Abstract
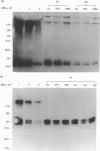
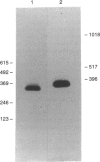
Human astrocytes express CD59, decay accelerating factor and membrane cofactor protein to restrict the damaging effect of complement (C) activation on their cell surface. 5I2 antigen (5I2 Ag) is the functional analogue of the latter two proteins in rats. We here demonstrate the surface expression on rat astrocytes of CD59 and 5I2 Ag and use sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting to confirm their identity and to quantify expression. Rat CD59 (MW 20,000) was expressed at 720 x 10(3) molecules per cell and 5I2 Ag (MW 58,000 and 64,000) at 625 x 10(3) molecules per cell. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using specific oligonucleotide primers demonstrated expression of mRNA for each protein. Twenty-four-hour stimulation with inflammatory cytokines (interferon-gamma, tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukins-1 beta, -2 and -6) or phorbol myristate acetate had no significant effect on the level of expression of either protein as determined by Western blotting. Lysis caused by classical pathway activation of C in human or rat serum was enhanced by blocking the function of CD59 and 5I2 Ag on rat astrocytes with monoclonal antibodies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston D. A., Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K., Wilkins P., Cole G., Thomas N. D., Jasani B. Immunocytochemical localization of the terminal complement complex in multiple sclerosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Jul-Aug;15(4):307–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J., Waldmann H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabashi K., Okada N., Matsuo S., Yamamoto T., Morgan B. P., Okada H. Tissue distribution of complement regulatory membrane proteins in rats. Immunology. 1994 Mar;81(3):444–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasque P., Fontaine M., Morgan B. P. Complement expression in human brain. Biosynthesis of terminal pathway components and regulators in human glial cells and cell lines. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4726–4733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasque P., Ischenko A., Legoedec J., Mauger C., Schouft M. T., Fontaine M. Expression of the complement classical pathway by human glioma in culture. A model for complement expression by nerve cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25068–25074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. L., Sadlon T. A., Wesselingh S. L., Russell S. M., Johnstone R. W., Purcell D. F. Human astrocytes express membrane cofactor protein (CD46), a regulator of complement activation. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Feb;36(2-3):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90051-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. L., Sadlon T., Hefford C., Adrian D. Expression of CD59, a regulator of the membrane attack complex of complement, on human astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Jun;18(4):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90098-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. R., Piddlesden S. J., Williams J. D., Harrison R. A., Morgan B. P. Isolation and characterization of a membrane protein from rat erythrocytes which inhibits lysis by the membrane attack complex of rat complement. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):169–176. doi: 10.1042/bj2840169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. U., Kinoshita T., Molina H., Hourcade D., Seya T., Wagner L. M., Holers V. M. Mouse complement regulatory protein Crry/p65 uses the specific mechanisms of both human decay-accelerating factor and membrane cofactor protein. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):151–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Lavoie S., Nussenzweig V. Regulatory proteins for the activated third and fourth components of complement (C3b and C4b) in mice. II. Identification and properties of complement receptor type 1 (CR1). J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2564–2570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Sallee C., Dehoff M., Foley S., Molina H., Holers V. M. Mouse Crry/p65. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies and the tissue distribution of a functional homologue of human MCP and DAF. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Morgan B. P., Scolding N. J., Wilkins P., Piddlesden S., Compston D. A. The role of complement in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Brain. 1989 Aug;112(Pt 4):895–911. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.4.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liszewski M. K., Atkinson J. P. Membrane cofactor protein. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;178:45–60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77014-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Mallat M. Primary cultures of murine astrocytes produce C3 and factor B, two components of the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Akiyama H., Itagaki S., McGeer E. G. Activation of the classical complement pathway in brain tissue of Alzheimer patients. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Dec 15;107(1-3):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90843-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Morgan B. P., Davies A., Daniels R. H., Olavesen M. G., Waldmann H., Lachmann P. J. Human protectin (CD59), an 18,000-20,000 MW complement lysis restricting factor, inhibits C5b-8 catalysed insertion of C9 into lipid bilayers. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Waldmann H., Lachmann P. J. Distribution of protectin (CD59), a complement membrane attack inhibitor, in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Meri S. Membrane proteins that protect against complement lysis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;15(4):369–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01837366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose M., Katoh M., Okada N., Kyogoku M., Okada H. Tissue distribution of HRF20, a novel factor preventing the membrane attack of homologous complement, and its predominant expression on endothelial cells in vivo. Immunology. 1990 Jun;70(2):145–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada R., Fujita T., Okada H. A novel membrane glycoprotein capable of inhibiting membrane attack by homologous complement. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):205–208. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddlesden S. J., Morgan B. P. Killing of rat glial cells by complement: deficiency of the rat analogue of CD59 is the cause of oligodendrocyte susceptibility to lysis. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Nov-Dec;48(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddlesden S. J., Storch M. K., Hibbs M., Freeman A. M., Lassmann H., Morgan B. P. Soluble recombinant complement receptor 1 inhibits inflammation and demyelination in antibody-mediated demyelinating experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5477–5484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigg R. J., Galishoff M. L., Sneed A. E., 3rd, Kim D. Isolation and characterization of complement receptor type 1 from rat glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1993 Mar;43(3):730–736. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Cooper N. R., Webster S., Schultz J., McGeer P. L., Styren S. D., Civin W. H., Brachova L., Bradt B., Ward P. Complement activation by beta-amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10016–10020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rus H. G., Kim L. M., Niculescu F. I., Shin M. L. Induction of C3 expression in astrocytes is regulated by cytokines and Newcastle disease virus. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada C., Seno H., Dohi N., Takizawa H., Nonaka M., Okada N., Okada H. Molecular cloning of the rat complement regulatory protein, 5I2 antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 15;198(3):819–826. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolding N. J., Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K., Compston D. A. Complement mediated serum cytotoxicity against oligodendrocytes: a comparison with other cells of the oligodendrocyte-type 2 astrocyte lineage. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Jul;97(2-3):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer I., Schachner M. Monoclonal antibodies (O1 to O4) to oligodendrocyte cell surfaces: an immunocytological study in the central nervous system. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90477-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa H., Okada N., Okada H. Complement inhibitor of rat cell membrane resembling mouse Crry/p65. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanguri P., Koski C. L., Silverman B., Shin M. L. Complement activation by isolated myelin: activation of the classical pathway in the absence of myelin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3290–3294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler C., Ulvestad E., Bjørge L., Conti G., Williams K., Mørk S., Matre R. The expression of CD59 in normal human nervous tissue. Immunology. 1994 Aug;82(4):542–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Jones J. L., Barnum S. R. Expression of decay-accelerating factor (CD55), membrane cofactor protein (CD46) and CD59 in the human astroglioma cell line, D54-MG, and primary rat astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Sep;47(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]