Abstract
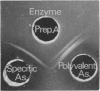
A specific antiserum to adult chicken liver cathepsin D was prepared by injecting rabbits with precipitin lines formed in agar gel between a purified enzyme preparation and a polyvalent antiserum. The specific antiserum was used to show the identity of cathepsin D from liver with that from spleen, heart, kidney, testis and brain of the adult, and from limb bones of the embryo chicken.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERLIN B. S., McKINNEY R. W. A simple device for making emulsified vaccines. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Oct;52(4):657–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTIN P. Application de la méthode d'Ouchterlony au système précipitant sérum albumine humaine-immunsérum de cheval. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1954;36(8):1021–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Lysosomal acid proteinase of rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1040601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A., FELL H. B. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 1. Effect of excess of vitamin A on the metabolism and composition of embryonic chick-limb cartilage grown in organ culture. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj0790497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN A. A., PARKMAN R. STUDIES WITH AN ANTIBODY TO RAT LYSOZYME. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:724–729. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudie R. B., Horne C. H., Wilkinson P. C. A simple method for producing antibody specific to a single selected diffusible antigen. Lancet. 1966 Dec 3;2(7475):1224–1226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENION W. F., SUTHERLAND E. W. Immunological differences of phosphorylases. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGEACHIN R. L., REYNOLDS J. M. Differences in mammalian amylases demonstrated by enzyme inhibition with specific antisera. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1456–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSELBAUM J. S., BODANSKY O. Reactions of lactic dehydrogenase from various rabbit organs with antirabbit muscle lactic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3276–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLAMOWITZ M., BODANSKY O. Tissue sources of human serum alkaline phosphatase, as determined by immunochemical procedures. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1433–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., GALLOP R. C., TOZER B. T. THE PRODUCTION OF SPECIFIC RABBIT ANTIBODIES BY INJECTING INDIVIDUAL ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES SEPARATED FROM MIXED ANTIGENS. Immunology. 1964 Mar;7:111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers C. A., James J. M. Specific antibodies produced against antigens of agar-gel precipitates. Immunology. 1967 Dec;13(6):547–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIEL J. Characterization of enzymes in specific immuneprecipitates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 8;103:956–979. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston P. D., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T. Specific inhibition of cartilage breakdown. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):285–286. doi: 10.1038/222285b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]