Abstract
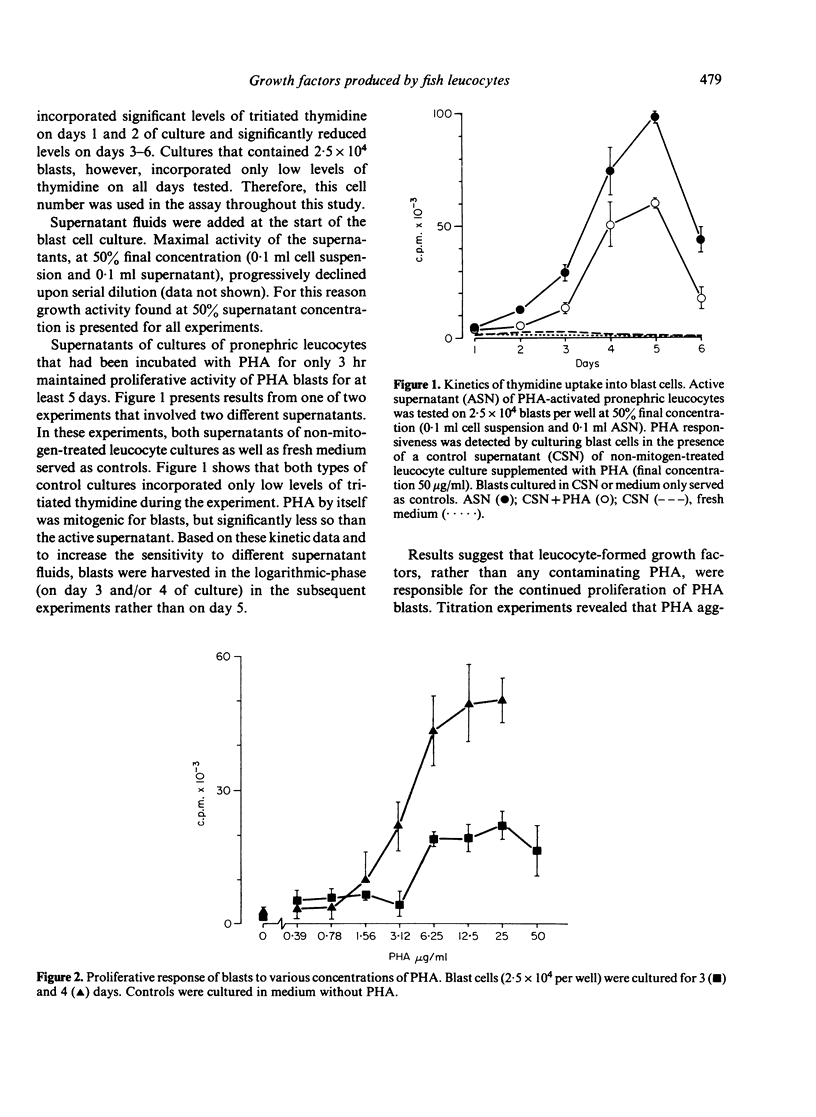
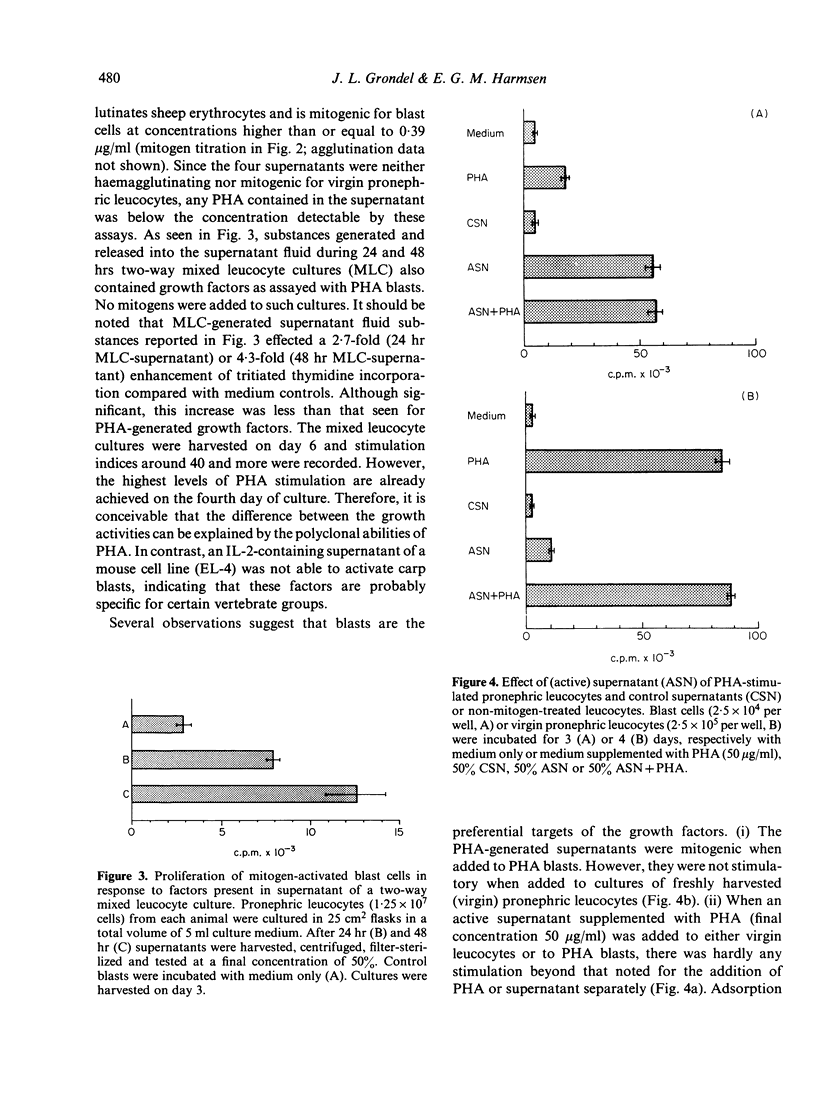
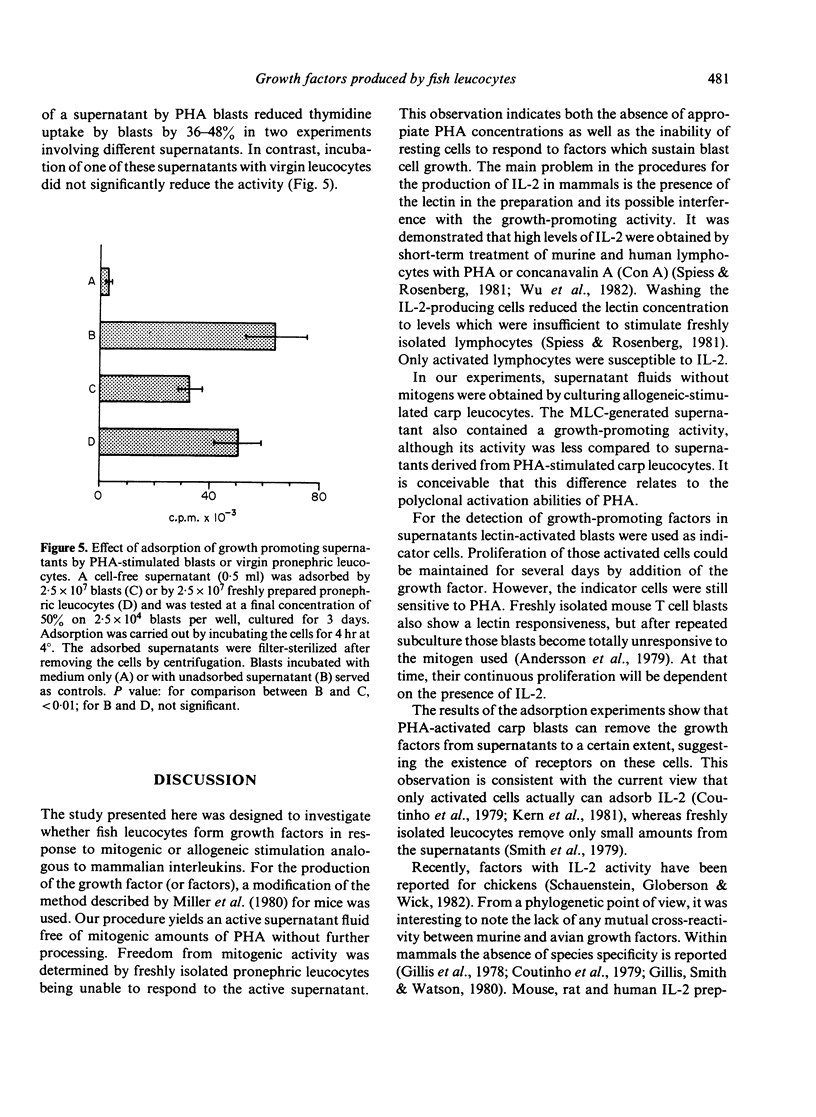
Supernatants of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA)-activated pronephric leucocytes from carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) contain a lymphocyte growth factor which can induce a proliferative response of purified lymphoblasts but not freshly isolated leucocytes. The growth-promoting activity can be reduced by absorbing the supernatant with mitogen-activated blasts. In addition, increased incorporation of tritiated thymidine into PHA-activated blast cells is also induced by supernatants from two-way mixed leucocyte cultures. The data show that even at the evolutionary level of teleost fish, amplifying/regulatory leucocyte products exist. It is suggested that these factors play as important a role in the regulation of the immune response in fish as they do in mammals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Grönvik K. O., Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. Studies on T lymphocyte activation. I. Requirements for the mitogen-dependent production of T cell growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):581–587. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Grönvik K. O., Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. Studies on T lymphocyte activation. I. Requirements for the mitogen-dependent production of T cell growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):581–587. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Fuller-Farrar J., Farrar W. L., Hilfiker M. L. Macrophage-independent activation of helper T cells. I. Production of Interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A., Watson J. Biochemical characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. II. Purification of a class of rat and human lymphokines. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1954–1962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. E., Gillis S., Okada M., Henney C. S. The role of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in the differentiatin of cytotoxic T cells: the effect of monoclonal anti-IL-2 antibody and absorption with IL-2 dependent T cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Andrus L., Prowse S. J. Role of lymphokine and antigen in the control of specific T cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:279–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson H. J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. B cell helper factors. I. Requirement for both interleukin 2 and another 40,000 mol wt factor. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1681–1693. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauenstein K., Globerson A., Wick G. Avian lymphokines: 1. Thymic cell growth factor in supernatants of mitogen stimulated chicken spleen cells. Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Summer;6(3):533–540. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(82)80039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J., Monticone V., Mills G., Paetkau V. Effects of costimulator on immune responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1974–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gillis S., Baker P. E., McKenzie D., Ruscetti F. W. T-cell growth factor-mediated T-cell proliferation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Lachman L. B., Oppenheim J. J., Favata M. F. The functional relationship of the interleukins. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess P. J., Rosenberg S. A. A simplified method for the production of murine T-cell growth factor free of lectin. J Immunol Methods. 1981;42(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susskind B. M., Faanes R. B. Effects of gamma-irradiation on lymphocyte subpopulations participating in the development of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1485–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Räollinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K., Hardt C., Johnscher G. T-T cell interactions during in vitro cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. II. Helper factor from activated Lyt 1+ T cells is rate limiting i) in T cell responses to nonimmunogenic alloantigen, ii) in thymocyte responses to allogeneic stimulator cells, and III) recruits allo- or H-2-restricted CTL precursors from the Lyt 123+ T subset. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Ernberg I., Masucci M. G., Johnson D., Klein E., Klein G. Human T cell growth factor (TCGF) produced by repeated stimulation of non-adherent human lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1982;51(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


