Abstract
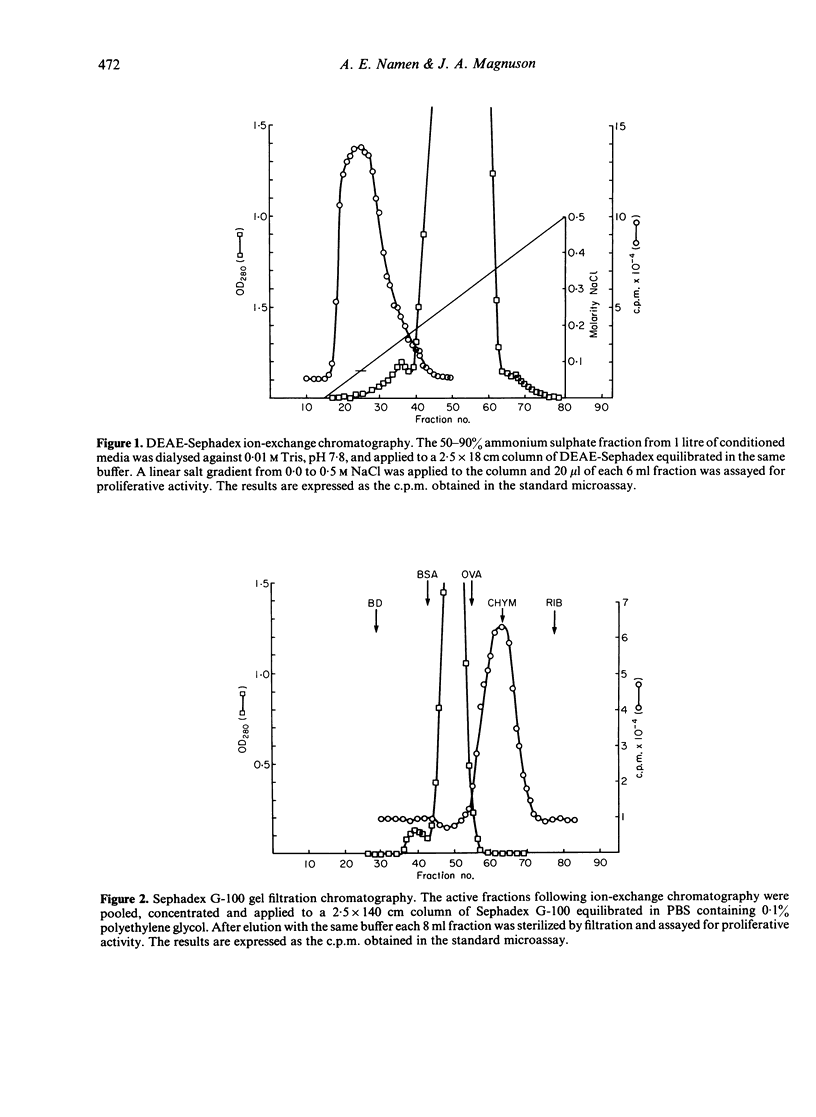
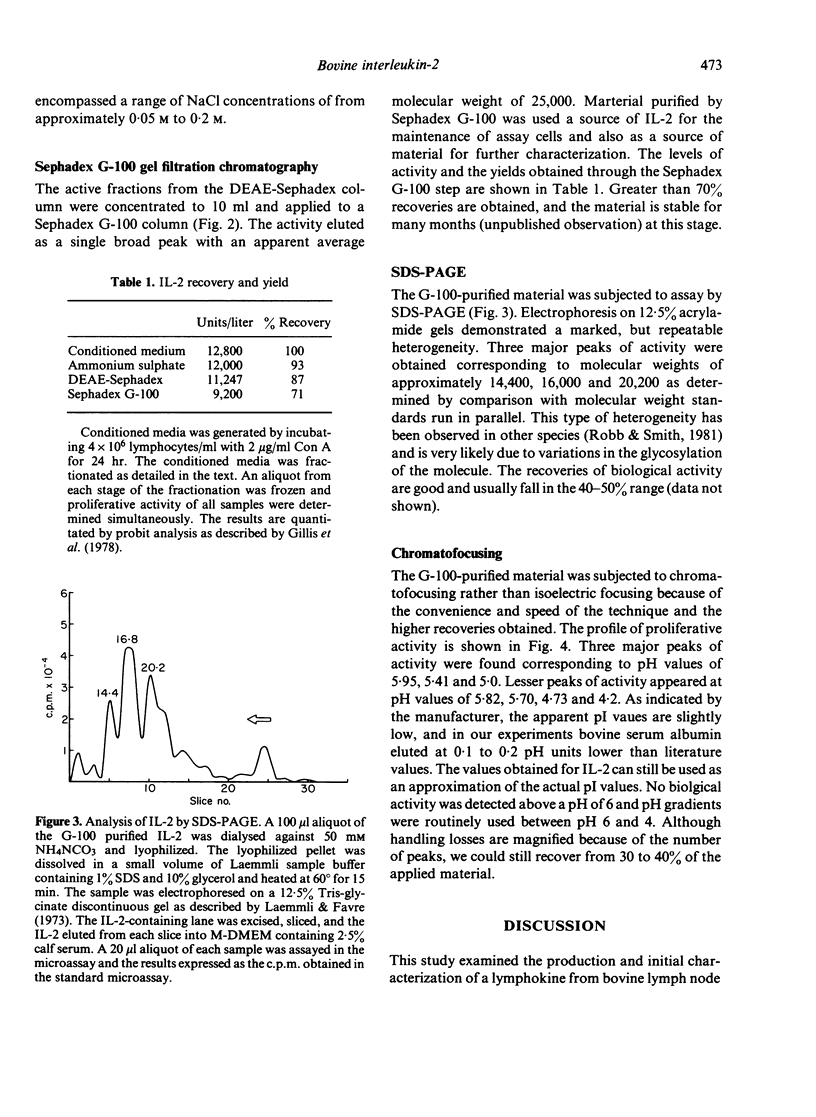
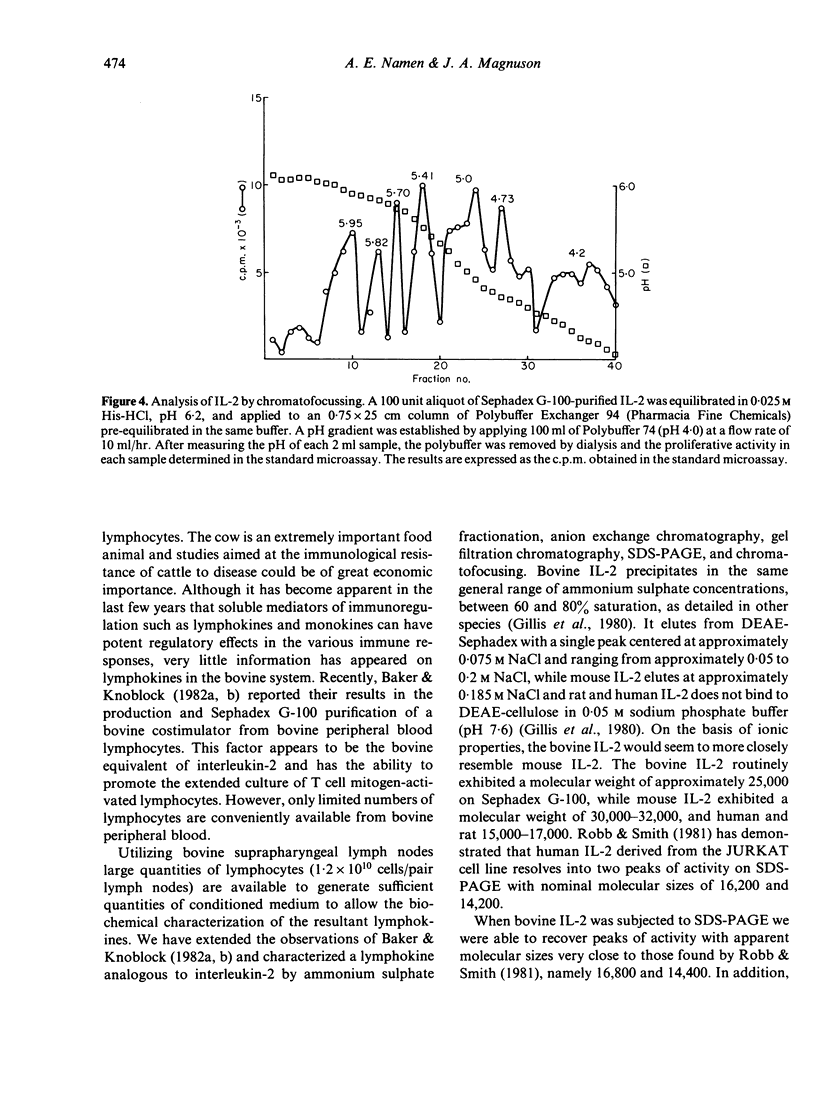
A lymphokine analogous to interleukin-2 from other species was generated from bovine suprapharyngeal lymph nodes and characterized biochemically. The isolated material can support the long-term growth of concanavalin A (Con-A) or mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR)-activated bovine T cells. The material elutes from DEAE-Sephadex at a low salt concentration, approximately 0.075 M, and exhibits molecular weight of approximately 25,000 on Sephadex G-100. When subjected to analysis by sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), three peaks of activity were observed, corresponding to molecular weights of 14,400, 16,800 and 20,200. Finally, the isolated material exhibited a marked heterogeneity when subjected to chromatofocussing. Three major peaks of activity, with pIs of approximately 5.95, 5.41 and 5.0 are present with peaks of lesser activity at pIs of 5.82, 5.70, 4.73 and 4.20.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VI. Isolation of concanavalin A by specific adsorption on cross-linked dextran gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Grönvik K. O., Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. Studies on T lymphocyte activation. I. Requirements for the mitogen-dependent production of T cell growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):581–587. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Knoblock K. F. Bovine costimulator. I. Production kinetics, partial purification, and quantification in serum-free Iscove's medium. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jul;3(4):365–379. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Knoblock K. F. Bovine costimulator. II. Generation and maintenance of a bovine costimulator-dependent bovine lymphoblastoid cell line. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jul;3(4):381–397. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mochizuki D. Y., Conlon P. J., Hefeneider S. H., Ramthun C. A., Gillis A. E., Frank M. B., Henney C. S., Watson J. D. Molecular characterization of interleukin 2. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:167–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A., Watson J. Biochemical characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. II. Purification of a class of rat and human lymphokines. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1954–1962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootenberg J. E., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. C. A biochemical variant of human T cell growth factor produced by a cutaneous T cell lymphoma cell line. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1499–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H. Preparation of large quantities of pure bovine lymphocytes and a monolayer technique for lymphocyte cultivation. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pure E., Isakson P. C., Paetkau V., Caplan B., Vitetta E. S., Krammer P. H. Interleukin-2 does not induce murine B cells to secrete Ig. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2420–2425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Smith K. A. Heterogeneity of human T-cell growth factor(s) due to variable glycosylation. Mol Immunol. 1981 Dec;18(12):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Gillis S., Marbrook J., Mochizuki D., Smith K. A. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. I. Purification of a class of murine lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):849–861. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Mochizuki D. Interleukin 2: a class of T cell growth factors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:257–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


