Abstract
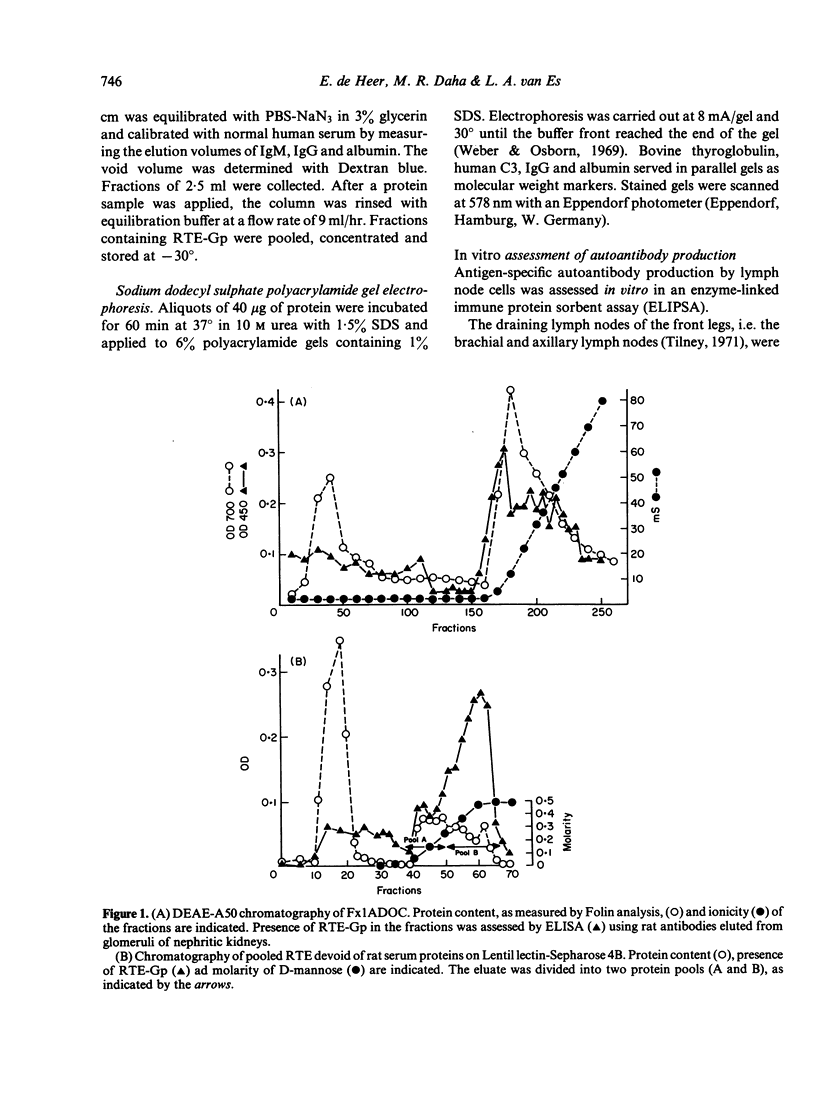
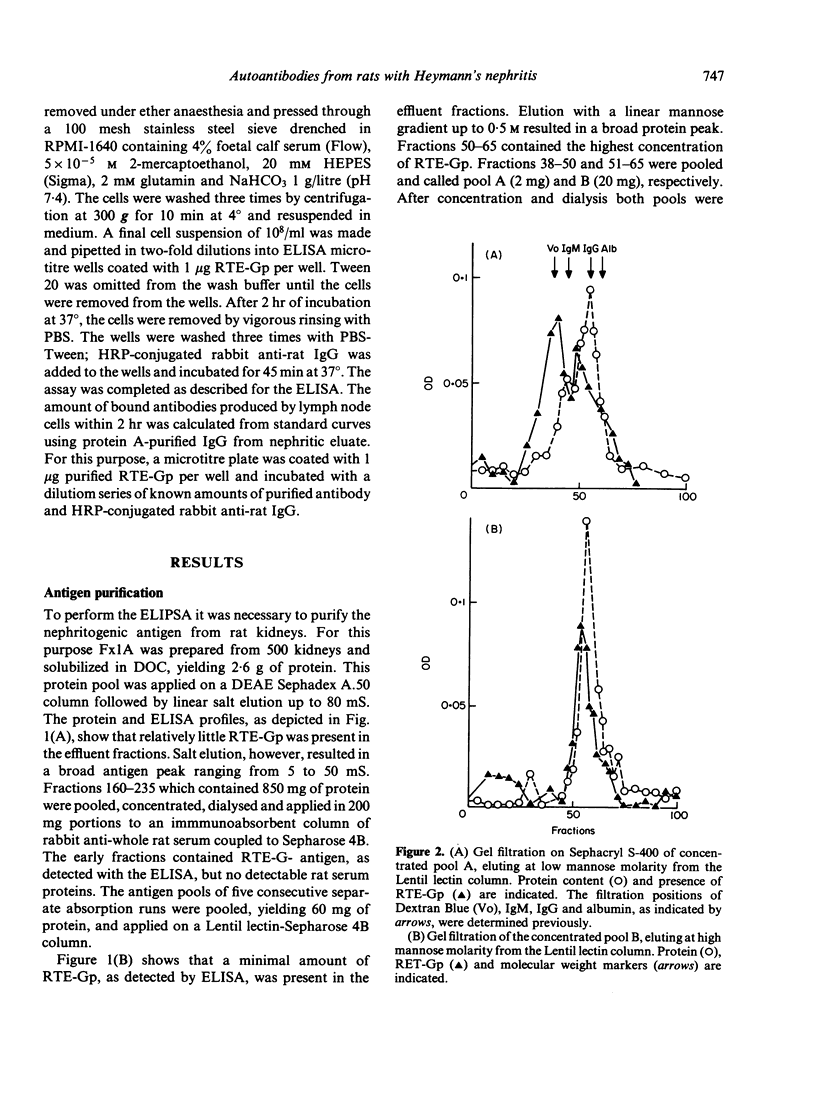
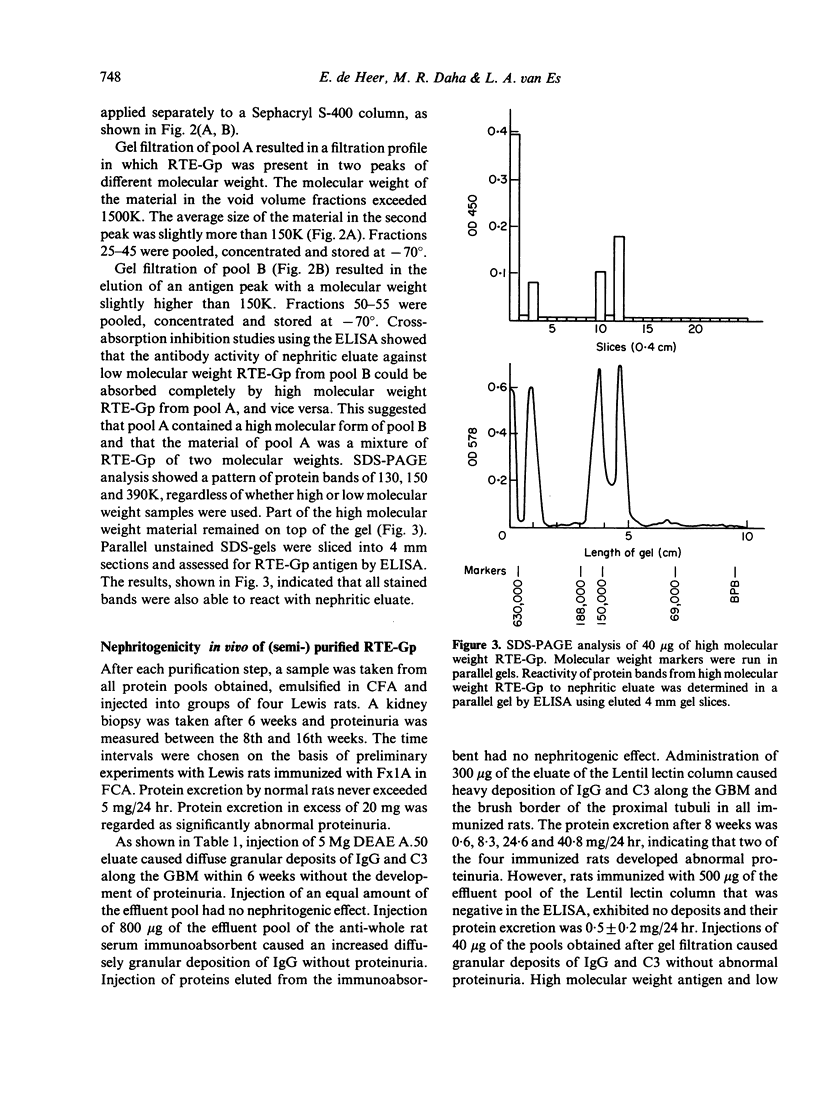
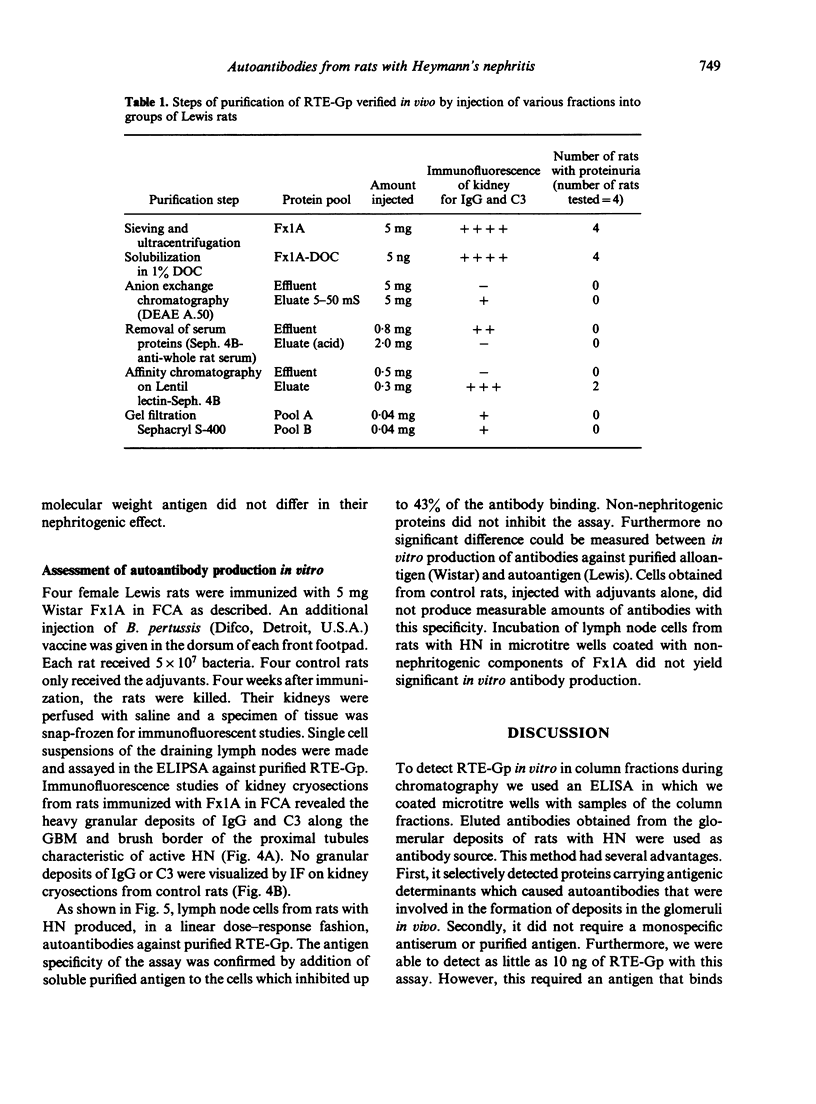
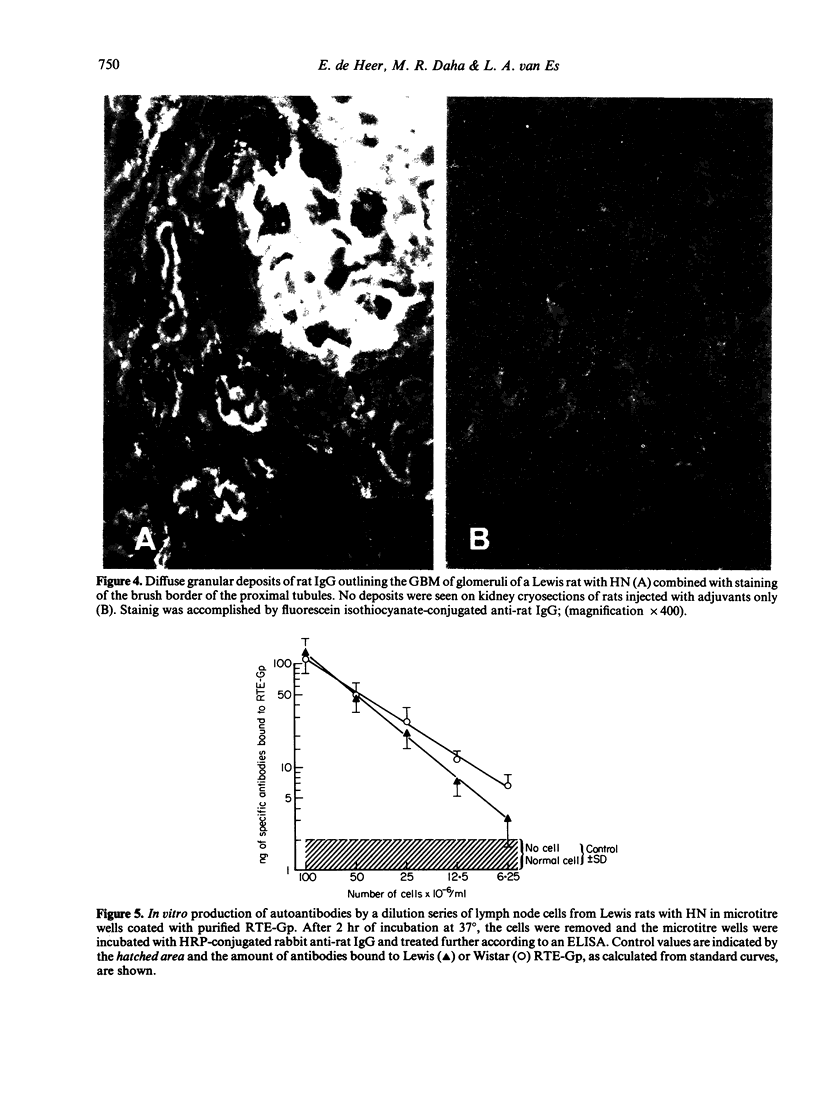
A method is described for the purification and identification of the nephritogenic glycoprotein in renal tubular epithelium (RTE-Gp) from Wistar and Lewis rats. This antigen is responsible for the induction of Heymann's nephritis (HN) in Lewis rats. RTE-Gp was detected in chromatographic fractions by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using rat antibodies eluted from glomeruli of Lewis rats with active HN. In each step of the purification procedure, an absolute correlation between detection of RTE-Gp in vitro and nephritogenicity in vivo was demonstrated. Lymph node cells obtained from rats with HN produced in vitro autoantibodies in a linear dose-response fashion against both allogeneic and autologous RTE-Gp, as detected by an enzyme-linked immune protein sorbent assay. During a 2 hr incubation period, 10(6) lymph node cells produced 10-40 ng of IgG. Antibody production above background levels could be detected with an input of 10(5) lymph node cells. This study shows that the specific autoimmune response in rats with NH can be measured at the cellular level.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alousi M. A., Post R. S., Heymann W. Experimental autoimmune nephrosis in rats. Morphogenesis of the glomerular lesion: immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1969 Jan;54(1):47–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerrigter G. H., Vos A., Scheper R. J. Direct measurement of in vitro antibody production using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant S., Silverman M. Immunologic characterization of plasma membranes from the renal proximal tubule of the dog. Kidney Int. 1977 May;11(5):348–356. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Stilmant M. M., Darby C. Autologous immune complex nephropathy. I. Sequential study of immune complex deposition, ultrastructural changes, proteinuria, and alterations in glomerular sialoprotein. Lab Invest. 1976 Jan;34(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassock R. J., Edgington T. S., Watson J. I., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. II. The pathogenetic mechanism. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):573–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon W. E., Grupe W. E., Parkman R. Control of autologous immune complex nephritis. I. Suppression of the disease in the presence of T cell sensitization. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1034–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin A., Adams L. E., Levy R., Cline S., Hess E. V. Cellular immunity in experimental glomerulonephritis of rats. I. Delayed hypersensitivity and lymphocyte stimulation studies with renal tubular antigens. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makker S. P. Evidence that the antigen of autologous immune complex glomerulonephritis of rats is a mannose- or glucose-containing glycoprotein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jan;163(1):95–99. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makker S. P., Kirson I. J., Moorthy B. Enhancement of in situ immune complex formation in isolated perfused kidneys in Heymann's nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):317–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendrick D. L., Noble B., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. Antibody-mediated injury to proximal tubules in Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):328–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Törnroth T., Tikkanen I., Virtanen I., Linder E. Heymann nephritis induced by kidney brush border glycoproteins. Lab Invest. 1980 Dec;43(6):547–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse T., Fukasawa T., Miyakawa Y. Laboratory model of membranous glomerulonephritis in rats induced by pronase-digested homologous renal tubular epithelial antigen. Lab Invest. 1975 Aug;33(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale T. J., Wilson C. B. Glomerular antigens in Heymann's nephritis: reactivity of eluted and circulating antibody. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Lucas Z. J. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes. V. Role of soluble toxin in macrophage-inhibited cultures of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):395–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Belok S., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G. A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI109987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki T., Klassen J., Andres G. A., Milgrom F., McCluskey R. T. Passive transfer of Heymann nephritis with serum. Kidney Int. 1973 Feb;3(2):66–73. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney N. L. Patterns of lymphatic drainage in the adult laboratory rat. J Anat. 1971 Sep;109(Pt 3):369–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



