Abstract
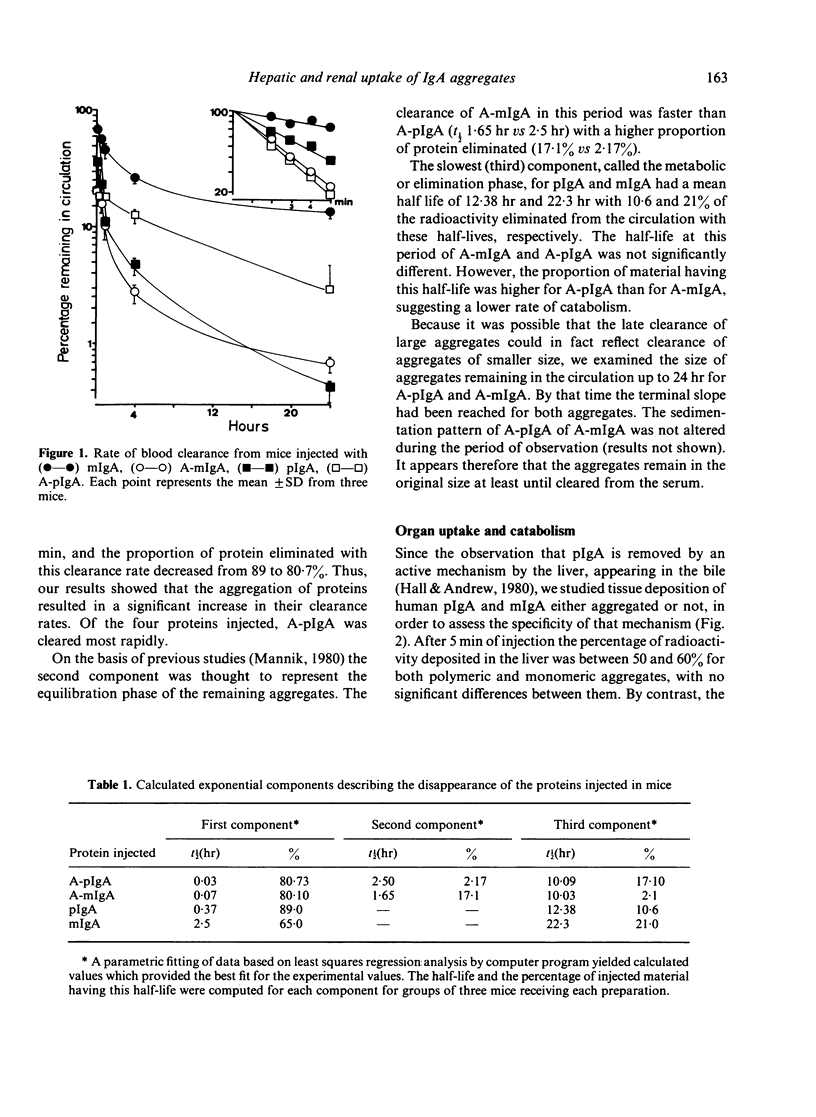
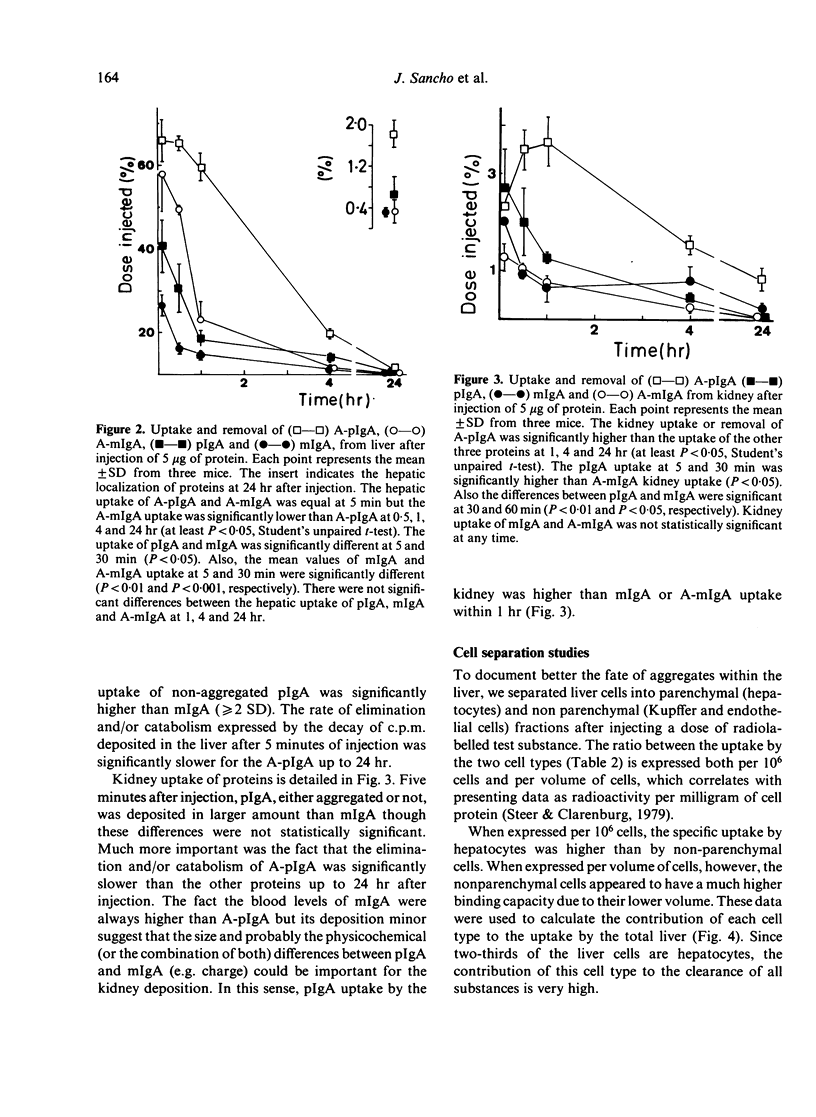
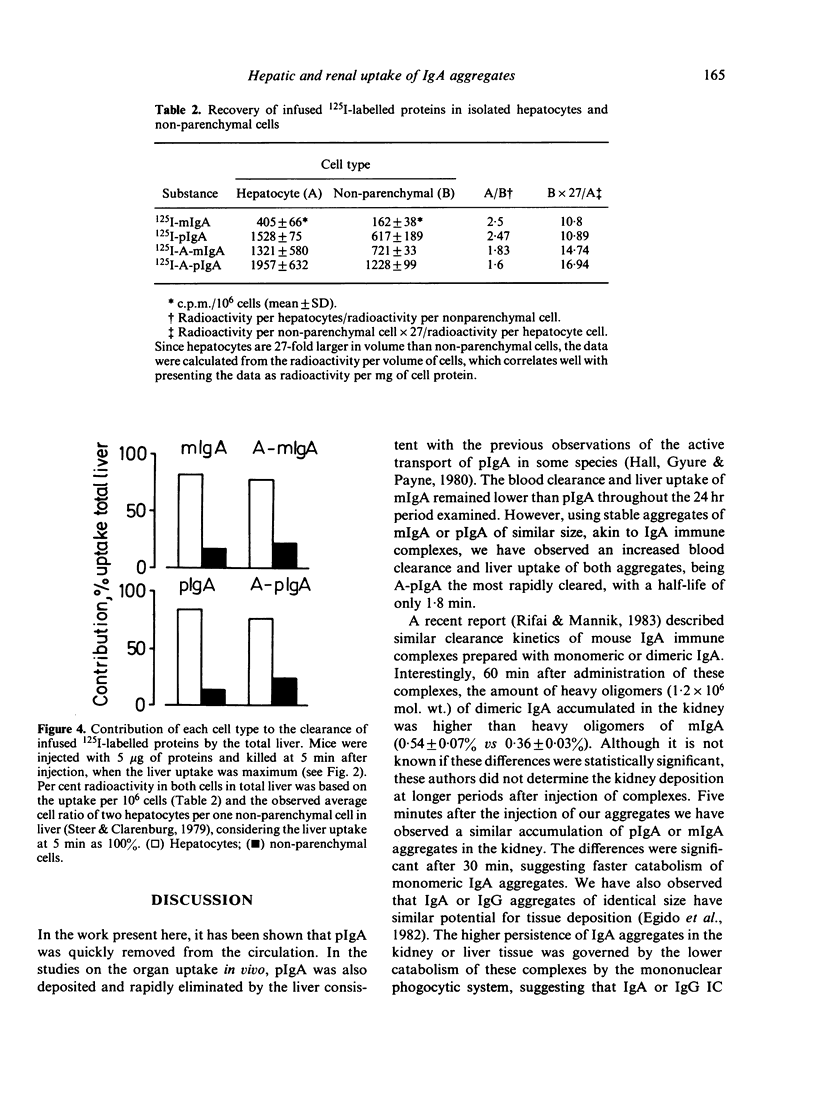
To investigate the handling of IgA by the mononuclear phagocytic system and by hepatocytes of mice, soluble, similar sized, heat-aggregated monomeric (A-mIgA) and polymeric IgA (ApIgA) were used as akin to IgA immune complexes. The half-life of the clearance from circulation decreased from 2.5 hr to 4.2 min and from 22 min to 1.8 min after aggregation of mIgA and pIgA, respectively. Tissue localization experiments indicated that the liver was the organ predominantly involved in the uptake and catabolism of the proteins injected. The rate of the liver catabolism and/or elimination of aggregated polymeric IgA was the slowest up to 24 hr of injection. Aggregated pIgA was deposited in the kidney in larger amounts than aggregated mIgA. The participation of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal liver cells was determined after isolation and purification of these cells. The four substances injected, pIgA, A-pIgA, mIgA and A-mIgA, were predominantly localized in nonparenchymal cells when the uptake was expressed per volume of cells, due to their lower protein content. However, when the results were expressed cell to cell there was a high ratio of IgA aggregates associated with hepatocytes to nonparenchymal cells. It seems probable, therefore, that hepatocytes are almost exclusively responsible for clearance of IgA aggregates from blood.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Egido J., Sancho J., Mampaso F., Lopez Trascasa M., Sanchez Crespo M., Blasco R., Hernando L. A possible common pathogenesis of the mesangial IgA glomerulonephritis in patients with Berger's disease and Schönlein-Henoch syndrome. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1980;17:660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommel D., Rachman R. Receptor for the Fc portion of IgG on the plasma membrane of the hepatocyte. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1979 Jul-Aug;130C(4):553–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Gyure L. A., Payne A. W. Comparative aspects of the transport of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):899–902. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Brown D. L. Clearance kinetics of soluble pre-formed immune complexes containing IgM antibodies in normal and decomplemented rabbits. Immunology. 1981 Feb;42(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Brandtzaeg P., Hütteroth T. H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. In vivo and in vitro binding of IgA to the plasma membrane of hepatocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(6):543–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Der Lelij A., Knutson W., Fleuren G. J., Vanes L. A. The influence of phagocyte function on glomerular localization of aggregated IgM in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 May;32(2):207–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Lentz H., van Es L. A. Isolation of stable aggregates of IgG by zonal ultracentrifugation in sucrose gradients containing albumin. Immunol Commun. 1979;8(3):337–345. doi: 10.3109/08820137909050047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M. Physicochemical and functional relationships of immune complexes. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 May;74(5):333–338. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Bhan A. K., Collins A. B., McCluskey R. T. Effect of circulating immune complexes on Fc and C3 receptors of Kupffer cells in vivo. Lab Invest. 1981 May;44(5):442–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Mannik M. Clearance kinetics and fate of mouse IgA immune complexes prepared with monomeric or dimeric IgA. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1826–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Small P. A., Jr, Teague P. O., Ayoub E. M. Experimental IgA nephropathy. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1161–1173. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Egido J., Sánchez-Crespo M., Blasco R. Detection of monomeric and polymeric IgA containing immune complexes in serum and kidney from patients with alcoholic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):327–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Clarenburg R. Unique distribution of glycoprotein receptors on parenchymal and sinusoidal cells of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4457–4461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Kressner M. S., Collins J. C., Sternlieb I., Morell A. G. IgA interaction with the asialoglycoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6229–6231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Day J. F., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. Carbohydrate-mediated clearance of immune complexes from the circulation. A role for galactose residues in the hepatic uptake of IgG-antigen complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6820–6825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trascasa M. L., Egido J., Sancho J., Hernando L. IgA glomerulonephritis (Berger's disease): evidence of high serum levels of polymeric IgA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):247–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


