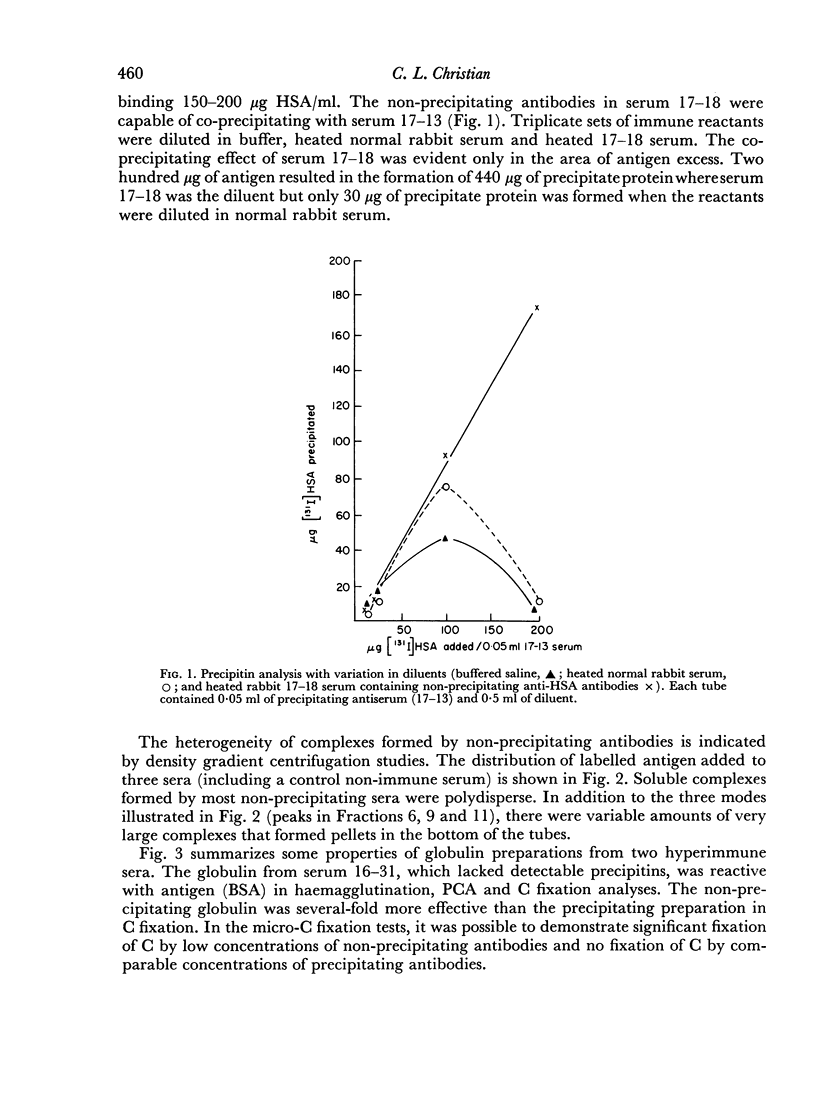
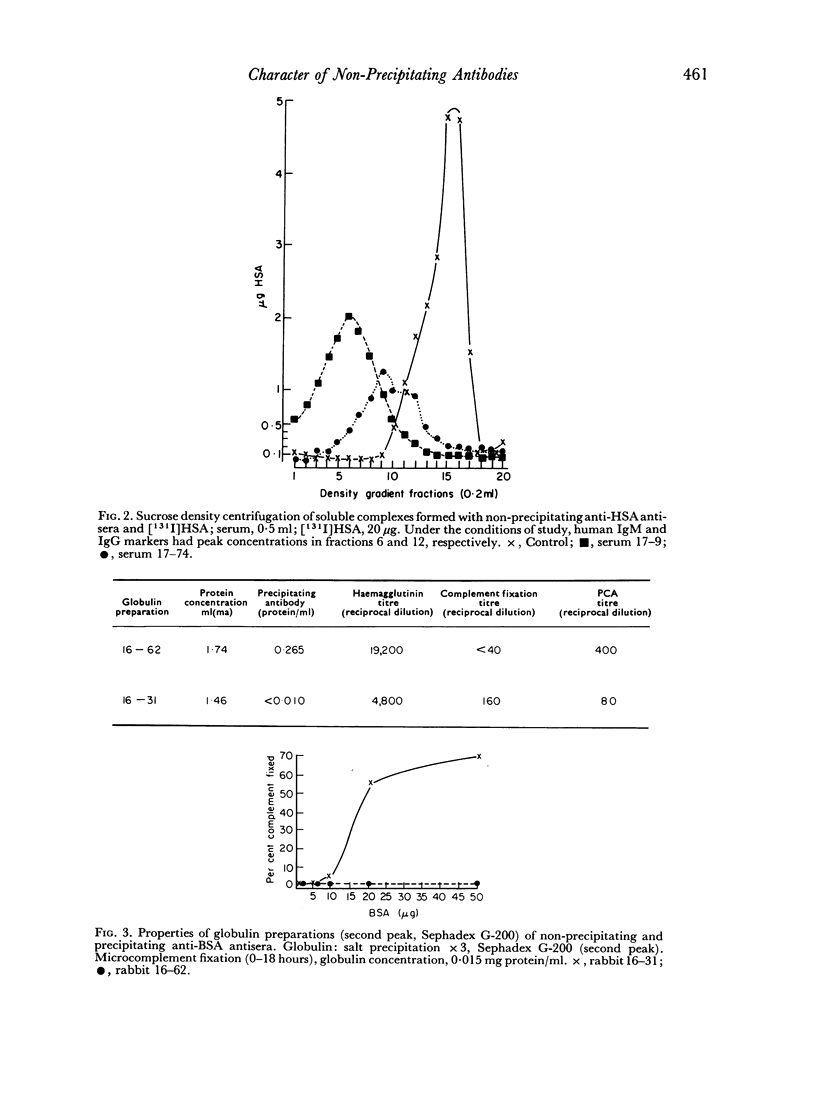
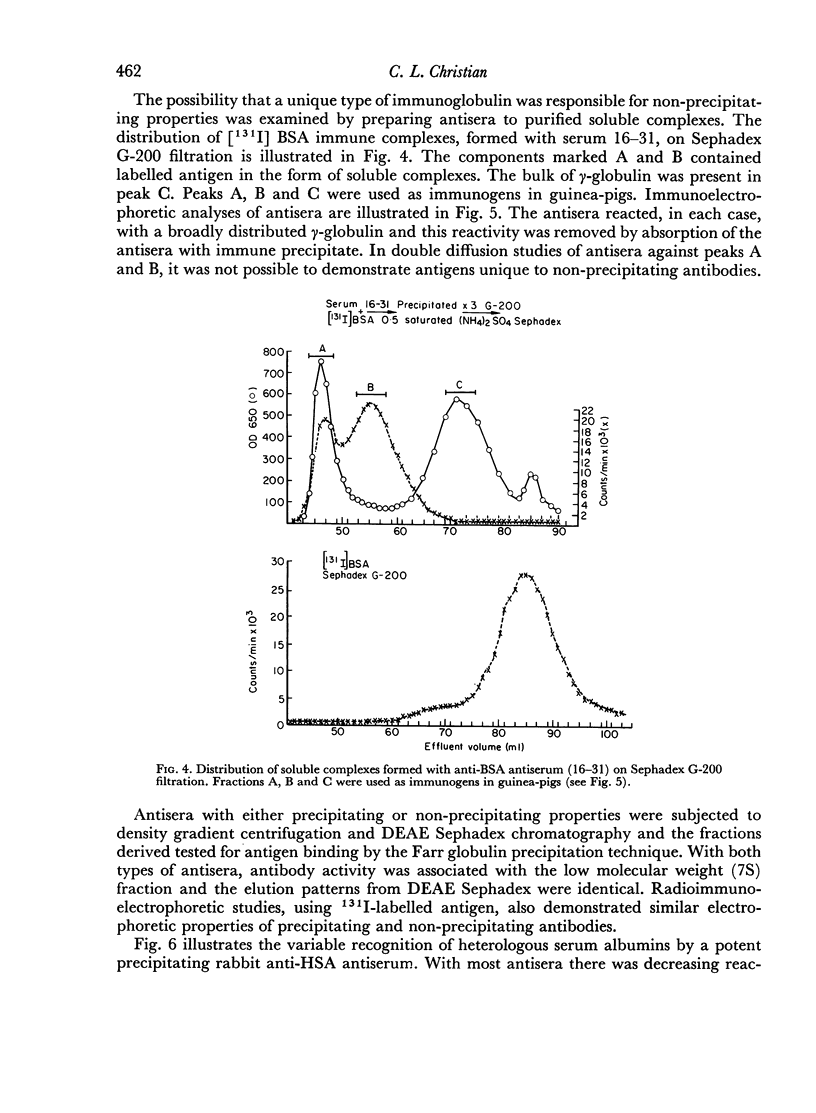
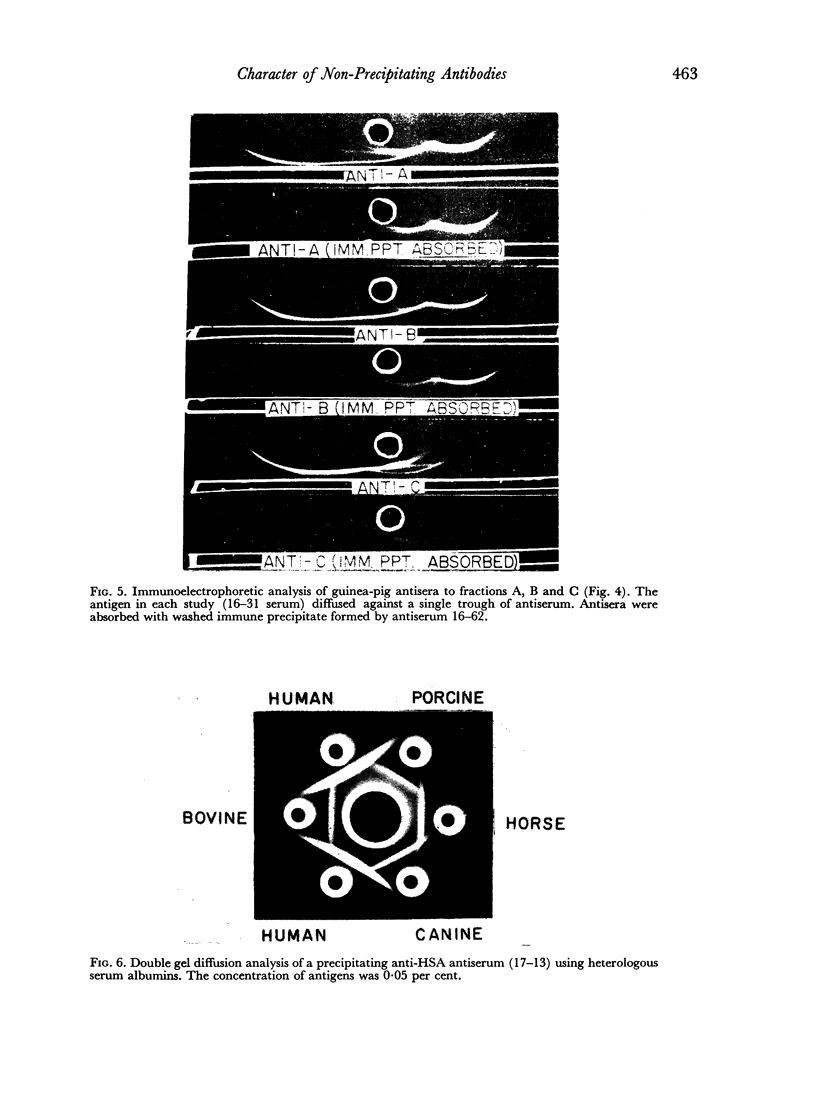
Abstract
A minority of rabbits immunized daily with soluble preparations of heterologous serum albumin respond with the formation of non-precipitating antibodies. Precipitating and non-precipitating antibodies, in the present study, were similar with regard to electrophoretic distribution, molecular size, and elution appearing on DEAE Sephadex. Guinea-pig antisera against purified non-precipitating antibodies did not recognize unique antigenic determinants. The present studies suggest that non-precipitating antibodies result from a limited recognition of multiple antigenic determinants on complex antigens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTIN P. Coexistence de complexes précipitants et non-précipitants dans la réaction entre la sérum-albumine humaine et les immunsérums spécifiques de chevaux; déductions quantitatives et conséquences théoriques. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1955;37(9-10):977–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. G., Harris T. N. Non-precipitating rabbit antibody to hapten: purification and properties. Immunology. 1967 Jan;12(1):75–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian C. L. Immune-complex disease. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 17;280(16):878–884. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904172801610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMUTH F. G., Jr, FLANAGAN C., MONTENEGRO M. R. The relationships between the chemical nature of the antigen, antigen dosage, rate of antibody synthesis and the occurrence of arteritis and glomerulonephritis in experimental hypersensitivity. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Sep;101(3):149–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z. [Quantitative studies in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis of the guinea pig]. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1952;3(2):162–174. doi: 10.1159/000227958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Haberkern R., Christian C. L. Experimental chronic glomerulitis. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):819–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbecke G. J., Benacerraf B. Tolerance in adult rabbits by repeated non-immunogenic doses of bovine serum albumin. Immunology. 1967 Aug;13(2):141–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O., MAURER P. H. The effect of complements on soluble antigen-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1957 Sep;79(3):211–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




