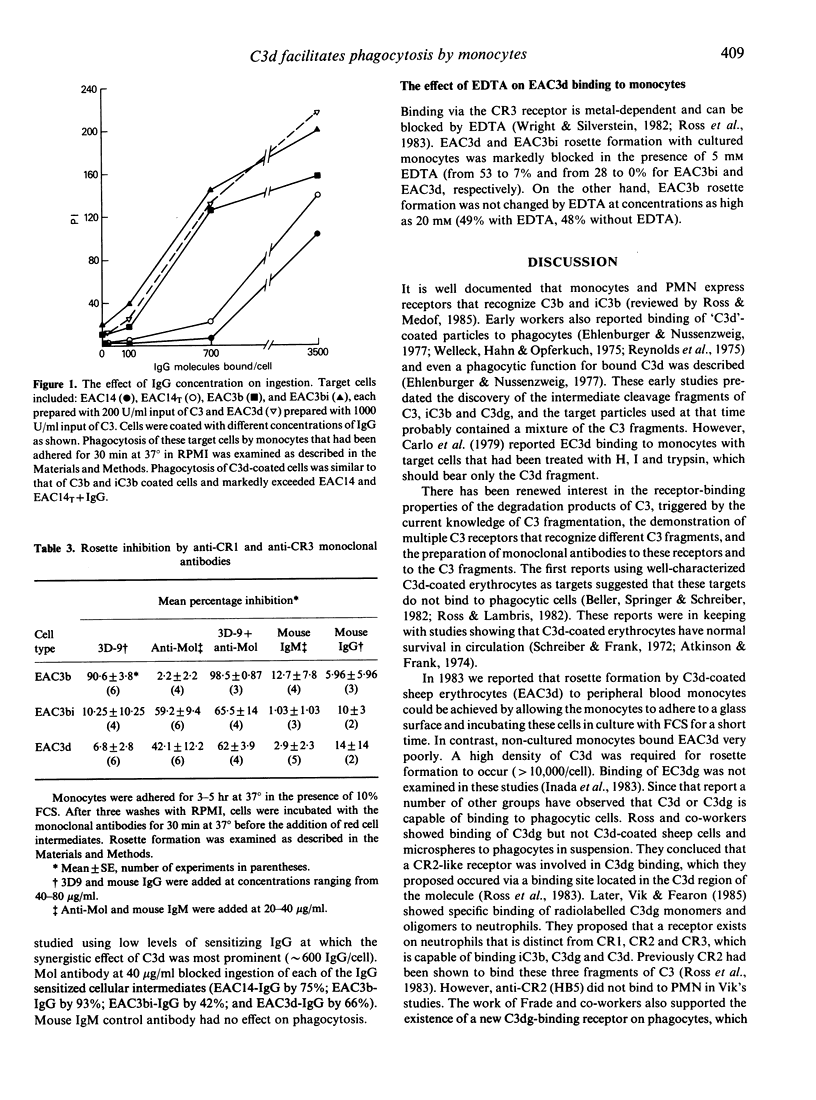
Two receptors for fragments of C3 are described for human monocytes: CR1 and CR3, which bind C3b and iC3b, respectively. Recently a leucocyte receptor that binds C3dg has also been described, designated CR4. We previously reported that IgM-sensitized sheep erythrocytes that are heavily coated with C3d (EAC3d) can bind to human monocytes that have been cultured in fetal calf serum (FCS). Here we determine whether such binding of C3d-coated targets can lead to phagocytosis, and identify the specific monocyte receptor involved in C3d binding. We confirm that EAC3d bearing greater than 10,000 C3d/cell bind to FCS-cultured monocytes. Furthermore, using non-cultured monocytes, we demonstrate that C3d enhances rosette formation of IgG-coated E and, like C3b and iC3b, C3d augments IgG Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Less than 100 C3d/cell are capable of enhancing phagocytosis, whereas 10,000 or more C3d/cell are required for rosette formation with cultured cells. These results indicate that the C3d-binding receptor is present on peripheral blood monocytes but has poor affinity for target particles coated only with C3d. Anti-CR2 monoclonal antibodies, which recognize the C3d receptor of lymphocytes, do not block EAC3d rosette formation with monocytes. In contrast anti-Mol, a monoclonal antibody against CR3, inhibits EAC3d rosettes by approximately 42%. Anti-CR1 increases this effect, but complete inhibition is not achieved. Ethylenediamine tetraacetate also markedly reduces EAC3d rosetting, reducing the numbers to less than 5%. Thus, the C3d-binding receptor on monocytes, unlike CR4, is metal dependent. Together these data indicate that CR3 is predominantly responsible for C3d binding to monocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A., Todd R. F., 3rd, Dana N., Melamed J., Schlossman S. F., Colten H. R. Inhibition of phagocytosis of complement C3- or immunoglobulin G-coated particles and of C3bi binding by monoclonal antibodies to a monocyte-granulocyte membrane glycoprotein (Mol). J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):171–179. doi: 10.1172/JCI110955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Frank M. M. Studies on the in vivo effects of antibody. Interaction of IgM antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):339–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI107769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Springer T. A., Schreiber R. D. Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Gaither I. A., Frank M. M. Complement receptors. Clin Immunol Rev. 1981;1(4):471–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Hosea S. W., Frank M. M. The use of conglutinin in a quantitative assay for the presence of cell-bound C3bi and evidence that a single molecule of C3bi is capable of binding conglutinin. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):860–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlo J. R., Ruddy S., Studer E. J., Conrad D. H. Complement receptor binding of C3b-coated cells treated with C3b inactivator, beta 1H globulin and trypsin. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlenberger A. G., Nussenzweig V. The role of membrane receptors for C3b and C3d in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):357–371. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Myones B. L., Barel M., Krikorian L., Charriaut C., Ross G. D. gp140, a C3b-binding membrane component of lymphocytes, is the B cell C3dg/C3d receptor (CR2) and is distinct from the neutrophil C3dg receptor (CR4). Eur J Immunol. 1985 Dec;15(12):1192–1197. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Gaither T. The effect of temperature on the reactivity of guinea-pig complement with gamma G and gamma M haemolytic antibodies. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):967–974. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. Studies of the molecular mechanisms of C3b inactivation and a simplified assay of beta 1H and the C3b inactivator (C3bINA). J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1195–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaither T. A., Magrath I. T., Berger M., Hammer C. H., Novikovs L., Santaella M., Frank M. M. Complement receptor expression by neoplastic and normal human cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):899–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Waldmann T. A. Separation of human blood monocytes and lymphocytes on a continuous Percoll gradient. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Nadler L., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the membrane receptor for the complement fragment C3d by means of a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1021–1033. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada S., Brown E. J., Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Takahashi T., Frank M. M. C3d receptors are expressed on human monocytes after in vitro cultivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2351–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J., Seligmann B. E., Metcalf J. A., Frank M. M., Gallin J. I. Evidence for distinct intracellular pools of receptors for C3b and C3bi in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2580–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. E., Wright S. D., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G. OKB7, a monoclonal antibody that reacts at or near the C3d binding site of human CR2. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jul;93(2):549–555. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Atkinson J. P., Newball H. H., Frank M. M. Receptors for immunoglobulin and complement on human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1813–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Lambris J. D., Cain J. A., Newman S. L. Generation of three different fragments of bound C3 with purified factor I or serum. I. Requirements for factor H vs CR1 cofactor activity. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2051–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Lambris J. D. Identification of a C3bi-specific membrane complement receptor that is expressed on lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):96–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Medof M. E. Membrane complement receptors specific for bound fragments of C3. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:217–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Newman S. L., Lambris J. D., Devery-Pocius J. E., Cain J. A., Lachmann P. J. Generation of three different fragments of bound C3 with purified factor I or serum. II. Location of binding sites in the C3 fragments for factors B and H, complement receptors, and bovine conglutinin. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):334–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Frank M. M. Role of antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes. II. Molecular nature of IgG and IgM complement-fixing sites and effects of their interaction with serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):583–589. doi: 10.1172/JCI106847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D. The chemistry and biology of complement receptors. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):221–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01893021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Arnaout M. A., Rosin R. E., Crowley C. A., Peters W. A., Babior B. M. Subcellular localization of the large subunit of Mo1 (Mo1 alpha; formerly gp 110), a surface glycoprotein associated with neutrophil adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1280–1290. doi: 10.1172/JCI111538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik D. P., Fearon D. T. Neutrophils express a receptor for iC3b, C3dg, and C3d that is distinct from CR1, CR2, and CR3. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2571–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Fearon D. T. Identification of a 145,000 Mr membrane protein as the C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):881–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellek B., Hahn H. H., Opferkuch W. Evidence for macrophage C3d-receptor active in phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1643–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate C3b and C3b' receptor-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1149–1164. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


