Abstract
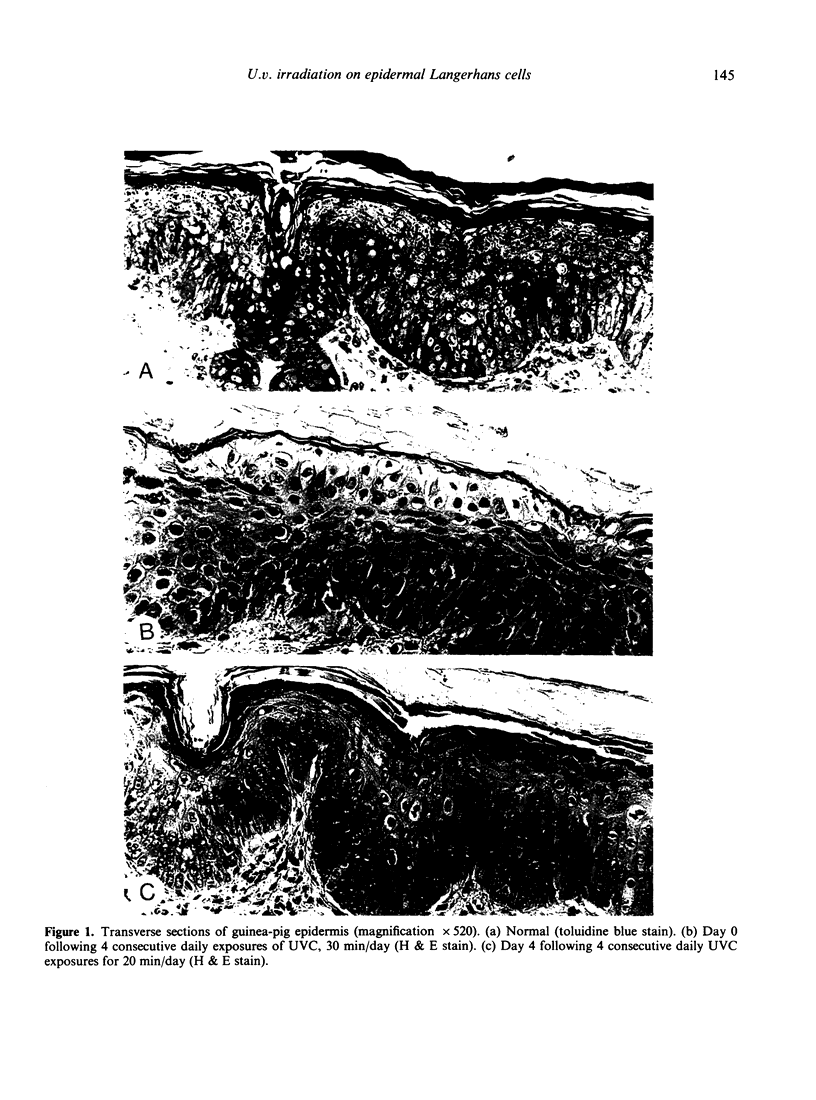
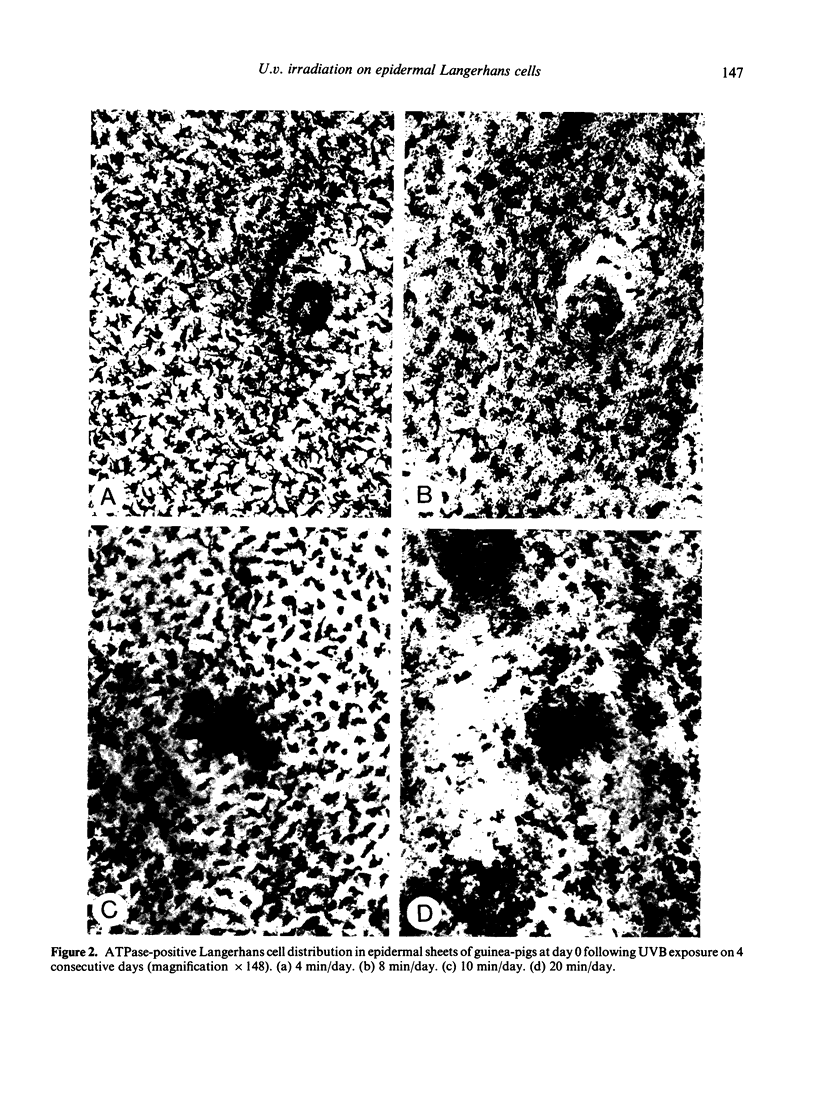
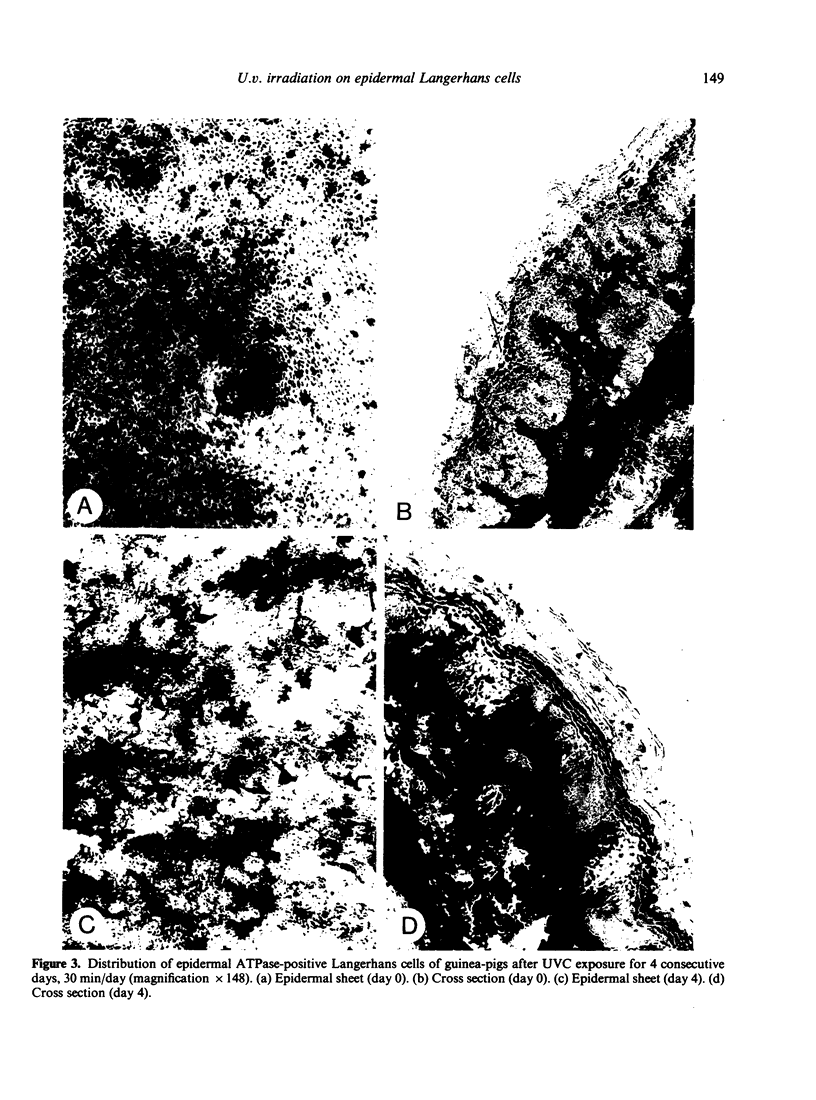
There is good evidence to suggest that u.v. irradiation (UVB) of the skin causes a reduction in the numbers of normal epidermal Langerhans cells (LC) in man and mouse. Little information is available on the effects of u.v. radiation on LC in guinea-pig skin. In this study, different dosages of UVB and UVC were applied to the ear skin of guinea-pigs. UVC irradiations were found more effective than UVB in causing depletions of ATPase-positive epidermal LC. Highly significant depletions, lasting 6 days after irradiation, were produced with little evidence of significant inflammatory reactions occurring in the epidermis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberer W., Schuler G., Stingl G., Hönigsmann H., Wolff K. Ultraviolet light depletes surface markers of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):202–210. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aberer W., Stingl G., Stingl-Gazze L. A., Wolff K. Langerhans cells as stimulator cells in the murine primary epidermal cell-lymphocyte reaction: alteration by UV-B irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Aug;79(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12500040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. R., Khalil H. M., Wikel S. K. Langerhans cells trap tick salivary gland antigens in tick-resistant guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):563–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. R., Parrish J. A. The optics of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Jul;77(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12479191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morison W. L., Parrish J. A., Woehler M. E., Bloch K. J. The influence of ultraviolet radiation on allergic contact dermatitis in the guinea-pig. I. UVB radiation. Br J Dermatol. 1981 Feb;104(2):161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb00039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nithiuthai S., Allen J. R. Significant changes in epidermal Langerhans cells of guinea-pigs infested with ticks (Dermacentor andersoni). Immunology. 1984 Jan;51(1):133–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Ackles A. E., Lerner A. B. The effects of ultraviolet light and certain drugs on La-bearing Langerhans cells in murine epidermis. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 1;60(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Greene M. I. Antigen presentation by epidermal Langerhans cells: loss of function following ultraviolet (UV) irradiation in vivo. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Aug;24(2):204–219. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G. New aspects of Langerhans' cell function. Int J Dermatol. 1980 May;19(4):189–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1980.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W., Bergstresser P. R. Langerhans cell function dictates induction of contact hypersensitivity or unresponsiveness to DNFB in Syrian hamsters. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Sep;77(3):272–277. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12482453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikel S. K. Immune responses to arthropods and their products. Annu Rev Entomol. 1982;27:21–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.27.010182.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]