Abstract
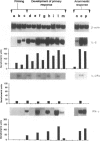
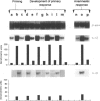
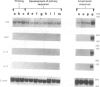
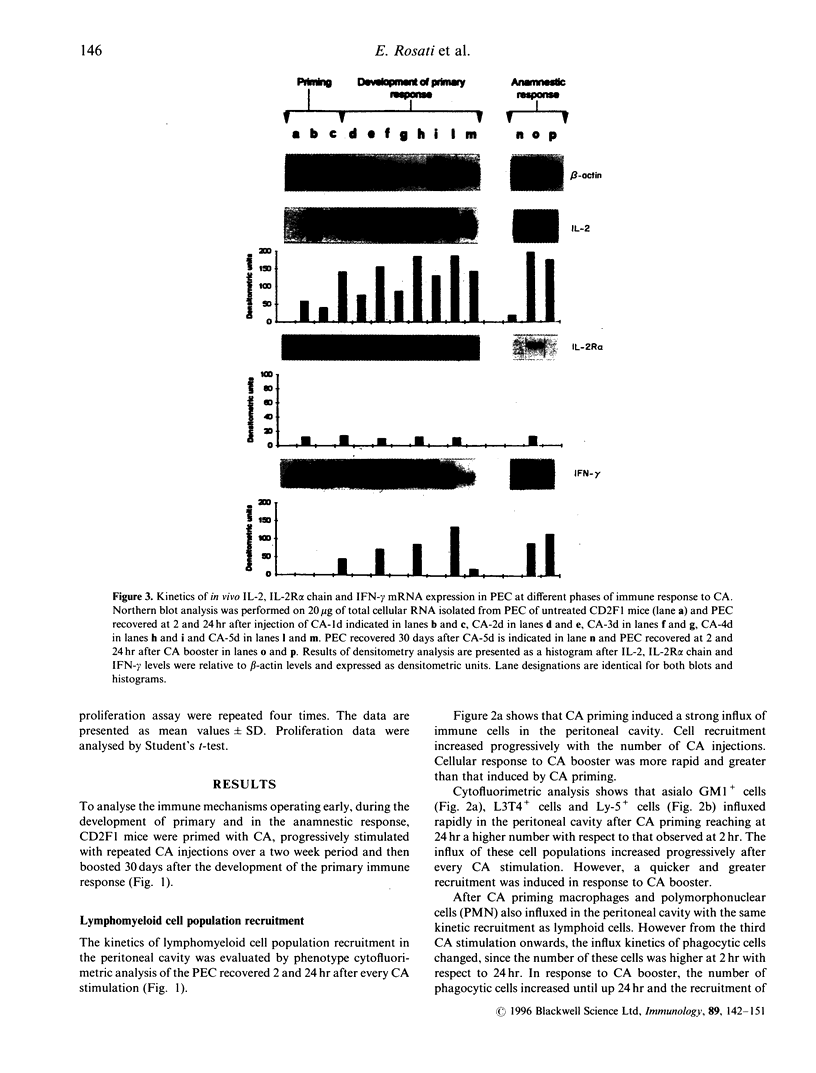
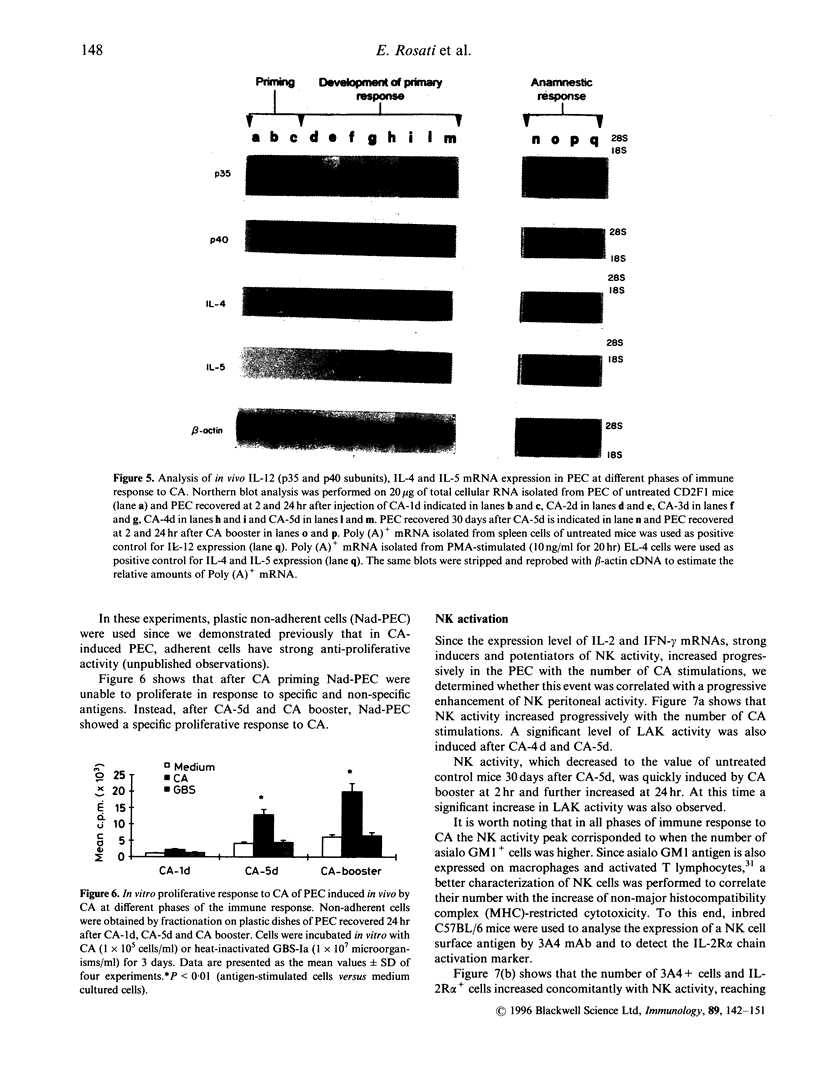
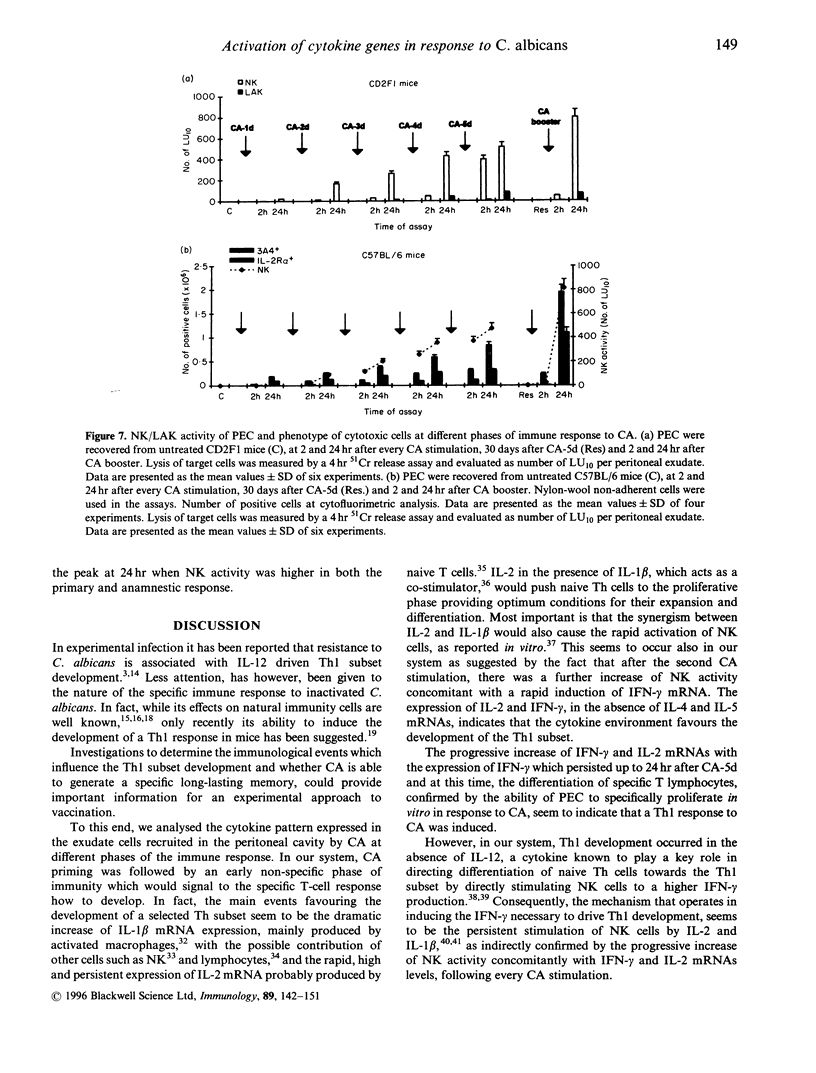
Recent evidence suggests that after repeated stimulations with inactivated C. albicans (CA) cells, CD2F1 mice respond with a cytokine pattern typical of T-helper 1 (ThI) subset development. The purpose of this study was to analyse the sequence of immunological events which, soon after priming mice with CA, lead to the development of primary and anamnestic response. A comprehensive kinetics analysis of cytokine mRNA expression was performed by Northern blot assay, in peritoneal exudate cells (PEC), at different phases of immune response to CA: after priming (one i.p. injection of 2 x 10(7) CA cells mouse), during development of the primary immune response (five progressive CA i.p. injections over a 2-week period) and in the anamnestic response (CA booster 30 days after the primary response). In vitro assays were performed 2 and 24 hr after every CA stimulation. The response to CA priming was characterized by an early and high expression of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-1 beta mRNAs At 24hr. IL-2 mRNA was still at a high level, while IL-1 beta had greatly decreased. A weak expression of IL-10 was only induced at 2 hr. whereas IL-12 p40 subunit, interferon-7 (IFN-7) IL-4 and IL-5 mRNAs were undetectable. In this phase no in vitro proliferative response of PEC to CA was observed, whereas a significant natural killer (NK) activity was induced. From the second CA injection, the IFN-7 mRNA was already induced at 2 hr. Its expression level increased progressively with the number of CA injections persisting up to 24 hr after the fifth stimulation. A progressive increase of IL-2 mRNA expression was also induced whereas IL-1 beta and IL-10 mRNAs were always transiently expressed at 2 hr at levels similar to those observed after the priming. IL-12 p40 subunit. IL-4 and IL-5 mRNAs were never detectable. The expression of this selected cytokine pattern typical of Thl response was correlated with the development of CA-specific T lymphocytes as confirmed by the in vitro proliferative response of CA-5d-induced PEC to CA. NK activity also increased progressively with the number of CA injections and after the fifth stimulation lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity was also induced. The anamnestic response to CA was characterized by a very quick induction of high levels of IL-2, II N-gamma and IL-1 beta mRNAs. IL-2 and IFN-gamma mRNAs remained high up to 24 hr while IL-1 beta mRNA decreased strongly. A weak, transient expression of IL-10 mRNA was induced at 2 hr whereas the IL-12 p40 subunit, IL-4 and IL-5 mRNAs were not detectable. The presence of CA-specific memory lymphocytes was confirmed by the in vitro specific proliferative response of PEC to CA. CA booster caused also a very rapid and high level of NK/LAK activation. In conclusion, these results indicate that CA is able to progressively trigger differential on of the Th1 subset which develops in the absence of IL-12, and that Th memory cells retain the same selected Th1 cytokine profile developed in the primary immune response.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bistoni F., Vecchiarelli A., Cenci E., Puccetti P., Marconi P., Cassone A. Evidence for macrophage-mediated protection against lethal Candida albicans infection. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):668–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.668-674.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley L. M., Croft M., Swain S. L. T-cell memory: new perspectives. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90161-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charley M. R., Mikhael A., Hackett J., Kumar V., Bennett M. Mechanism of anti-asialo GM1 prevention of graft-vs-host disease: identification of allo-antigen activated T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Sep;91(3):202–206. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomarat P., Rissoan M. C., Banchereau J., Miossec P. Interferon gamma inhibits interleukin 10 production by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):523–527. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump W. L., 3rd, Owen-Schaub L. B., Grimm E. A. Synergy of human recombinant interleukin 1 with interleukin 2 in the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Movat H. Z., Dinarello C. A. Role of interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in acute inflammation. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 May-Jun;138(3):505–512. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Schmidt J. A., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 1: an immunological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Mielke M. E., Blankenstein T., Hahn H. Kinetic analysis of cytokine gene expression in the livers of naive and immune mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. The immediate early phase in innate resistance and acquired immunity. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3016–3022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Vieira P., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., Moore K. W., O'Garra A. IL-10 acts on the antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3444–3451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Mutha S. S., Locksley R. M. Production of interferon gamma, interleukin 2, interleukin 4, and interleukin 10 by CD4+ lymphocytes in vivo during healing and progressive murine leishmaniasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7011–7015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Schoenhaut D. S., Rerko R. M., Rosser L. E., Gately M. K. Recombinant interleukin 12 cures mice infected with Leishmania major. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1505–1509. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel G., Weiss D. L., McCoy R., Deloughery T., Tara D., Brown M. A. A DNase I-hypersensitive site in the second intron of the murine IL-4 gene defines a mast cell-specific enhancer. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3239–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., O'Garra A. Biological properties of interleukin 10. Immunol Today. 1992 Jun;13(6):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90153-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Lagrange P. H., Michel J. C. Systemic candidiasis in mice. II.--Main role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in resistance to infection. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1980 Jan-Feb;131C(1):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan I. A., Matsuura T., Kasper L. H. Interleukin-12 enhances murine survival against acute toxoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):1639–1642. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.1639-1642.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian P. L., Kaffka K. L., Stern A. S., Woehle D., Benjamin W. R., Dechiara T. M., Gubler U., Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Lomedico P. T. Interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta bind to the same receptor on T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4509–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi P., Scaringi L., Tissi L., Boccanera M., Bistoni F., Bonmassar E., Cassone A. Induction of natural killer cell activity by inactivated Candida albicans in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.297-303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A., Howard M. IL-10 production by CD5 B cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 May 4;651:182–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb24615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A. T., Gerard J. P., Henderson L. E., Farrar W., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Herberman R. B., Rabin H. Effects of natural and recombinant IL 2 on regulation of IFN gamma production and natural killer activity: lack of involvement of the Tac antigen for these immunoregulatory effects. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):779–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puccetti P., Mencacci A., Cenci E., Spaccapelo R., Mosci P., Enssle K. H., Romani L., Bistoni F. Cure of murine candidiasis by recombinant soluble interleukin-4 receptor. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jun;169(6):1325–1331. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: doubt no more. Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):256–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90120-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Induction of TH1 and TH2 responses: a key role for the 'natural' immune response? Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90083-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mencacci A., Cenci E., Spaccapelo R., Mosci P., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. CD4+ subset expression in murine candidiasis. Th responses correlate directly with genetically determined susceptibility or vaccine-induced resistance. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):925–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mencacci A., Grohmann U., Mocci S., Mosci P., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Neutralizing antibody to interleukin 4 induces systemic protection and T helper type 1-associated immunity in murine candidiasis. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):19–25. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani L., Mocci S., Bietta C., Lanfaloni L., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Th1 and Th2 cytokine secretion patterns in murine candidiasis: association of Th1 responses with acquired resistance. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4647–4654. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4647-4654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosati E., Scaringi L., Cornacchione P., Fettucciari K., Sabatini R., Rossi R., Marconi P. Cytokine response to inactivated Candida albicans in mice. Cell Immunol. 1995 May;162(2):256–264. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers T. J., Mason L. H., Wiltrout T. A. Trafficking and activation of murine natural killer cells: differing roles for IFN-gamma and IL-2. Cell Immunol. 1990 May;127(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90135-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Allavena P., Djeu J. Y., Kasahara T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B., Oppenheim J. J. Human large granular lymphocytes are potent producers of interleukin-1. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):56–59. doi: 10.1038/309056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringi L., Cornacchione P., Rosati E., Boccanera M., Cassone A., Bistoni F., Marconi P. Induction of LAK-like cells in the peritoneal cavity of mice by inactivated Candida albicans. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):271–287. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringi L., Cornacchione P., Rosati E., Fettucciari K., Rossi R., Marconi P. Induction and persistence in vivo of NK/LAK activity by a mannoprotein component of Candida albicans cell wall. Cell Immunol. 1994 May;155(2):265–282. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringi L., Marconi P., Boccanera M., Tissi L., Bistoni F., Cassone A. Cell wall components of Candida albicans as immunomodulators: induction of natural killer and macrophage-mediated peritoneal cell cytotoxicity in mice by mannoprotein and glucan fractions. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1265–1274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. IL-12: initiation cytokine for cell-mediated immunity. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):496–497. doi: 10.1126/science.8097337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Gazzinelli R., Sher A., Paul W. E. Interleukin 12 acts directly on CD4+ T cells to enhance priming for interferon gamma production and diminishes interleukin 4 inhibition of such priming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Kumar V., Koo G., Bennett M. Effector cell expression of NK1.1, a murine natural killer cell-specific molecule, and ability of mice to reject bone marrow allografts. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1847–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Bradley L. M., Croft M., Tonkonogy S., Atkins G., Weinberg A. D., Duncan D. D., Hedrick S. M., Dutton R. W., Huston G. Helper T-cell subsets: phenotype, function and the role of lymphokines in regulating their development. Immunol Rev. 1991 Oct;123:115–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Weinberg A. D., English M. CD4+ T cell subsets. Lymphokine secretion of memory cells and of effector cells that develop from precursors in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1788–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn R. M., Henney C. S. Kinetic analysis of target cell destruction by effector T cells. I. Delineation of parameters related to the frequency and lytic efficiency of killer cells. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2213–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and its role in the generation of TH1 cells. Immunol Today. 1993 Jul;14(7):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90230-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Ortaldo J. R. One-signal requirement for interferon-gamma production by human large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]