Abstract
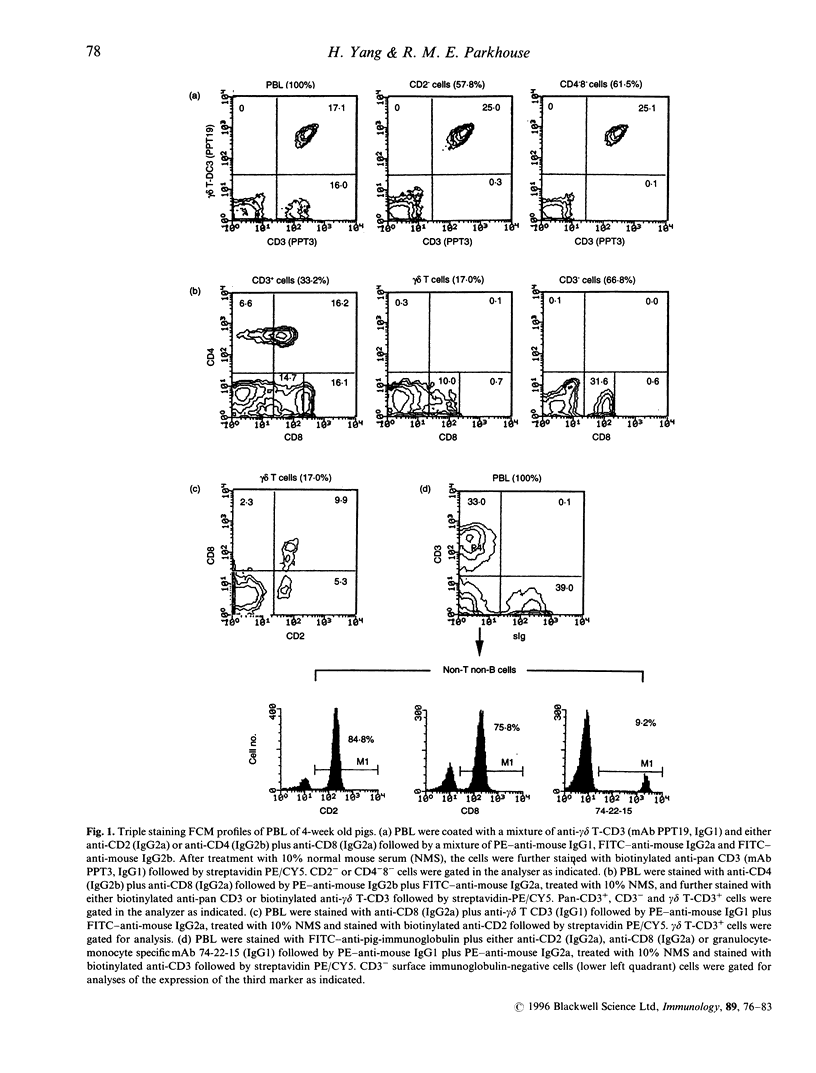
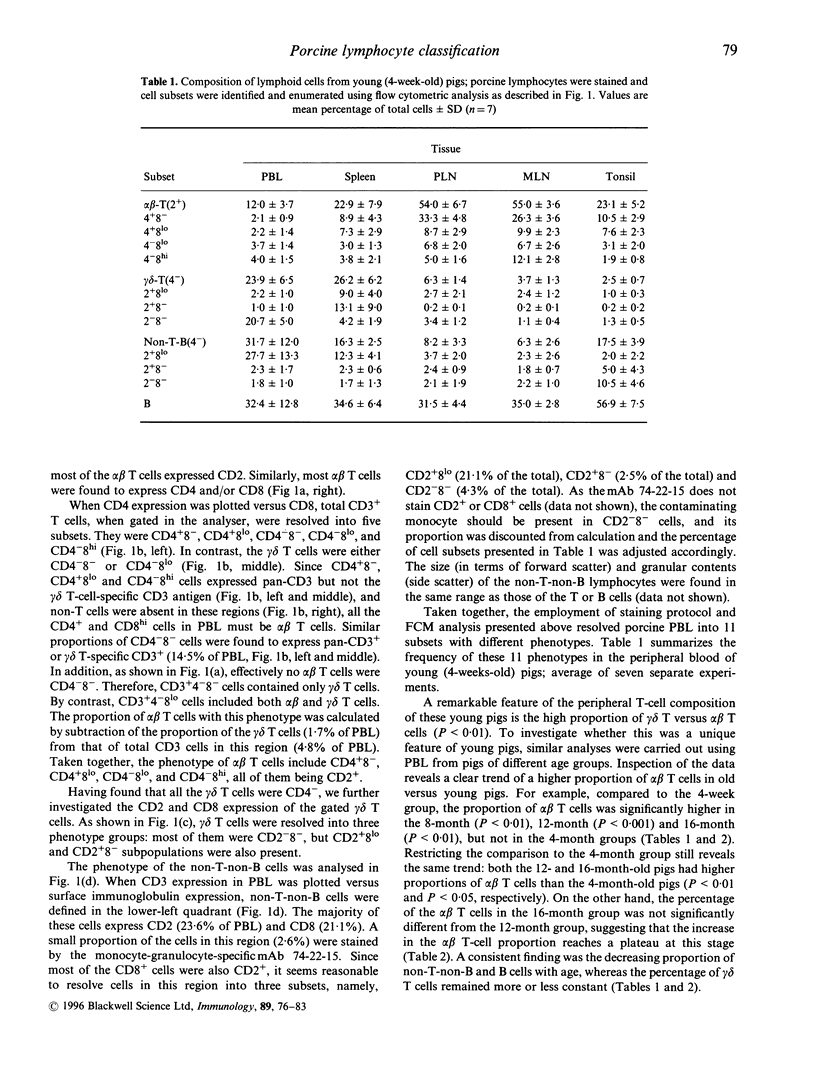
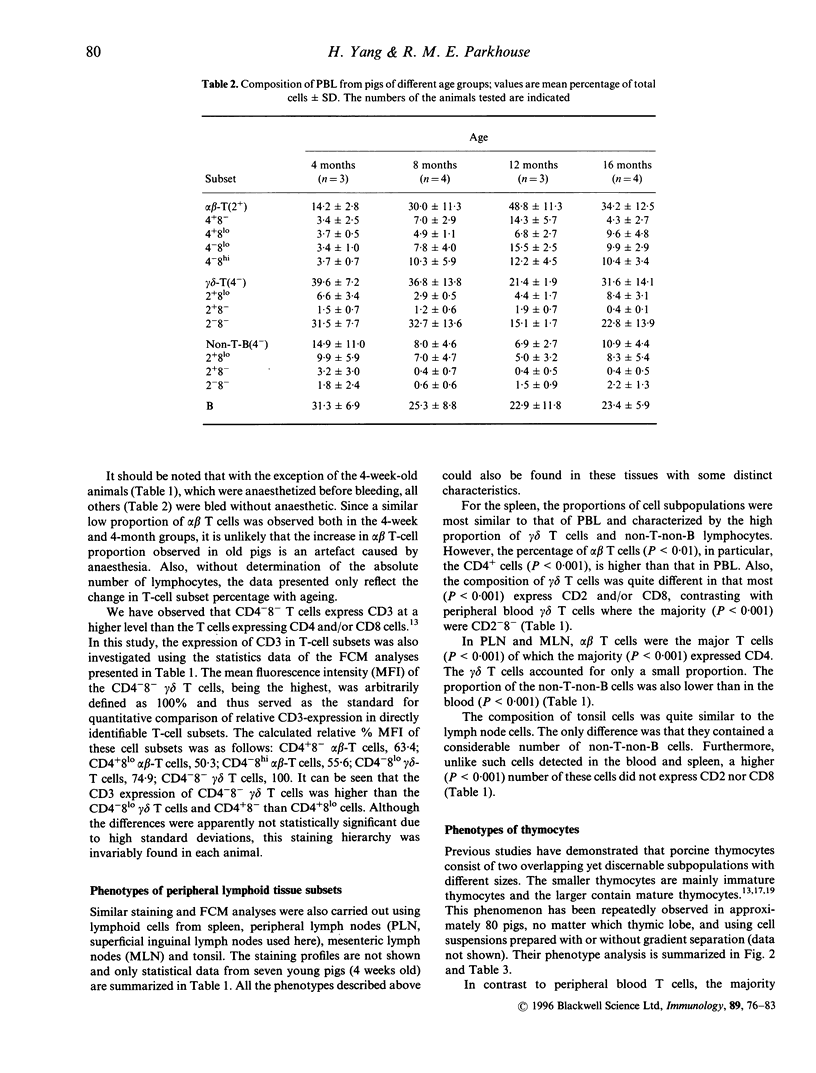
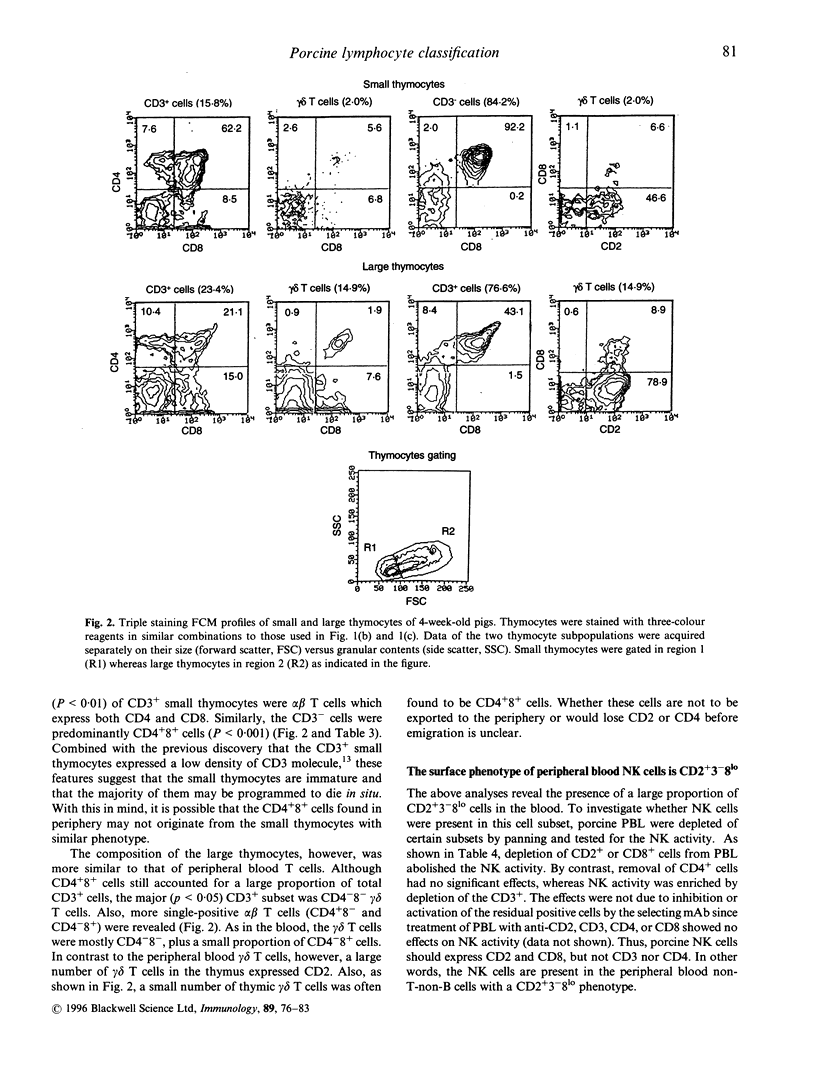
The pig is a useful model for the heterogeneity of the mammalian immune system and has also recently received attention as a possible source of organs for human transplantation. Here we report a detailed analysis of porcine lymphocyte phenotypes. Peripheral blood alpha beta T cells consisted of four subsets (CD4+8-, CD4+8lo, CD4-8lo and CD4-8hi) and gamma delta T cells of three (CD2-4-8-, CD2+4-8lo and CD2+4-8-). There were in addition, a large proportion of non-T-non-B lymphocytes with CD2+3-4-8lo surface immunoglobulin-negative phenotype containing natural killer (NK) activity. A striking observation was the relatively low frequency of alpha beta T cells in the blood of young pigs. Similar phenotypes were also identified in the cells from peripheral lymphoid tissues, though the proportions of the gamma delta T cells and the non-T-non-B lymphocytes in the lymph nodes and tonsil were much lower and the majority of the gamma delta T cells in the lymphoid tissues bore CD2 and or CD8. In thymus, the small thymocytes were predominantly CD3-4+8+ while the mature large thymocytes displayed phenotypes similar to those of peripheral T cells. Thus this work has directly defined porcine alpha beta and gamma delta T cells demonstrated the T-cell nature of the unique CD4+8+ subset of peripheral lymphocytes, revealed the high heterogeneity of the CD8+ cells, and established the phenotype of NK cells. The functional properties of these defined porcine lymphocyte subsets can now be experimentally determined in health and disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., Havran W. L. The immunobiology of T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:679–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Duncan I. A., Powis S. J., Hutchings A., Butcher G. W. Subsets of null and gamma delta T-cell receptor+ T lymphocytes in the blood of young pigs identified by specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1992 Oct;77(2):219–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. The Null/gamma delta TCR+ T cell family in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. M., Howard C. J., Sopp P., Manser J. M., Parsons K. R. Expression on porcine gamma delta lymphocytes of a phylogenetically conserved surface antigen previously restricted in expression to ruminant gamma delta T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1994 Jan;81(1):36–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. A., Binns R. M., Duffus W. P. The null T cell in pig blood is not an NK cell. Immunology. 1989 Nov;68(3):392–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg C., Schurig G. G. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against swine leukocytes. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Feb;11(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt W., Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J. Distinct gamma/delta T cell receptors define two subsets of circulating porcine CD2-CD4-CD8- T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):265–269. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with swine lymphocytes. I. Antibodies to membrane structures that define the cytolytic T lymphocyte subset in the swine. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara Y., Chen C. H., Cooper M. D. Growth requirements for avian gamma delta T cells include exogenous cytokines, receptor ligation and in vivo priming. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2230–2236. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Hein W. R. A large proportion of bovine T cells express the gamma delta T cell receptor and show a distinct tissue distribution and surface phenotype. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):540–545. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Saalmüller A., Hirt W. Gamma/delta T-lymphocyte subsets in swine. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;173:113–117. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76492-9_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Bryant J. Characteristics of porcine T lymphocytes and T-cell lines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Maurer S., Weiland E. Discrimination between two subsets of porcine CD8+ cytolytic T lymphocytes by the expression of CD5 antigen. Immunology. 1994 Apr;81(4):578–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Hirt W., Reddehase M. J. Porcine gamma/delta T lymphocyte subsets differing in their propensity to home to lymphoid tissue. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2343–2346. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saalmüller A., Reddehase M. J., Bühring H. J., Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Simultaneous expression of CD4 and CD8 antigens by a substantial proportion of resting porcine T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1297–1301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs D. H. The pig as a potential xenograft donor. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ohtsuka K., Watanabe H., Asakura H., Abo T. Detailed characterization of gamma delta T cells within the organs in mice: classification into three groups. Immunology. 1993 Nov;80(3):380–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spetz A. L., Kourilsky P., Larsson-Sciard E. L. Induction of CD8 molecules on thymic gamma/delta T cells in vitro is dependent upon alpha/beta T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2755–2759. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thome A., Saalmüller A., Pfaff E. Molecular cloning of porcine T cell receptor alpha, beta, gamma and delta chains using polymerase chain reaction fragments of the constant regions. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1005–1010. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H., Binns R. M. Expression and regulation of the porcine CD44 molecule. Cell Immunol. 1993 Jun;149(1):117–129. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H., Hutchings A., Binns R. M. Preparation and reactivities of anti-porcine CD44 monoclonal antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Apr;37(4):490–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


