Abstract
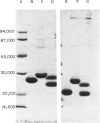
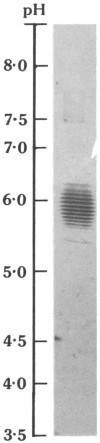
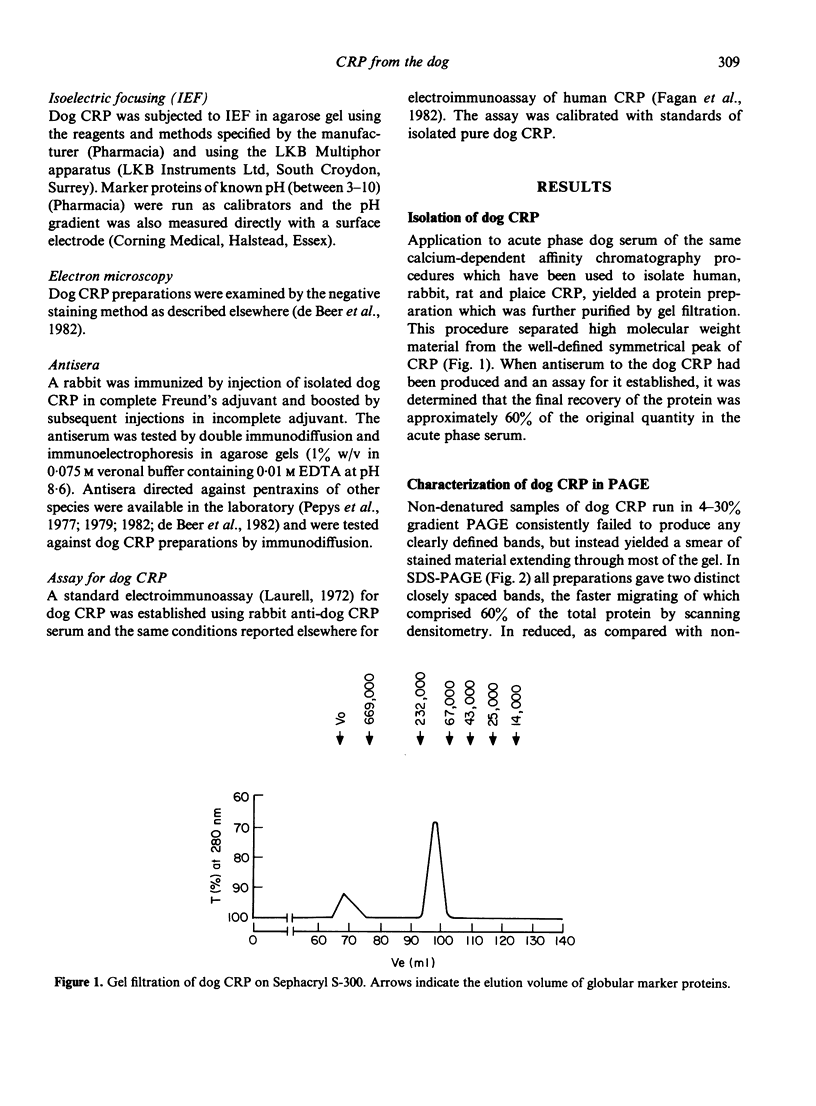
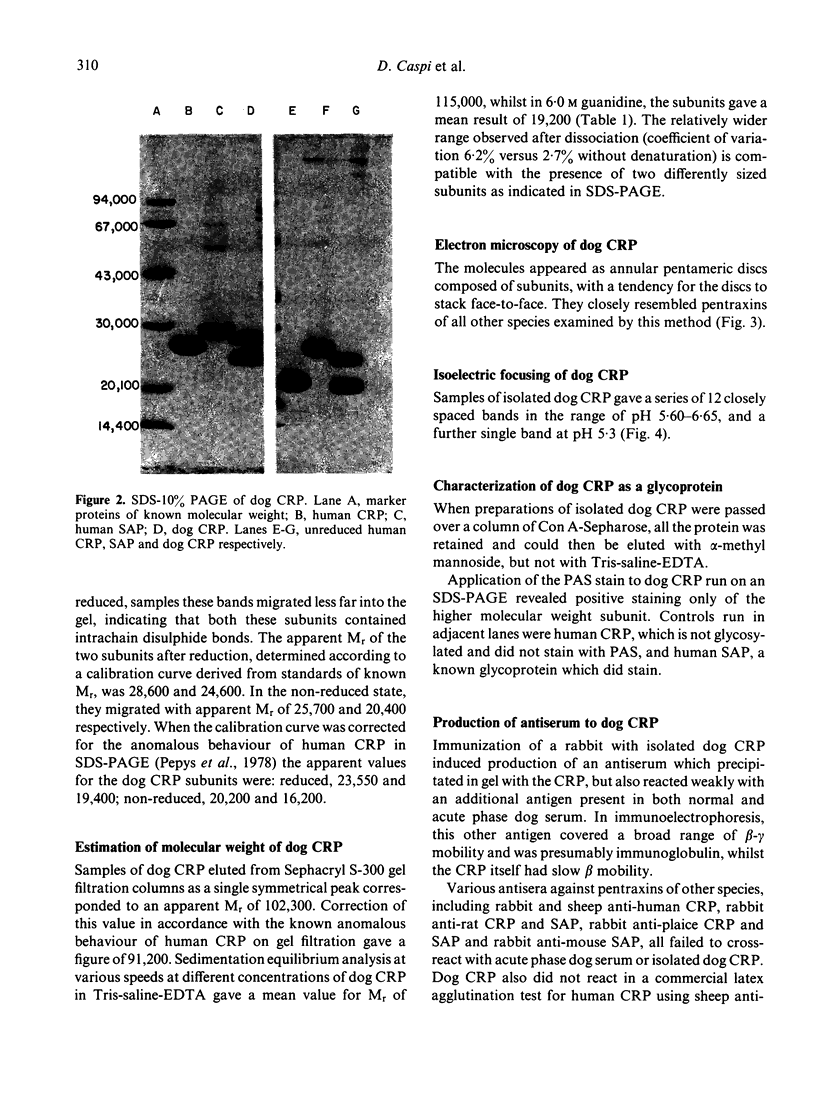
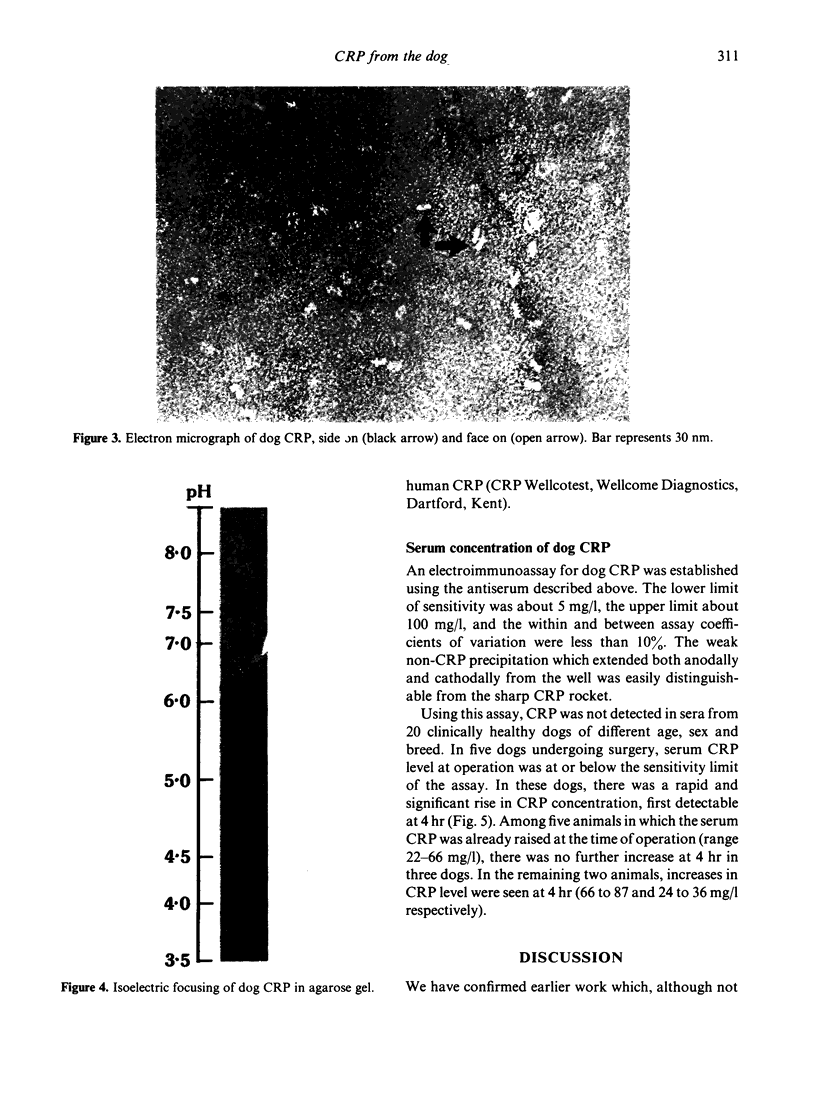
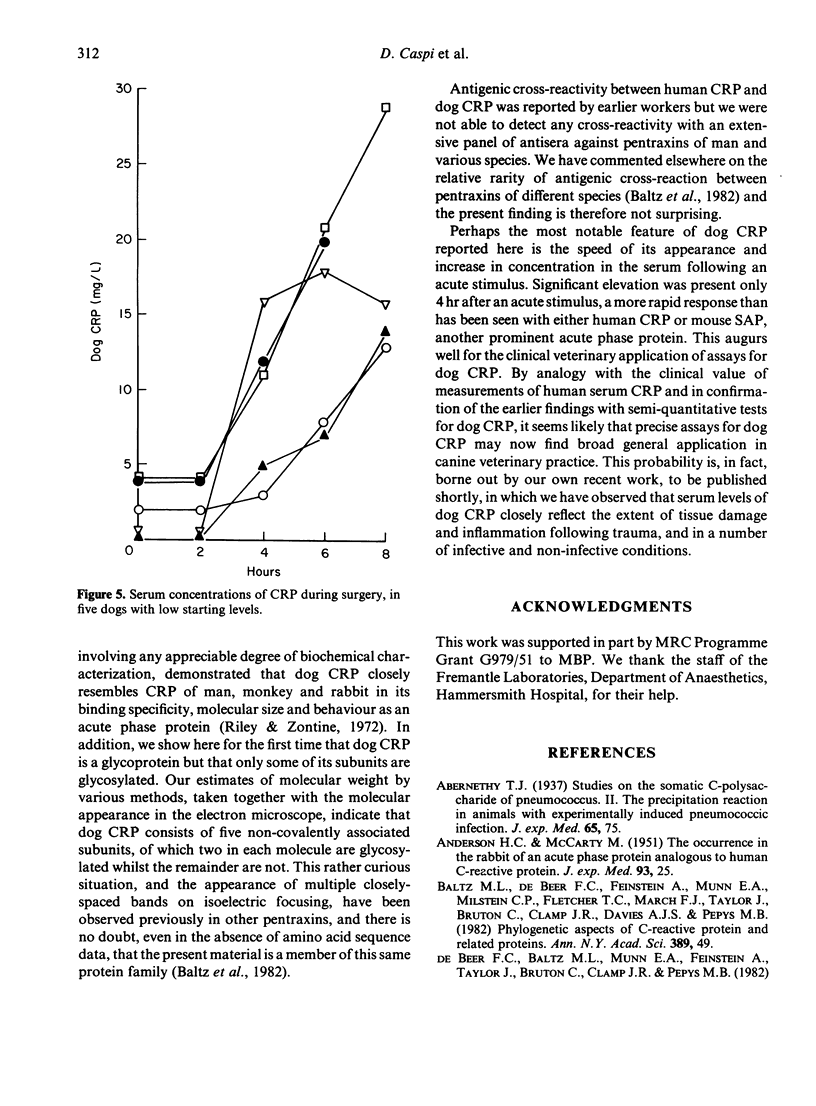
Using calcium-dependent affinity chromatography on Sepharose-bearing, covalently-coupled pneumococcal C-polysaccharide, a protein was isolated from the serum of dogs that had undergone general anaesthesia and major surgery. This protein was confirmed as the canine analogue of C-reactive protein (CRP) in other species by virtue of its electron microscopic appearance, subunit composition and behaviour as an acute phase reactant. Dog CRP had an apparent molecular weight of approximately 100,000 and was composed of five subunits of approximately 20,000 MW each. Two of the five subunits in each molecule were glycosylated. Negatively stained preparations had the typical cyclic pentameric disc-like structure of proteins of the pentraxin family, and in some preparations had a tendency to form stacks. Serum from normal healthy dogs of various strains usually contained less than 5 mg/l of CRP but, following the stimulus of major surgery, an increase in the CRP concentration was first detected at 4 hr.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON H. C., McCARTY M. The occurrence in the rabbit of an acute phase protein analogous to human C reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1951 Jan;93(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Feinstein A., Munn E. A., Milstein C. P., Fletcher T. C., March J. F., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R. Phylogenetic aspects of C-reactive protein and related proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:49–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillman R. C., Coles E. H. A canine serum fraction analogous to human C-reactive protein. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Nov;27(121):1769–1775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Dyck R. F., Maton P. N., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S., Petrie A., Pepys M. B. Serum levels of C-reactive protein in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;12(4):351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb02244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTSCHLICH E., STETSON C. A., Jr Immunologic cross-reactions among mammalian acute phase proteins. J Exp Med. 1960 Apr 1;111:441–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Friedenson B., Gewurz H., Painter R. H., Hofmann T., Shelton E. Characterization of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent C1t as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M., Gomer K., Davies A. J., Doenhoff M. Serum amyloid P-component is an acute-phase reactant in the mouse. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):259–261. doi: 10.1038/278259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Ashley M. J. Isolation of C-reactive protein by affinity chromatography. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Fletcher T. C., Richardson N., Munn E. A., Feinstein A. Analogues in other mammals and in fish of human plasma proteins, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):168–170. doi: 10.1038/273168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., De Beer F. C., Milstein C. P., March J. F., Feinstein A., Butress N., Clamp J. R., Taylor J., Bruton C., Fletcher T. C. C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component in the plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.), a marine teleost, are homologous with their human counterparts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;704(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. F., Zontine W. Further observations on the properties of dog C-reactive protein and the C-reactive protein response in the dog. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Nov;80(5):698–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]