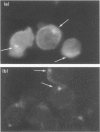
Abstract
Interaction of Fas/APO-1 (CD95) and its ligand (FasL) plays an important role in the activation-induced cell death (AICD) of T lymphocytes. In the present work, the contribution of soluble FasL to AICD of the human T-cell line Jurkat has been studied. Jurkat cells prestimulated with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) induced the death of non-activated Jurkat cells, and also of L1210Fas, but not that of Fas-negative L1210 cells. Culture supernatants from prestimulated Jurkat cells were highly toxic to their non-activated counterparts. Time-course analysis revealed that PHA-stimulated Jurkat cells quickly release (less than 15 min) to the medium a toxic molecule following a biphasic pattern, with maximal cytotoxic activities at 1 hr and 7 hr after stimulation. The cytotoxic effect of those supernatants was prevented by the addition of a blocking anti-Fas monoclonal antibody, suggesting that PHA-stimulated Jurkat cells exert Fas-based cytotoxicity mainly through the release of soluble FasL. The constitutive intracellular expression of FasL in non-activated Jurkat cells and its release as a consequence of PHA activation were detected by immunostaining and immunoblotting using an anti-FasL antibody. These data indicate that, at least in Jurkat cells, AICD is mainly mediated by the rapid release of performed FasL in soluble form upon stimulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alava M. A., DeBell K. E., Conti A., Hoffman T., Bonvini E. Increased intracellular cyclic AMP inhibits inositol phospholipid hydrolysis induced by perturbation of the T cell receptor/CD3 complex but not by G-protein stimulation. Association with protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):189–199. doi: 10.1042/bj2840189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderson M. R., Tough T. W., Davis-Smith T., Braddy S., Falk B., Schooley K. A., Goodwin R. G., Smith C. A., Ramsdell F., Lynch D. H. Fas ligand mediates activation-induced cell death in human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):71–77. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley M. C., Scudiero D. A., Monks A., Hursey M. L., Czerwinski M. J., Fine D. L., Abbott B. J., Mayo J. G., Shoemaker R. H., Boyd M. R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 1;48(3):589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anel A., Buferne M., Boyer C., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Golstein P. T cell receptor-induced Fas ligand expression in cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is blocked by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cyclosporin A. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2469–2476. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anel A., Gamen S., Alava M. A., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Piñeiro A., Naval J. Role of oxidative damage and IL-1 beta-converting enzyme-like proteases in Fas-based cytotoxicity exerted by effector T cells. Int Immunol. 1996 Jul;8(7):1173–1183. doi: 10.1093/intimm/8.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner T., Mogil R. J., LaFace D., Yoo N. J., Mahboubi A., Echeverri F., Martin S. J., Force W. R., Lynch D. H., Ware C. F. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):441–444. doi: 10.1038/373441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Daniel P. T., Trauth B. C., Oehm A., Möller P., Krammer P. H. Induction of apoptosis by monoclonal antibody anti-APO-1 class switch variants is dependent on cross-linking of APO-1 cell surface antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3166–3173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf D., Müller S., Korthäuer U., van Kooten C., Weise C., Kroczek R. A. A soluble form of TRAP (CD40 ligand) is rapidly released after T cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jun;25(6):1749–1754. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. S., Brunner T., Fletcher S. M., Green D. R., Ferguson T. A. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis as a mechanism of immune privilege. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1189–1192. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hameed A., Olsen K. J., Lee M. K., Lichtenheld M. G., Podack E. R. Cytolysis by Ca-permeable transmembrane channels. Pore formation causes extensive DNA degradation and cell lysis. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):765–777. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M., Lowin B., Peitsch M., Becker K., Tschopp J. Interaction of peptides derived from the Fas ligand with the Fyn-SH3 domain. FEBS Lett. 1995 Oct 16;373(3):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01051-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Panka D. J., Cui H., Ettinger R., el-Khatib M., Sherr D. H., Stanger B. Z., Marshak-Rothstein A. Fas(CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):444–448. doi: 10.1038/373444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayagaki N., Kawasaki A., Ebata T., Ohmoto H., Ikeda S., Inoue S., Yoshino K., Okumura K., Yagita H. Metalloproteinase-mediated release of human Fas ligand. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):1777–1783. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krammer P. H., Dhein J., Walczak H., Behrmann I., Mariani S., Matiba B., Fath M., Daniel P. T., Knipping E., Westendorp M. O. The role of APO-1-mediated apoptosis in the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1994 Dec;142:175–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. H., Ramsdell F., Alderson M. R. Fas and FasL in the homeostatic regulation of immune responses. Immunol Today. 1995 Dec;16(12):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani S. M., Matiba B., Bäumler C., Krammer P. H. Regulation of cell surface APO-1/Fas (CD95) ligand expression by metalloproteases. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Aug;25(8):2303–2307. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Golstein P. The Fas death factor. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1449–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7533326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvier E., Luciani M. F., Golstein P. Fas involvement in Ca(2+)-independent T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):195–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Activation-induced death of mature T cells in the regulation of immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Jun;7(3):382–388. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Rush B., Weaver C., Wang R. Mature T cells of autoimmune lpr/lpr mice have a defect in antigen-stimulated suicide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4409–4413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer G. G., Abbas A. K. The fas antigen is involved in peripheral but not thymic deletion of T lymphocytes in T cell receptor transgenic mice. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):365–371. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Nagata S. Purification and characterization of the Fas-ligand that induces apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):873–879. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Okazaki T., Naito Y., Yokota T., Arai N., Ozaki S., Nakao K., Nagata S. Expression of the Fas ligand in cells of T cell lineage. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3806–3813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Takahashi T., Golstein P., Nagata S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Tanaka M., Brannan C. I., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Suda T., Nagata S. Generalized lymphoproliferative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Suda T., Haze K., Nakamura N., Sato K., Kimura F., Motoyoshi K., Mizuki M., Tagawa S., Ohga S. Fas ligand in human serum. Nat Med. 1996 Mar;2(3):317–322. doi: 10.1038/nm0396-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Suda T., Takahashi T., Nagata S. Expression of the functional soluble form of human fas ligand in activated lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 15;14(6):1129–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaux F., Golstein P. Fas-based lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against syngeneic activated lymphocytes: a regulatory pathway? Eur J Immunol. 1994 Apr;24(4):923–927. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaux F., Vivier E., Malissen B., Depraetere V., Nagata S., Golstein P. TCR/CD3 coupling to Fas-based cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):781–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Fukunaga R., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Nagata S. Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):314–317. doi: 10.1038/356314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. W., Doriaux M., Farquhar M. G. Transferrin receptors recycle to cis and middle as well as trans Golgi cisternae in Ig-secreting myeloma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):277–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M. A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (anti-Fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1747–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]