Abstract
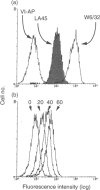
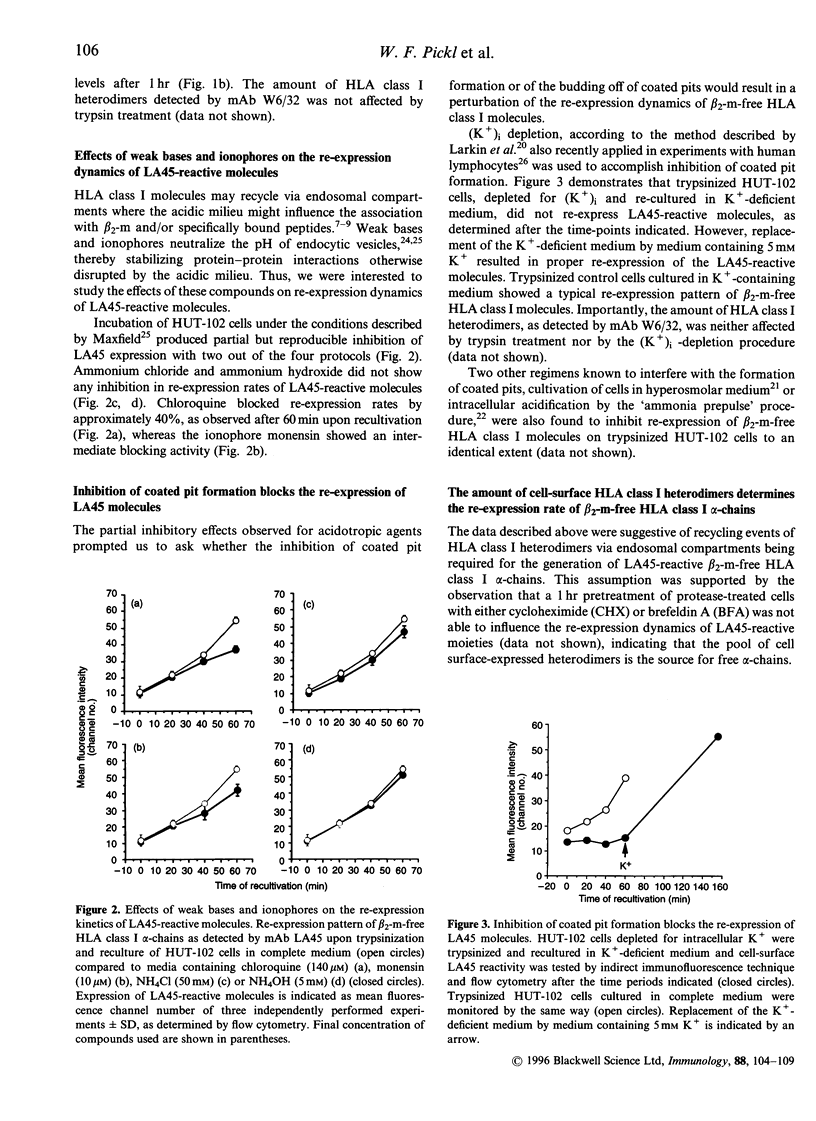
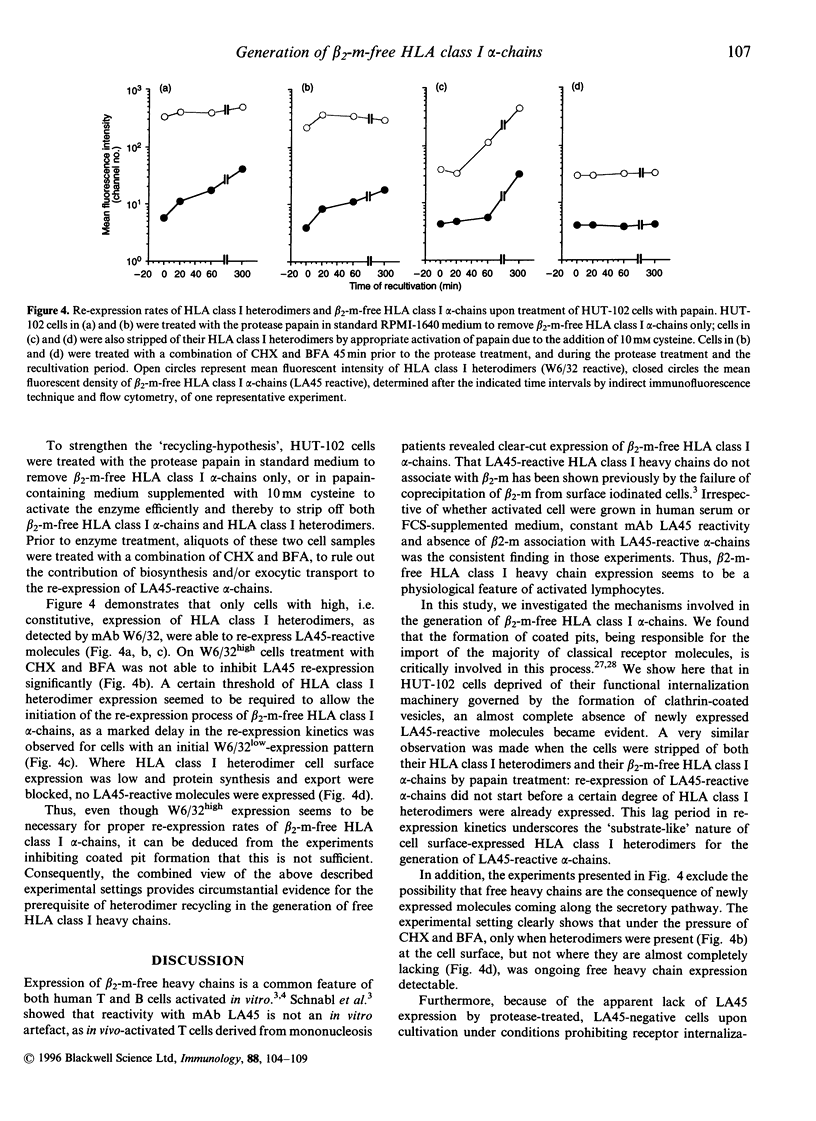
HLA class I molecules on activated T cells are expressed as heterodimers associated with beta 2-microglobulin (beta 2-m) and also beta 2-m-free HLA class I alpha-chains. Mechanisms leading to the expression of the activation associated beta 2-m-free HLA class I alpha-chains are poorly defined, however. Upon enzymatical removal of HLA class I alpha-chains on activated T cells, re-expression is observed within minutes upon reculture, reaching half-maximal levels within 1 hr. This process is independent of de novo protein synthesis and of export of newly synthesized proteins. Inhibition of the formation of coated pits by potassium depletion of cells abrogated the re-expression of HLA class I alpha-chains, suggesting that recycling events of HLA class I heterodimers via endosomal compartments are required for the generation of monoclonal antibody LA45-reactive alpha-chains. Furthermore, the rate of alpha-chain generation seems to be governed by the amount of cell surface-expressed HLA class I heterodimers. Taken together these findings suggest that beta 2-m-free HLA class I alpha-chains are generated during the process of class I heterodimer recycling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. J., Madrigal J. A., Parham P. Peptide binding to empty HLA-B27 molecules of viable human cells. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):74–77. doi: 10.1038/351074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaria S., Bushkin Y. CD8 and beta 2-microglobulin-free MHC class I molecules in T cell immunoregulation. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1993;23(2):61–69. doi: 10.1007/BF02592285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaria S., Schwab R., Bushkin Y. The origin and fate of beta 2m-free MHC class I molecules induced on activated T cells. Cell Immunol. 1992 Jun;142(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90272-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaria S., Schwab R., Gottesman S. R., Bushkin Y. Soluble beta 2-microglobulin-free class I heavy chains are released from the surface of activated and leukemia cells by a metalloprotease. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6689–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichholtz T., Vossebeld P., van Overveld M., Ploegh H. Activation of protein kinase C accelerates internalization of transferrin receptor but not of major histocompatibility complex class I, independent of their phosphorylation status. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22490–22495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Cerundolo V., Elvin J., Townsend A. Peptide-induced conformational change of the class I heavy chain. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):402–406. doi: 10.1038/351402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Cerundolo V., Townsend A. Short peptides assist the folding of free class I heavy chains in solution. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3121–3125. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Anderson R. G. Hypertonic media inhibit receptor-mediated endocytosis by blocking clathrin-coated pit formation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):389–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Effects of cytoplasmic acidification on clathrin lattice morphology. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):401–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman J. H., Jiang H., Matyus L., Edidin M., Pernis B. Endocytosis and dissociation of class I MHC molecules labeled with fluorescent beta-2 microglobulin. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1862–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Trowbridge I. S. Internalization and processing of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in human carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):508–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilondo M. M., Courtoy P. J., Geiger D., Carpentier J. L., Rousseau G. G., De Meyts P. Intracellular potassium depletion in IM-9 lymphocytes suppresses the slowly dissociating component of human growth hormone binding and the down-regulation of its receptors but does not affect insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G. Depletion of intracellular potassium arrests coated pit formation and receptor-mediated endocytosis in fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter M. L., Lubin M. Control of protein synthesis in human fibroblasts by intracellular potassium. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 15;105(2):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machy P., Truneh A., Gennaro D., Hoffstein S. Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules internalized via coated pits in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):724–726. doi: 10.1038/328724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal J. A., Belich M. P., Benjamin R. J., Little A. M., Hildebrand W. H., Mann D. L., Parham P. Molecular definition of a polymorphic antigen (LA45) of free HLA-A and -B heavy chains found on the surfaces of activated B and T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1085–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R. Weak bases and ionophores rapidly and reversibly raise the pH of endocytic vesicles in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):676–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mommaas A. M., Wijsman M. C., Verduijn W., Vermeer B. J., Claas F. M. Internalization of MHC class I molecules is a prerequisite for endocytosis of endorphin by lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):170–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers N. B., Lie W. R., Nett M., Rubocki R. J., Hansen T. H. The conformation of Ld induced by beta 2-microglobulin is fixed during de novo synthesis and irreversible by exchange or dissociation. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2751–2758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Dierx J., Ploegh H. L. The effect of anchor residue modifications on the stability of major histocompatibility complex class I-peptide interactions. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):840–845. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Momburg F., Hämmerling G. J. Selective and ATP-dependent translocation of peptides by the MHC-encoded transporter. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):769–771. doi: 10.1126/science.8342042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J., Quaranta V. Chloroquine affects biosynthesis of Ia molecules by inhibiting dissociation of invariant (gamma) chains from alpha-beta dimers in B cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1371–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten G. R., Bikoff E., Ribaudo R. K., Kozlowski S., Margulies D. H., Germain R. N. Peptide and beta 2-microglobulin regulation of cell surface MHC class I conformation and expression. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3723–3732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Neefjes J. J., Oorschot V., Ploegh H. L., Geuze H. J. Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):669–676. doi: 10.1038/349669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickl W. F., Majdic O., Faé I., Reuschel R., Holter W., Knapp W. The soluble pool of beta 2-microglobulin free HLA class I alpha-chains. Qualitative and quantitative characterization. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2613–2622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. A., Watts C. Cycling of cell-surface MHC glycoproteins through primaquine-sensitive intracellular compartments. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):655–657. doi: 10.1038/346655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabl E., Stockinger H., Majdic O., Gaugitsch H., Lindley I. J., Maurer D., Hajek-Rosenmayr A., Knapp W. Activated human T lymphocytes express MHC class I heavy chains not associated with beta 2-microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse D. B., Pernis B. Spontaneous internalization of Class I major histocompatibility complex molecules in T lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):193–207. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. A., Strominger J. L. Constitutive endocytosis of HLA class I antigens requires a specific portion of the intracytoplasmic tail that shares structural features with other endocytosed molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2688–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]