Abstract
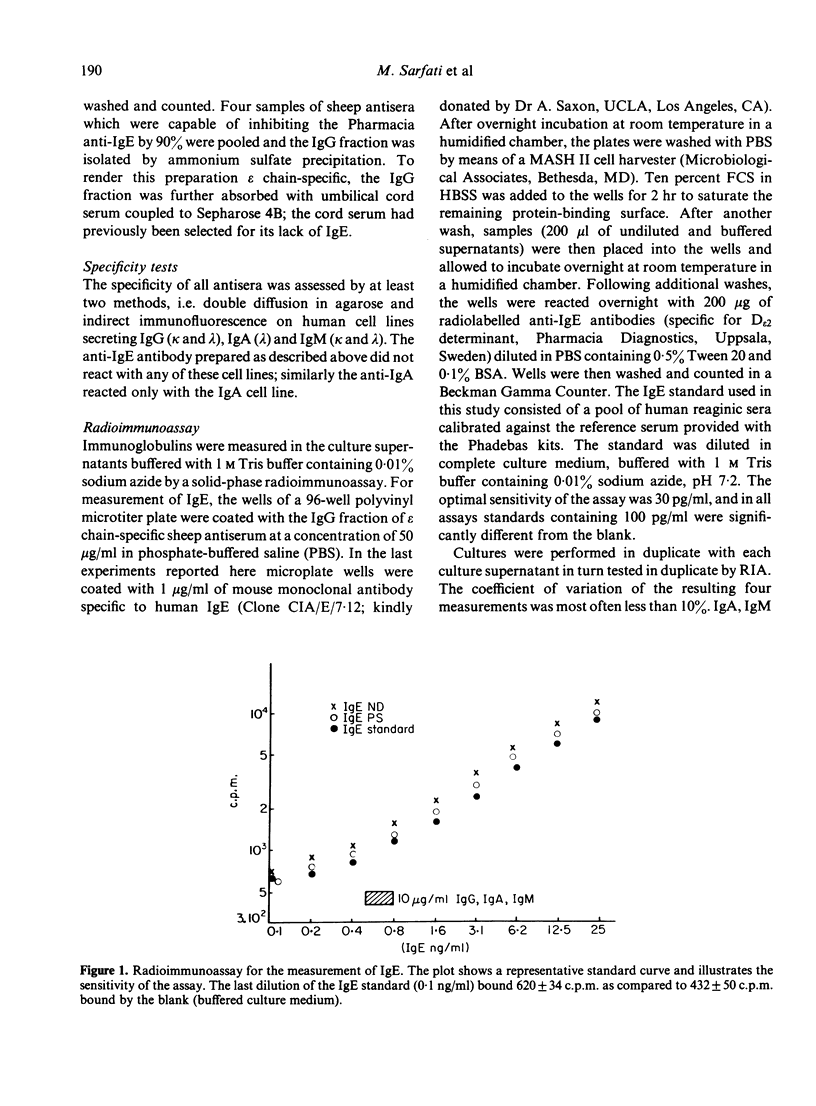
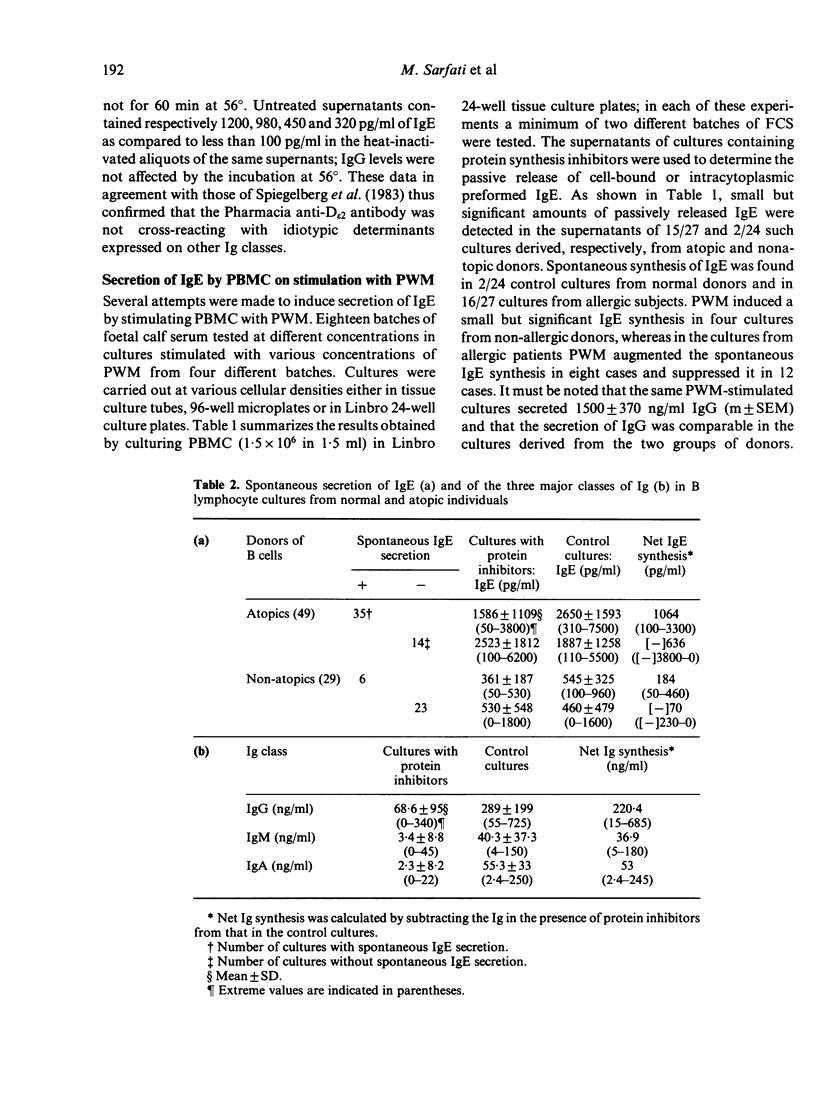
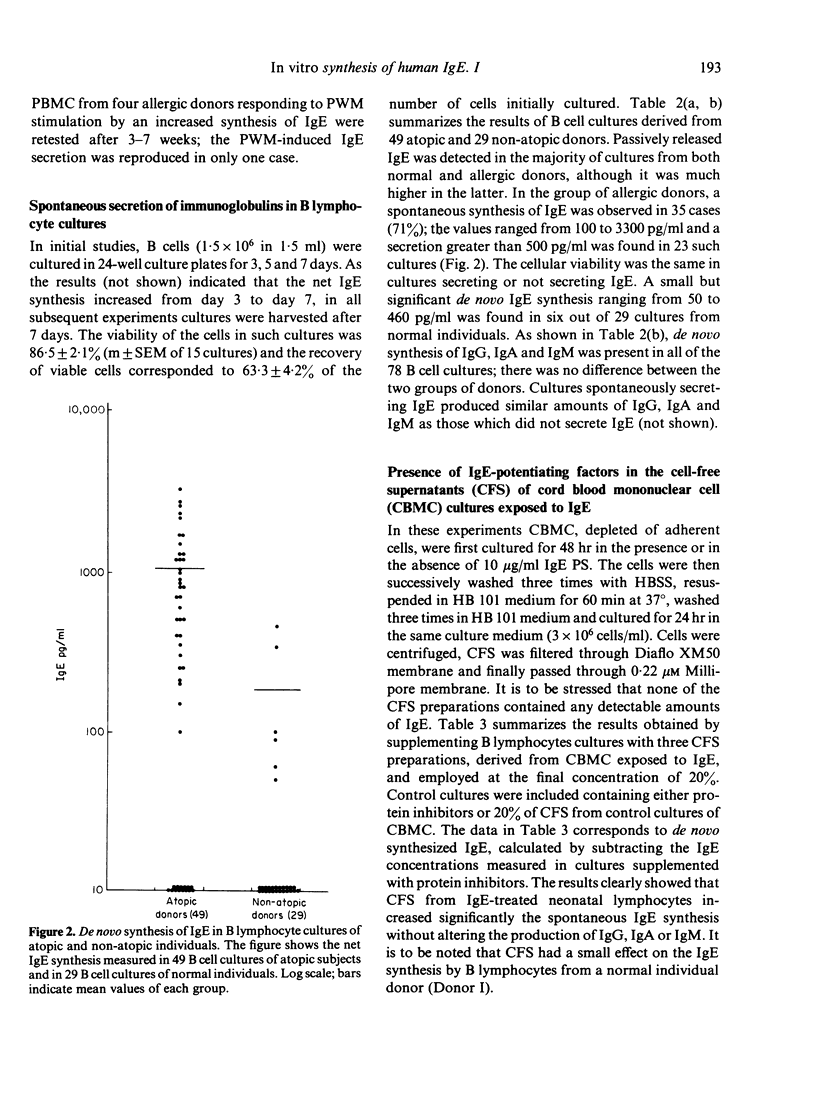
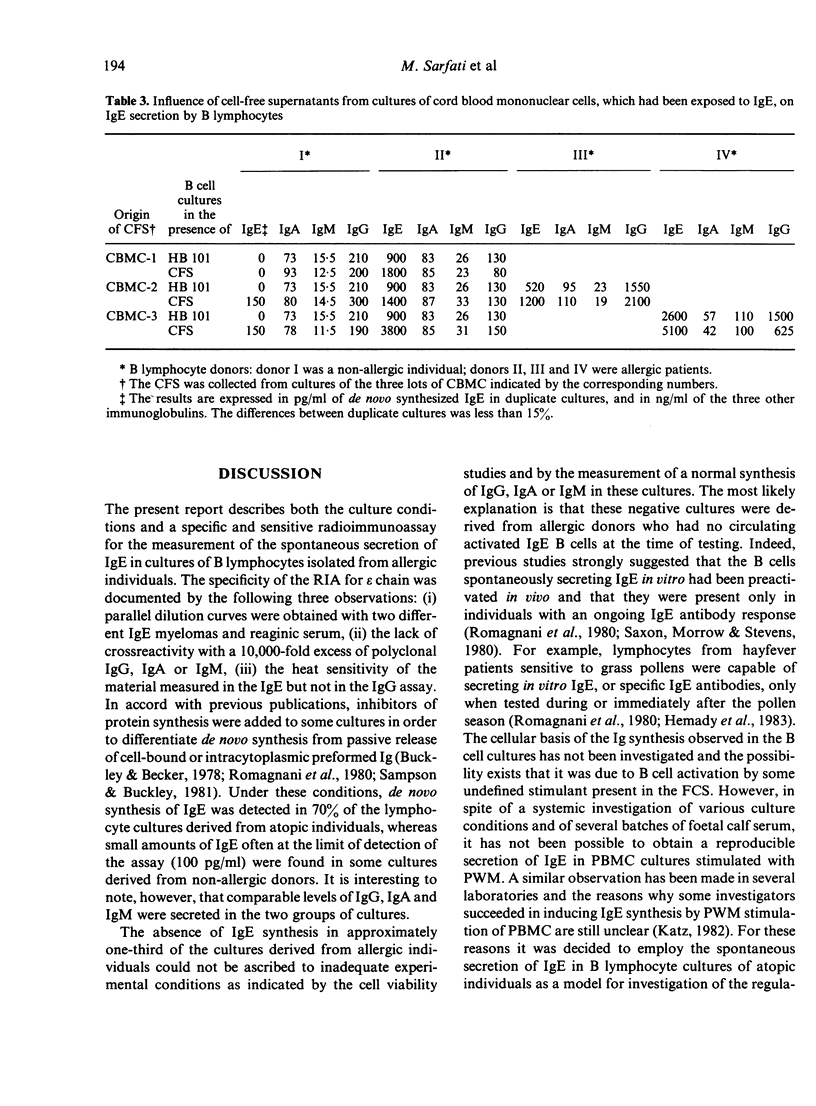
In view of the controversial data in the literature regarding the in vitro IgE synthesis by human lymphocytes, the conditions for culture of lymphocytes and the methodology for measurement of the IgE produced are described in detail. In the absence of any added mitogen, enriched B cell preparations derived from 70% of allergic donors actively secreted 100 to 3200 pg/ml of IgE after culture for 7 days, at which time the cell viability was higher than 85%. In comparable B cell cultures derived from non-allergic donors, only trace amounts of de novo synthesized IgE were detected in 20% of the cases. All B cell cultures actively secreted IgG, IgA, IgM and there was no apparent relationship between the secretion of IgE and that of the other classes of Ig. By contrast, the synthesis of IgE by unfractionated peripheral blood mononuclear cells of allergic individuals, which were stimulated with pokeweed mitogen (PWM) under several experimental conditions, was not consistently reproducible, i.e. the spontaneous synthesis of IgE in such cultures was either suppressed or enhanced by PWM. The most important finding was that the secretion of IgE was selectively enhanced by supplementing the B cell cultures with cell-free supernatants (CFS) of cultures of neonatal lymphocytes which had been preincubated with 10 micrograms/ml IgE. It is, therefore, concluded that B cell cultures from allergic individuals constitute an appropriate model for investigations of the mechanisms underlying the regulation of human IgE synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazaral M., Orgel H. A., Hamburger R. N. IgE levels in normal infants and mothers and an inheritance hypothesis. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):794–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow. Introduction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:7–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiser P. M., Buckley R. H. Human IgE biosynthesis in vitro: studies with atopic and normal blood mononuclear cells and subpopulations. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1788–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausset P., Delespesse G., Hubert C., Kennes B., Govaerts A. In vitro response of subpopulations of human lymphocytes. II. DNA synthesis induced by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):446–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Colten H. R., Schneeberger E., Merler E. Cooperation between human thymus-derived and bone marrow-derived lymphocytes in the antibody response to ragweed antigen E in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):386–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemady Z., Blomberg F., Gellis S., Rocklin R. E. IgE production in vitro by human blood mononuclear cells: a comparison between atopic and nonatopic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Mar;71(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Sandberg K. Formation of IgE binding factors by human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1692–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H. IgE antibody responses in vitro: from rodents to man. Prog Allergy. 1982;32:105–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman H. S. Allergy in the newborn: skin test reactions confirmed by the Prausnitz-Küstner test at birth. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):363–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. IgE class-specific suppressor T cells and regulation of the IgE response. Prog Allergy. 1982;32:265–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman N. I. Predictive value of high IgE levels in children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Jul;65(4):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Taylor R. B. General methods for the study of cells and serum during the immune response: the response to dinitrophenyl in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):473–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F. B., Bousquet J., Greillier P., Robinet-Levy M., Coulomb Y. Comparison of cord blood immunoglobulin E concentrations and maternal allergy for the prediction of atopic diseases in infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jun;65(6):422–430. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Hiravonen T., Gitlin D. Synthesis of IgE by the human conceptus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Sep;52(3):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Coppleson L. W. A THREE-CELL INTERACTION REQUIRED FOR THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):542–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Zuraw B. L., O'Hair C. H., Katz D. H. Stimulation of primary in vitro IgE antibody responses in culture of human peripheral mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1574–1581. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Suszko I. M., Hsu C. C., Roberts M., Oh S. H. In vitro production of IgE by lymphocytes from a patient with hyperimmunoglobulinaemia E, eosinophilia and increased lymphocytes carrying surface IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):265–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A. Local production of IgG, IgA and IgE antibodies in grass pollen hay fever. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2218–2225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryjma J., Muñoz J., Virella G., Fudenberg H. H. Evaluation of IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, and IgE secretion by human peripheral blood lymphocytes in cultures stimulated with pokeweed mitogen and Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajs J., Finnström O., Wesström G. Aortic aneurysm developing after umbilical artery catheterization. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Jul;65(4):495–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Maggi E., Del Prete G. F., Ricci M. IgE synthesis in vitro induced by T cell factors from patients with elevated serum IgE levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):85–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Maggi E., Del Prete G. F., Troncone R., Ricci M. In vitro production of IgE by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. I. Rate of IgE biosynthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Oct;42(1):167–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Buckley R. H. Human IgE synthesis in vitro: a reassessment. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saryan J. A., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Induction of human IgE synthesis by a factor derived from T cells of patients with hyper-IgE states. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Morrow C., Stevens R. H. Subpopulations of circulating B cells and regulatory T cells involved in in vitro immunoglobulin E production in atopic patients with elevted serum immunoglobulin E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1457–1468. doi: 10.1172/JCI109810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Stevens R. H. Stimulation and regulation of human IgE production in vitro using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Dec;14(4):474–488. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Lymphocytes bearing Fc receptors for IgE. Immunol Rev. 1981;56:199–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb01052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Plummer J. M., Ruedi J., Thompson L. F., Mellon M. H., Zeiger R. S. Lack of pokeweed mitogen-induced IgE formation in vitro by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: detection of cross-reacting idiotypic determinants on polyclonal Ig by antibodies to a single IgE myeloma protein. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3001–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D. D., Orgel H. A., Hamburger R. N., Reid R. T. Development of IgE in newborn human infants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Aug;48(2):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjio A. H., Hull W. M., Gleich G. J. Production of human immunoglobulin E antibody in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):2131–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil G. J., Hussain R., Kumaraswami V., Tripathy S. P., Phillips K. S., Ottesen E. A. Prenatal allergic sensitization to helminth antigens in offspring of parasite-infected mothers. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1124–1129. doi: 10.1172/JCI110862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuraw B. L., Nonaka M., O'Hair C., Katz D. H. Human IgE antibody synthesis in vitro: stimulation of IgE responses by pokeweed mitogen and selective inhibition of such responses by human suppressive factor of allergy (SFA). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1169–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


