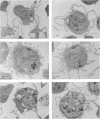
Abstract
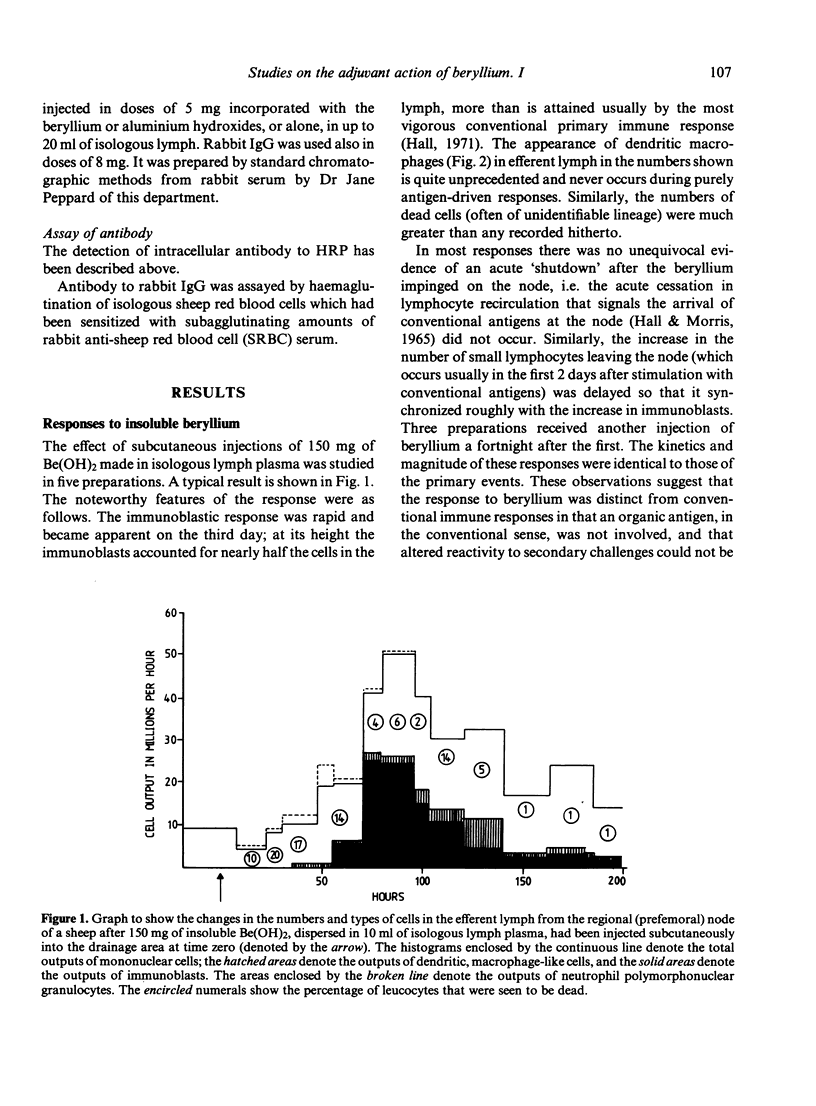
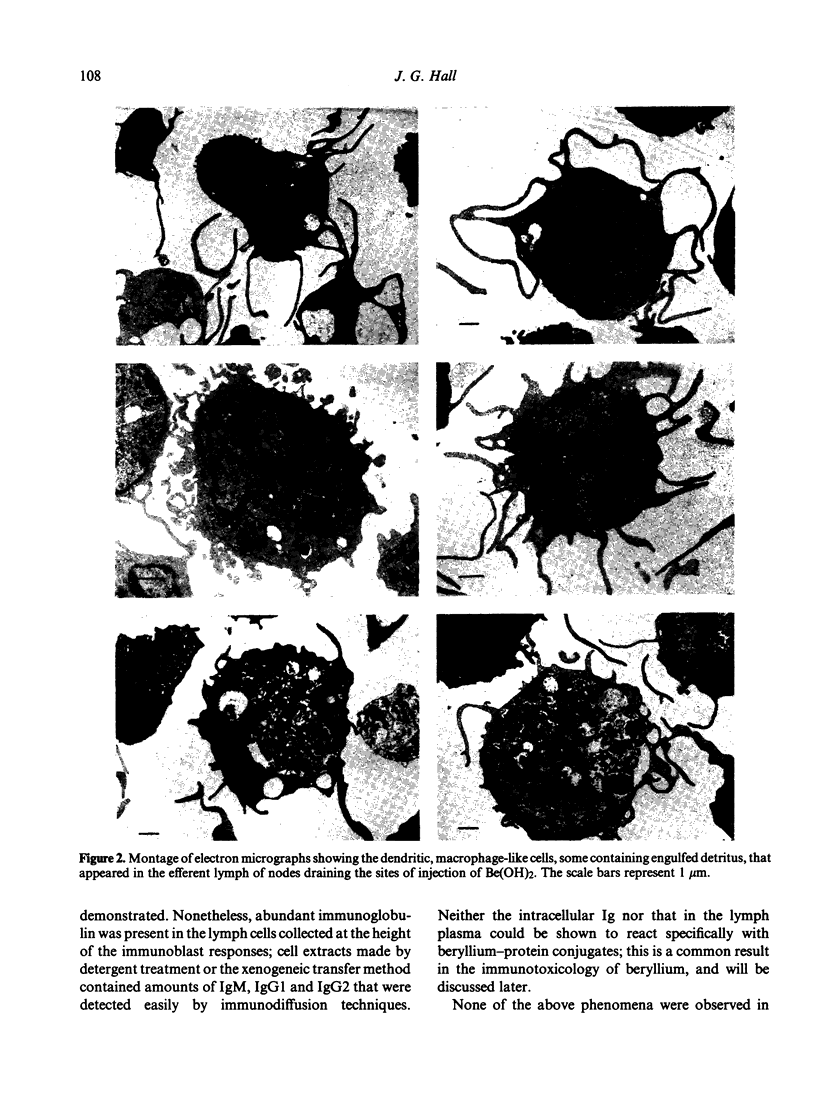
Beryllium was injected subcutaneously (s.c.) into sheep in the form of a suspension of insoluble Be(OH)2 in isologous lymph plasma. Even in the absence of added antigen, doses of 50-150 mg induced rapid and vigorous proliferative responses in the regional lymph nodes so that large numbers of immunoblasts appeared in the efferent lymph within 4 days. Dendritic macrophages and dead white cells, which are excluded normally from efferent lymph, also appeared in significant numbers. When horseradish peroxidase was added to the injections of Be(OH)2, specific, high-affinity antibody appeared in the immunoblasts. This did not happen when the antigen was injected on its own or in combination with conventional, alum adjuvant. By the incorporation of radioactive 7Be in the injected material, it was shown that most of the Be(OH)2 remained at the site of injection and relatively little reached the node. In spite of this the cellular composition of peripheral lymph draining directly from the sites of injection showed no significant changes, and it was concluded that a 'depot' effect was unlikely to account for the heightened immune responses. These observations on the effects of beryllium are consistent with the view that its adjuvant action results from damage to intra-nodal macrophages, and that factors released from such cells caused intense immunoblastic proliferation.
Full text
PDF

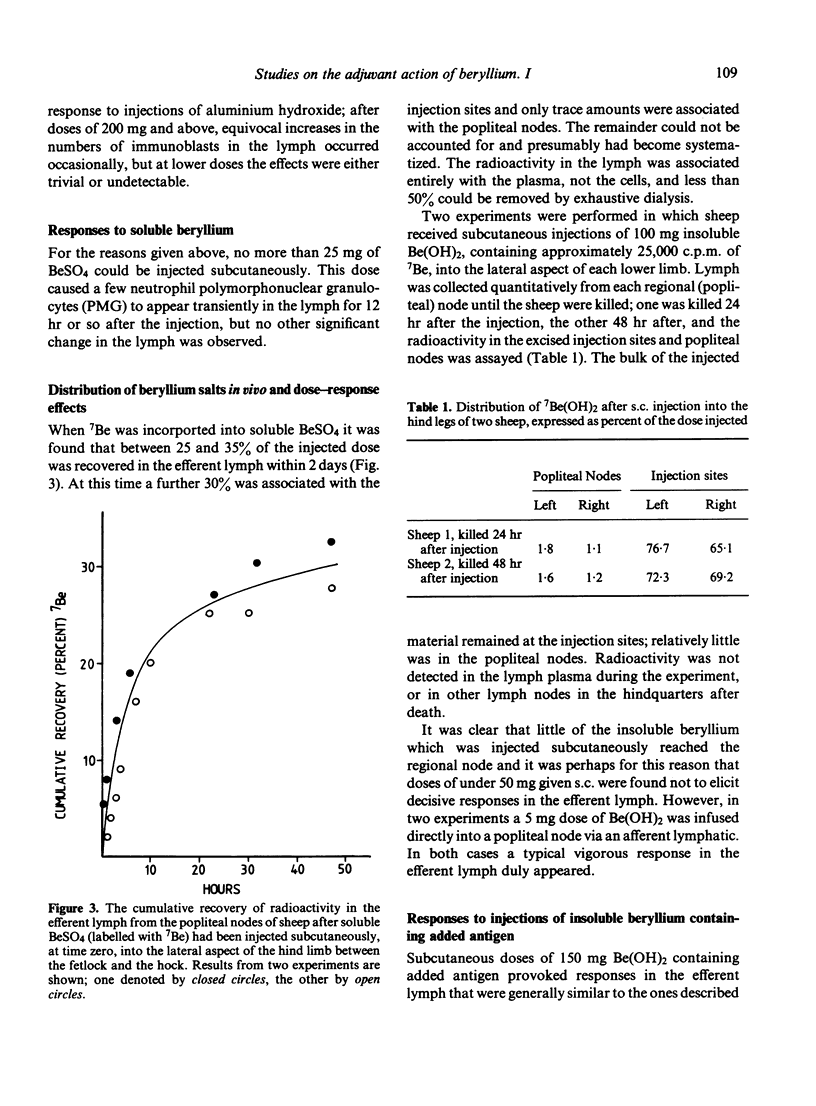
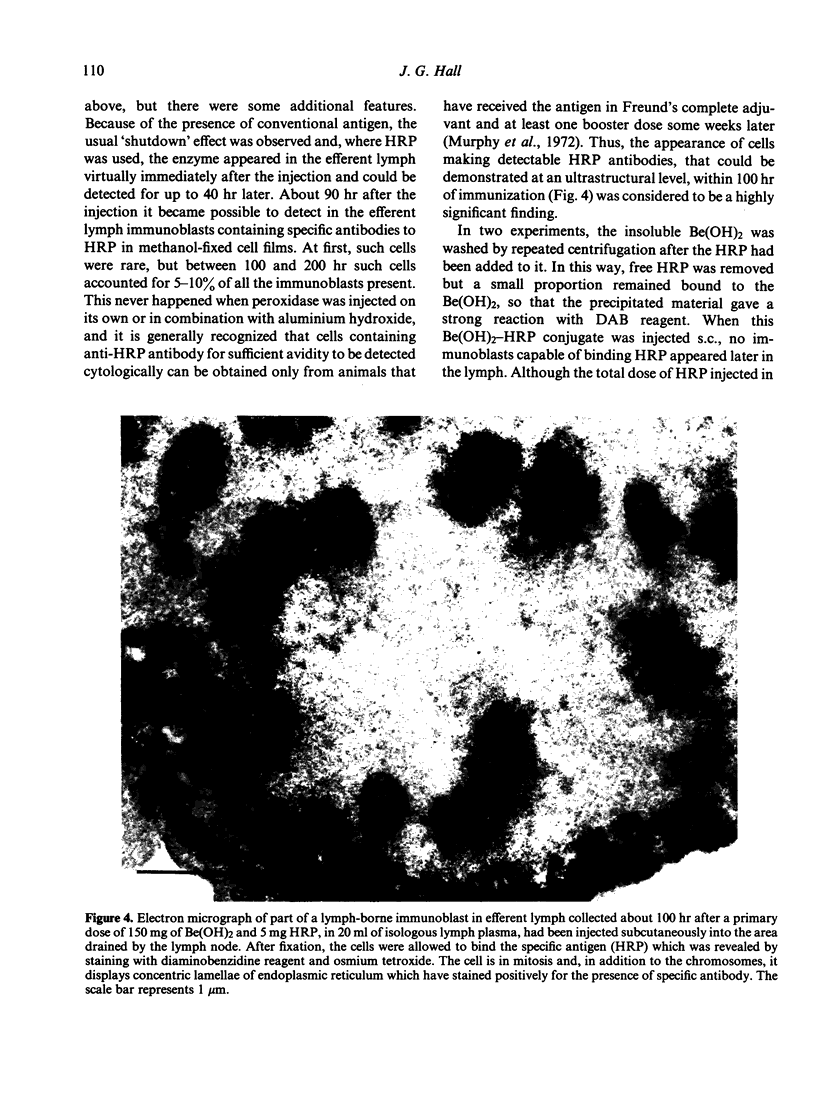



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dinsdale D., Skilleter D. N., Seawright A. A. Selective injury to rat liver Kupffer cells caused by beryllium phosphate: an explanation of reticuloendothelial blockade. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):383–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Taub R. N., Krantz A. R. The effect of localized injection of adjuvant material on the draining lymph node. II. Circulating lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970 May;18(5):663–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The lymph-borne cells of the immune response. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Jul;48:235–247. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The output of cells in lymph from the popliteal node of sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:360–369. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. A method for collecting lymph from the prefemoral lymph node of unanaesthetised sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Apr;52(2):200–205. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Birbeck M. S., Robertson D., Peppard J., Orlans E. The use of detergents and immunoperoxidase reagents for the ultrastructural demonstration of internal immunoglobulin in lymph cells. J Immunol Methods. 1978;19(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Hopkins J., Orlans E. Studies on the lymphocytes of sheep. III. Destination of lymph-borne immunoblasts in relation to their tissue of origin. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Jan;7(1):30–37. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Hopkins J., Reynolds J. Studies of efferent lymph cells from nodes stimulated with oxazolone. Immunology. 1980 Feb;39(2):141–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Morris B. The immediate effect of antigens on the cell output of a lymph node. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Aug;46(4):450–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Parry D., Smith M. E. Antibody production by lymph-borne immunoblasts following subcutaneous injection into xenogeneic recipients. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):625–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Hay J. B., Morris B., Bessis M. C. Ultrastructural analysis of antibody synthesis in cells from lymph and lymph nodes. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jan;66(1):25–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvaggio J. E., Flax M. H., Leskowitz S. Studies in immunization. 3. The use of beryllium as a granuloma-producing agent in Freund's adjuvant. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):846–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D. Granuloma formation in normal guinea pigs injected intradermally with aluminum and zirconium compounds. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Jun;68(6):336–340. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12496358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A., Allison A. C. A role of macrophages in the stimulation of immune responses by adjuvants. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]