Abstract
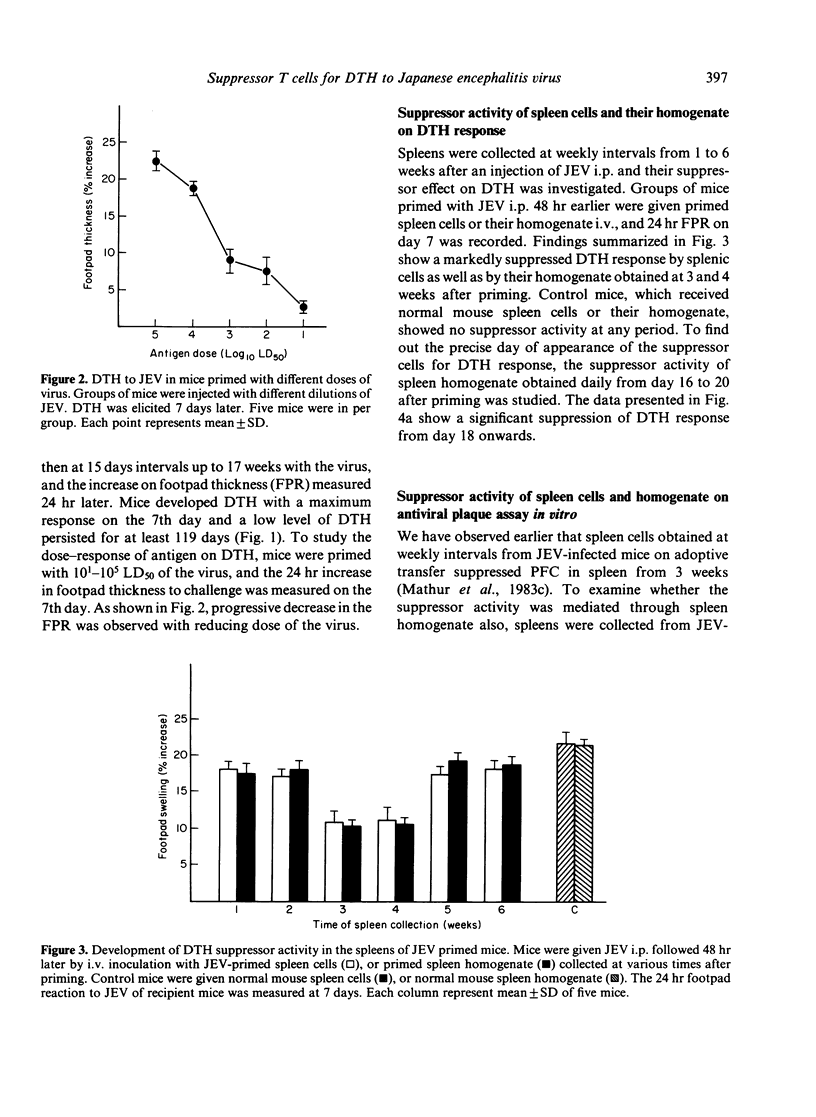
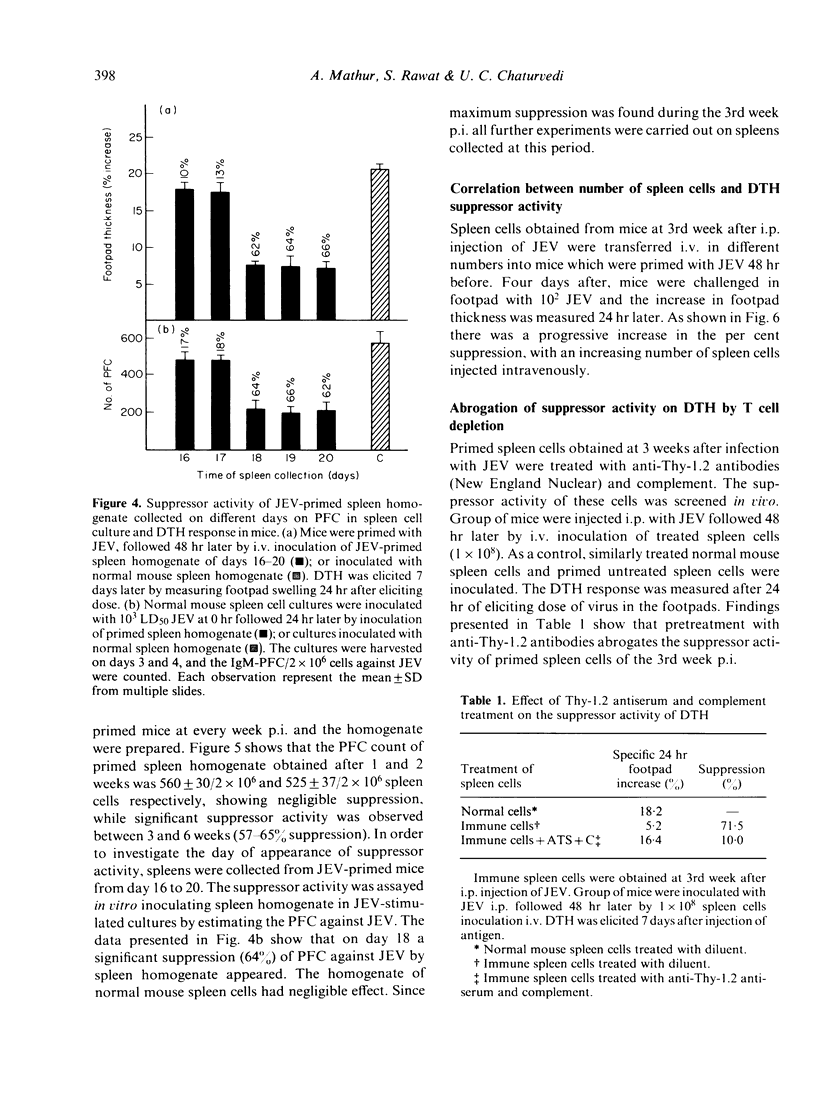
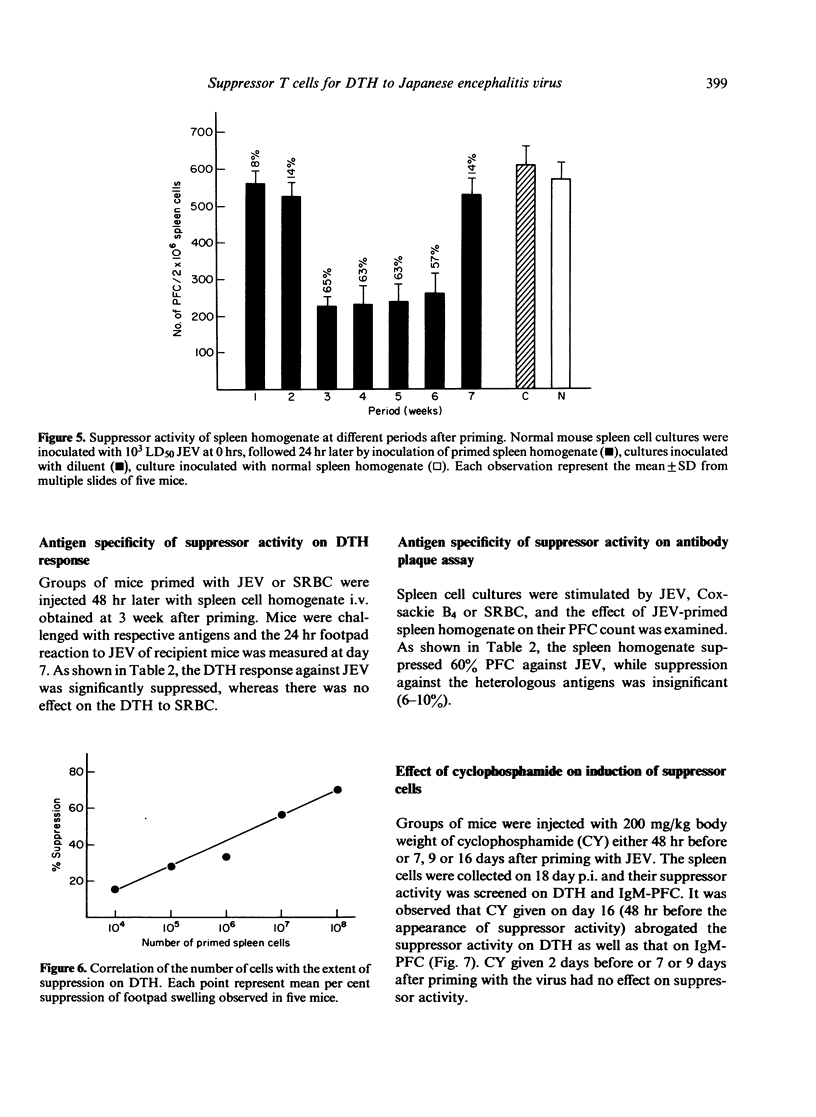
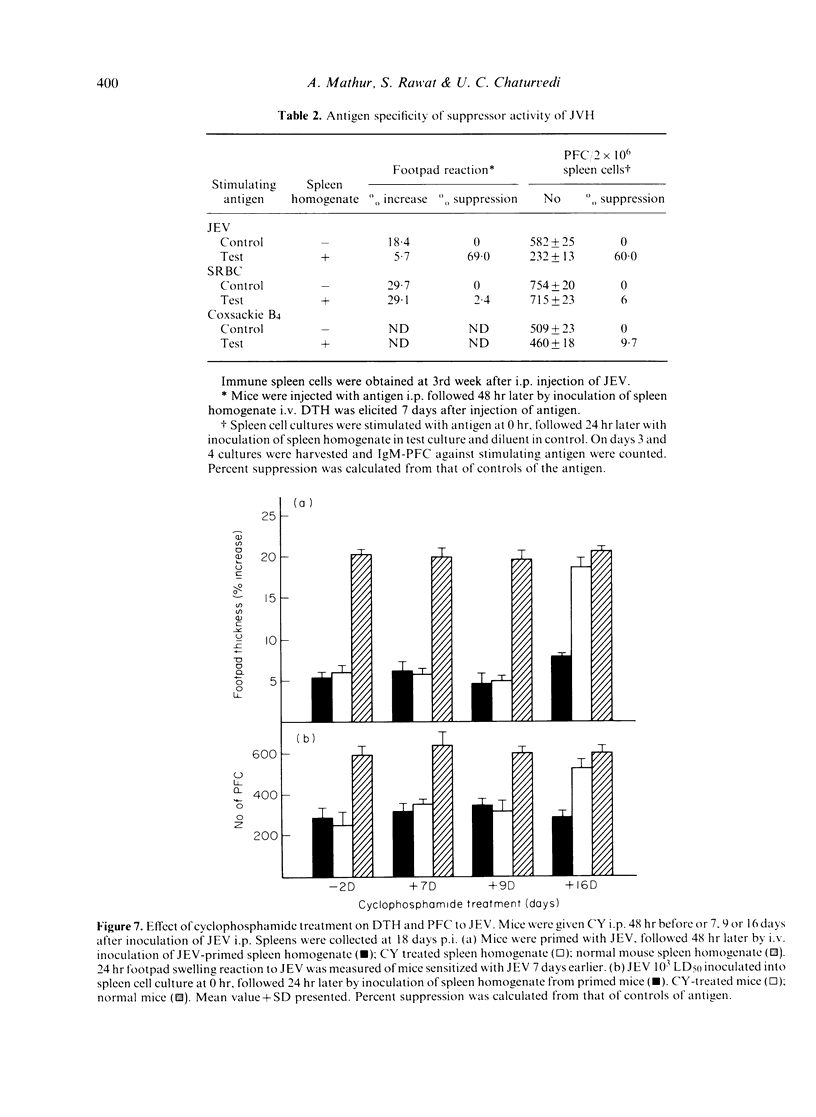
The delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) to Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and the suppressor cells controlling it and the antibody-forming cells in inbred Swiss mice have been studied. JEV induces DTH, with a peak response at day 7 following infection which persists at low levels at least up to 119 days. Suppressor activity appeared on day 18. It was transferable by immune spleen cells. Treatment of spleen cells with anti-Thy-1.2 antisera and complement abrogated the suppressor activity. The homogenate of the spleen was equally effective in mediating suppression of DTH and the humoral response as measured by direct antibody plaque-forming cell (IgM-PFC) assay. The suppressor activity was antigen-specific both on DTH and T helper for antibody response as the immune responses against SRBC or Coxsackie B4 virus were not suppressed. The suppressor cells were sensitive to cyclophosphamide treatment when the drug was given 48 hr before their appearance. It is, therefore, concluded that in JEV infection of mice, antigen-specific suppressor T cells are generated, both for DTH and IgM antibody, which are cyclophosphamide-sensitive and mediate suppression through soluble product(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaturvedi U. C., Shukla M. I. [Characterization of the suppressor factor produced in the spleen of dengue virus-infected mice]. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1981 May-Jun;132C(3):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0769-2625(81)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S. Brain-associated theta antigen: reactivity of rabbit anti-mouse brain with mouse lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene M. I., Weiner H. L. Delayed hypersensitivity in mice infected with reovirus. II. Induction of tolerance and suppressor T cells to viral specific gene products. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Parker D., Turk J. L. B-cell suppression of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):550–551. doi: 10.1038/251550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A., Murahata R., Terpenning M., Cantrell J., Zighelboim J. Activation and mechanism of action of suppressor macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Oct;64(1):150–161. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Russell S. M. Delayed-type hypersensitivity to influenza virus. Induction of antigen-specific suppressor T cells for delayed-type hypersensitivity to hemagglutinin during influenza virus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):799–814. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Congenital infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):26–29. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.26-29.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Host defence mechanisms against Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Immune response to Japanese Encephalitis virus in mother mice and their congenitally infected offspring. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):2027–2031. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Transplacental Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection in mice during consecutive pregnancies. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):213–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Rawat S., Chaturvedi U. C. Induction of suppressor cells in Japanese encephalitis virus infected mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1983 Jun;64(3):336–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori R., Kimoto K., Takeya K. The role of the thymus in antibody production and in resistance to Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):32–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01253877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa S., Baba M., Harada T., Mitsuoka A. Studies on delayed hypersensitivity in mice. III. Evidence for suppressive regulatory T1-cell population in delayed hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):237–248. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Okumura K. The role of antigen-specific T cell factors in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. B., Basten A. Suppressor cells in humoral immunity and tolerance. Br Med Bull. 1976 May;32(2):152–157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


