Abstract
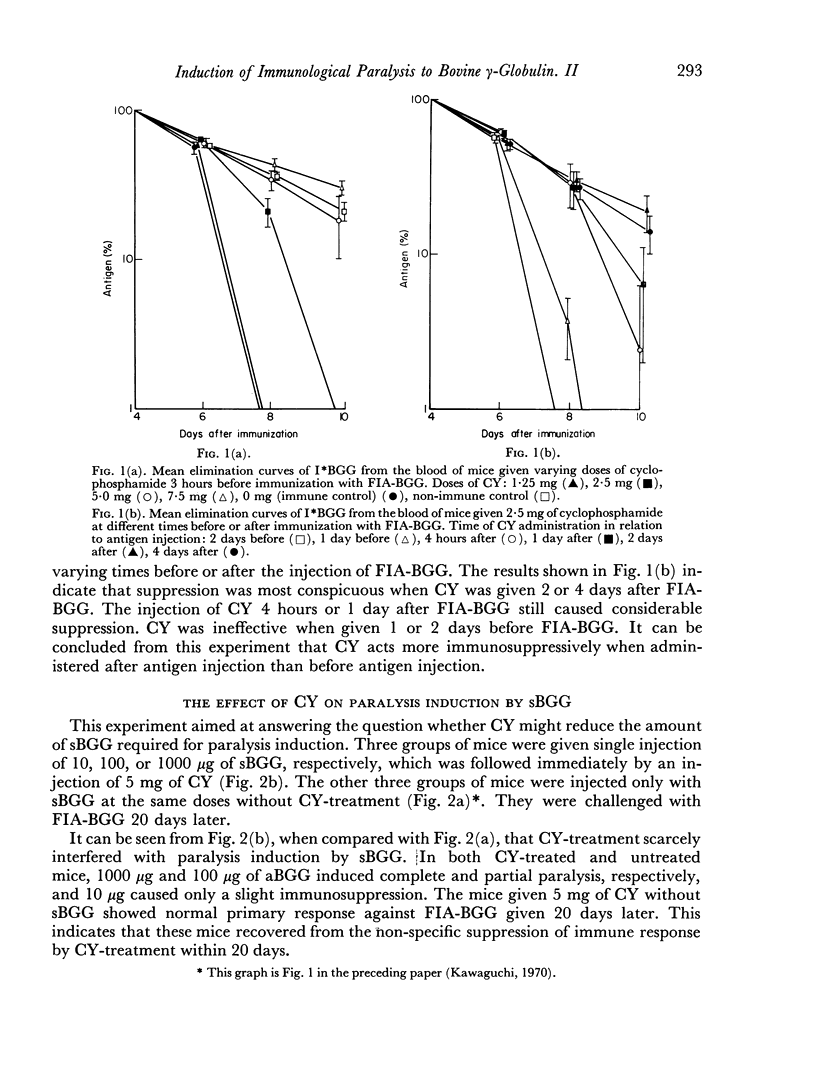
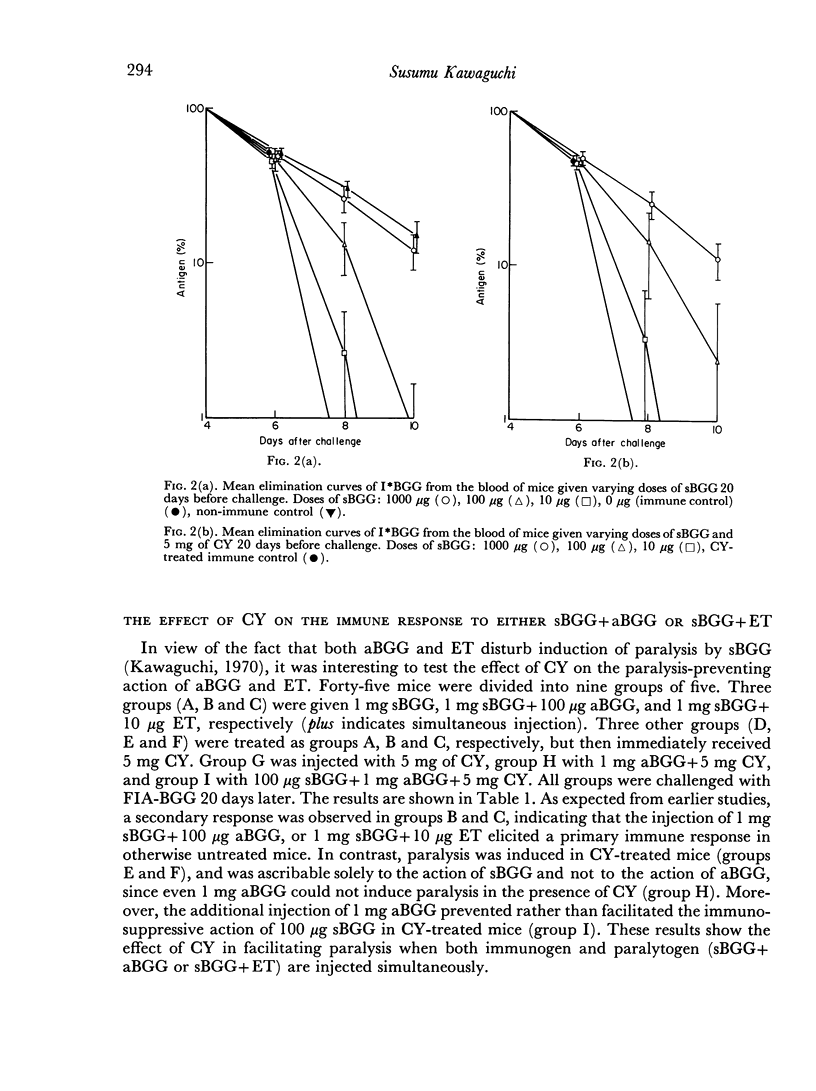
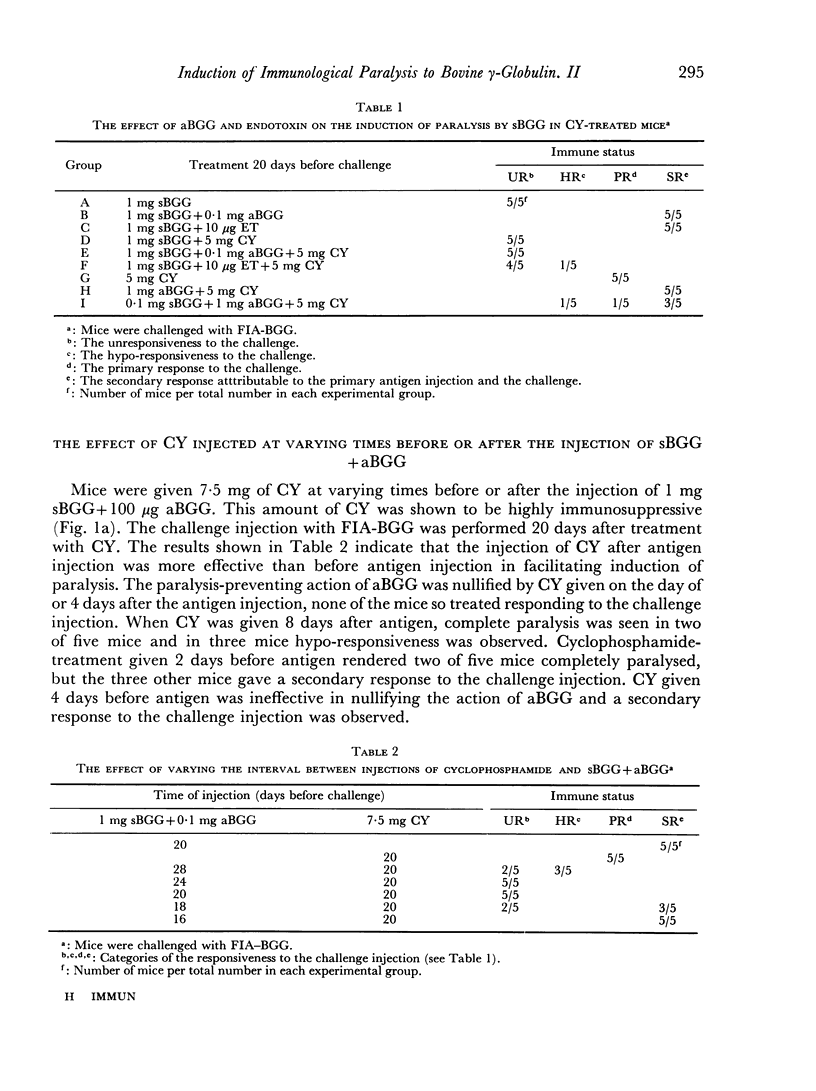
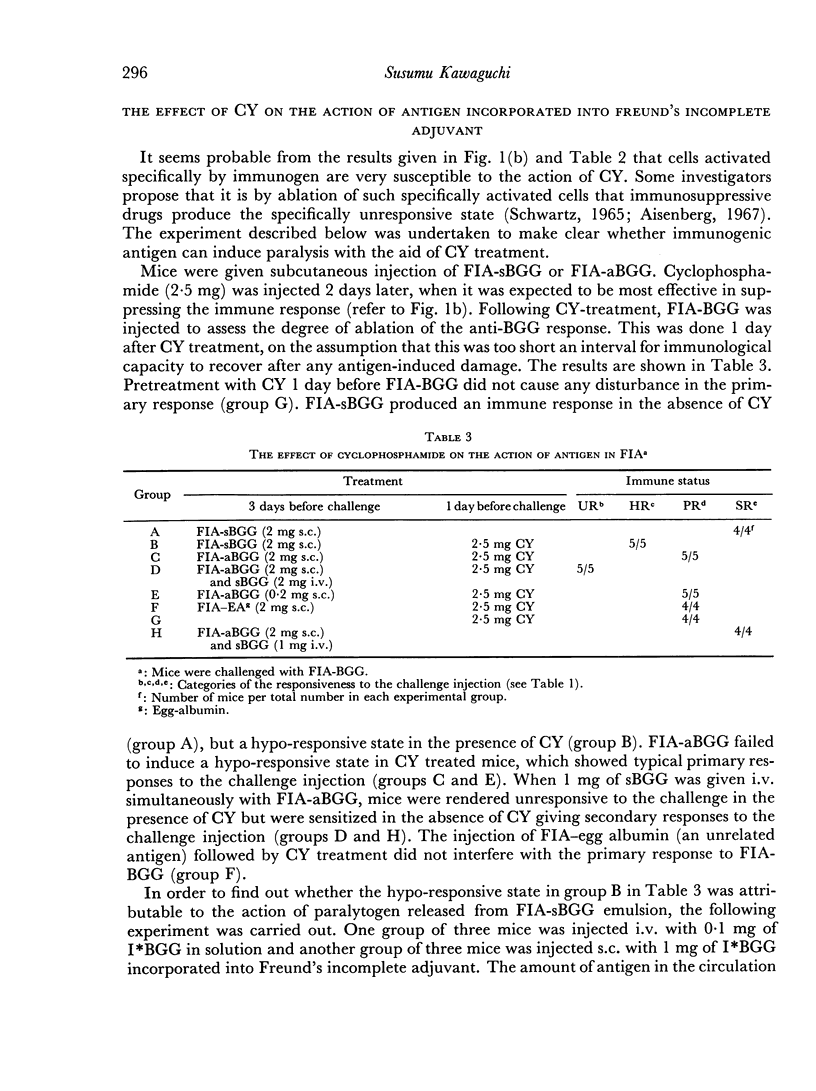
The immune response elicited by immunogenic forms of bovine γ-globulin (BGG), such as heat aggregated BGG (aBGG), BGG in Freund's incomplete adjuvant (FIA) or BGG plus endotoxin (ET), was interrupted by a single injection of cyclophosphamide. The amount of soluble BGG (sBGG) required to induce paralysis did not differ significantly between cyclophosphamide-treated mice and untreated mice. The injection of 1 mg sBGG together with 100 μg aBGG or 10 μg ET caused an immune response in normal mice but induced paralysis in cyclophosphamide-treated mice. However, without sBGG, the administration of aBGG suspension or aBGG in FIA could not induce paralysis, even with the aid of cyclophosphamide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisenberg A. C. Studies on cyclophosphamide-induced tolerance to sheep erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1967 May 1;125(5):833–845. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENBAUM M. C., BROWN I. N. DOSE-RESPONSE RELATIONSHIPS FOR AGENTS INHIBITING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Mitchison N. A. The mechanism of immunological paralysis. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:129–181. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRISCH A. W., DAVIES G. H. INHIBITION OF HEMAGGLUTININ SYNTHESIS BY CYTOXAN. Cancer Res. 1965 Jun;25:745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Feldman M. The role of macrophages in the induction of antibody in x-irradiated animals. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):197–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi S. Studies on the induction of immunological paralysis to bovine gamma-globulin in adult mice. I. The competition between immunogen and paralytogen. Immunology. 1970 Aug;19(2):277–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskowitz S. Tolerance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:157–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. The immunogenic capacity of antigen taken up by peritoneal exudate cells. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):1–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. A study of the 'termination' of tolerance to BSA with DNP-BSA in rabbits: relative affinities of the antibodies for the immunizing and the paralysing antigens. Immunology. 1967 Aug;13(2):147–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ R. S., DAMESHEK W. THE ROLE OF ANTIGEN DOSAGE IN DRUG-INDUCED IMMUNOLOGIC TOLERANCE. J Immunol. 1963 May;90:703–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


