Abstract
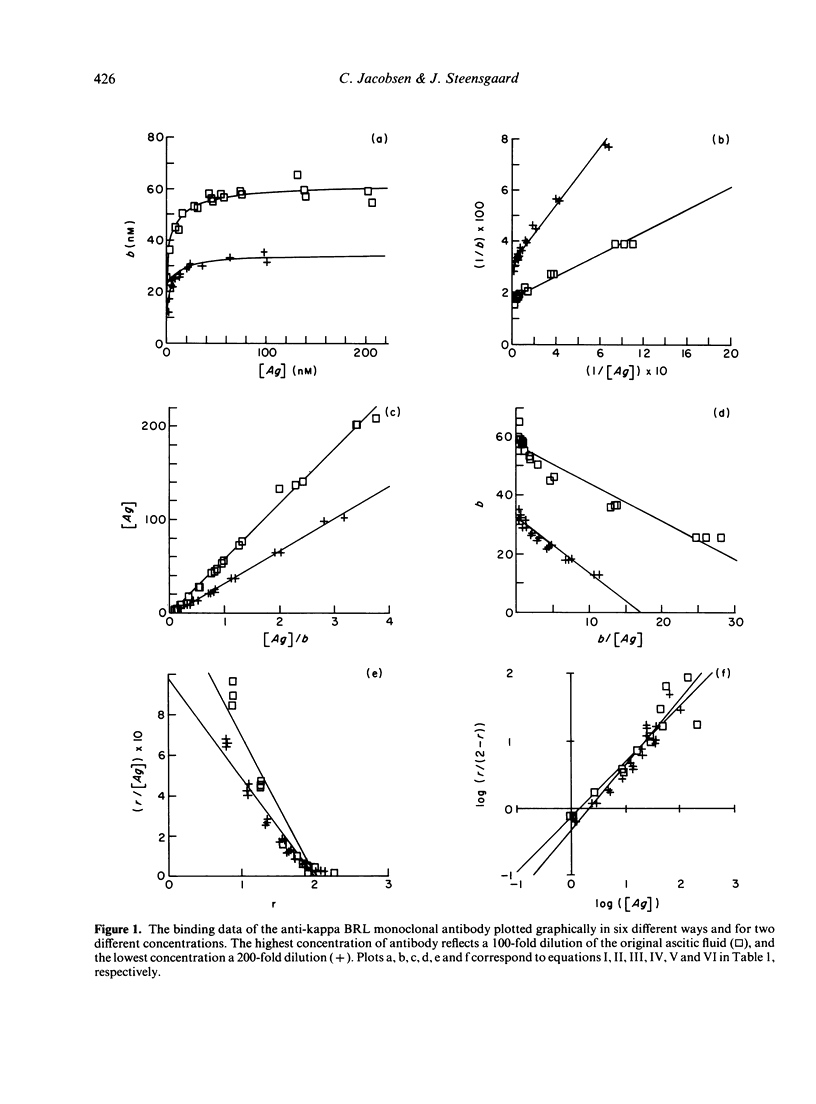
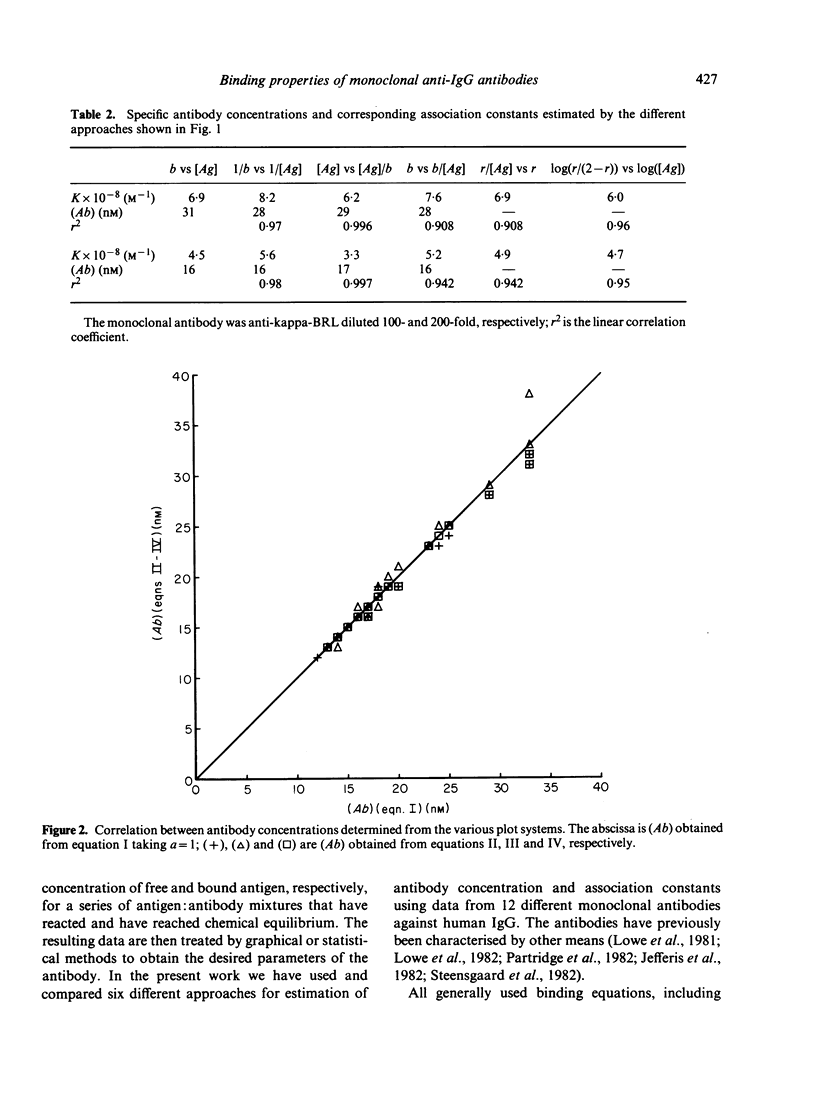
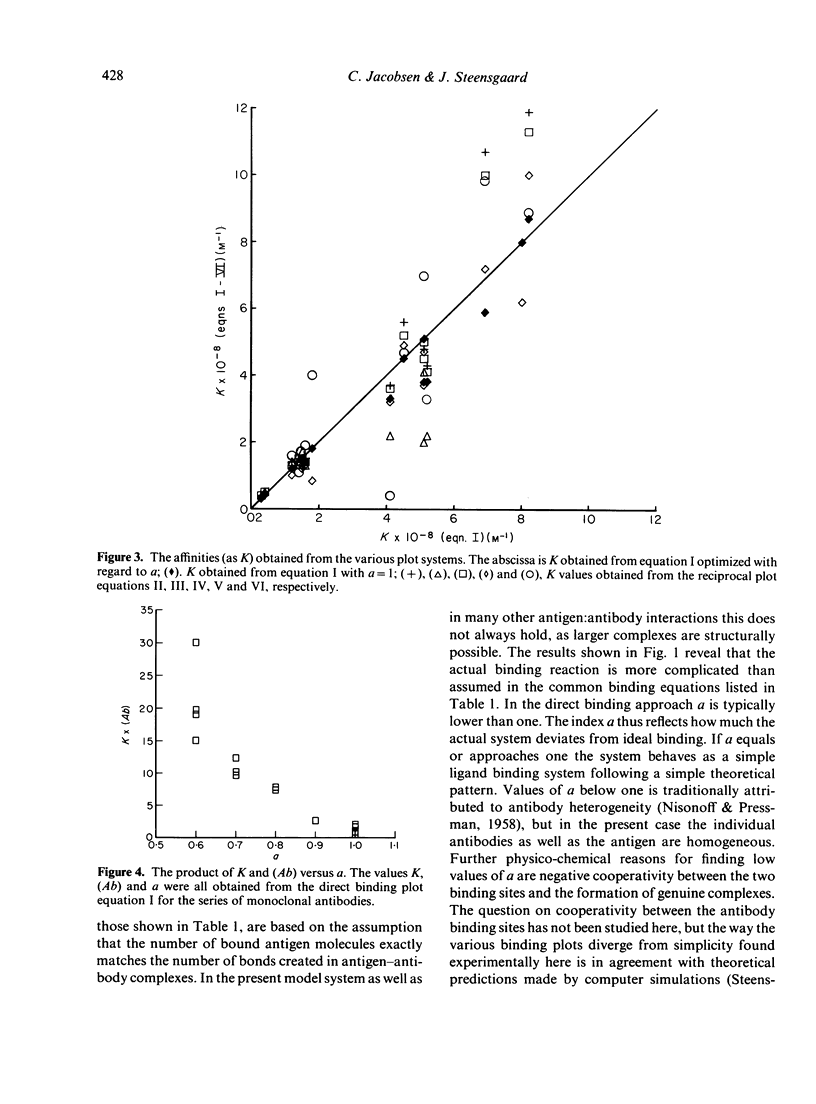
The binding properties of an immune complex-forming system comprising human IgG and mouse monoclonal antibodies against human IgG have been studied. A refined binding assay has been applied directly on ascitic fluid containing monoclonal antibody. Complete sets of binding data of a series of different monoclonal antibodies were collected and analysed by various graphical and statistical methods. Special attention was given to methods which allow determination of specific monoclonal antibody concentration as well as antibody affinity. It was found that the formation of genuine antigen: antibody complexes per se gives rise to deviations from expected linearity in commonly used binding equations. Good correlation was found between the antibody concentrations obtained by various graphical approaches, whereas the size of the association constant seemed to depend on the method in use. The binding pattern was found to be dependent on the concentration of antibody. Most reliable parameters were obtained if the product of the antibody concentration and the association constant was below 10.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jacobsen C., Frich J. R., Steensgaard J. Determination of affinity of monoclonal antibodies against human IgG. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C., Steensgaard J. Measurements of precipitin reactions by difference turbidimetry: a new method. Immunology. 1979 Feb;36(2):293–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Bird P., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R. Monoclonal antibodies (McAbs) to determinants on human gamma chains: properties of antibodies showing subclass restriction or subclass specificity. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):329–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R., Drysdale P., Richardson P., Raykundalia C., Catty D., Appleby P., Drew R. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to human immunoglobulin kappa and lambda chains. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):649–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. J., Lowe J., Hardie D. L., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. Immunogenic and antigenic epitopes of immunoglobulins. II. Antigenic differences between secreted and membrane IgG demonstrated using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensgaard J., Jacobsen C., Lowe J., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. Theoretical and ultracentrifugal analysis of immune complex formation between monoclonal antibodies and human IgG. Immunology. 1982 Aug;46(4):751–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensgaard J., Johansen A. S. Biochemical aspects of immune complex formation and immune complex diseases. Allergy. 1980 Sep;35(6):457–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensgaard J., Steward M. W., Frich J. R. The significance of antibody affinity heterogeneity in antigen-antibody reactions demonstrated by computer simulation. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jun;17(6):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Petty R. E. The use of ammonium sulphate globulin precipitation for determination of affinity of anti-protein antibodies in mouse serum. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):747–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


